The big news today is that — finally — we have Amazon’s selection of cities for its dual second headquarters (Northern Virginia and NYC). Then some notes on China. But first, semiconductors and open sourcing analysis.
We are experimenting with new content forms at TechCrunch. This is a rough draft of something new – provide your feedback directly to the authors: Danny at danny@techcrunch.com or Arman at Arman.Tabatabai@techcrunch.com if you like or hate something here.
Pivot: Future of semiconductors, chips, AI, etc.
Last week, I focused on SoftBank’s debt and Form D filings by startups. On Friday, I asked what I should start to analyze next. There were several feedback hotspots, but the one that popped out to me was around next-generation chips and the battle for dominance at the hardware layer.
As a software engineer, I know almost nothing about silicon (the beauty of abstraction). But it is clear that the future of all kinds of workflows will increasingly be driven by capabilities at the hardware/silicon level, particularly in future applications like artificial intelligence, machine learning, AR/VR, autonomous driving, and more. Furthermore, China and other countries are spending billions to go after the leaders in this space such as Nvidia and Intel. Startups, funding, competition, geopolitics — we’ve got it all here.
Arman and I are now diving deeper into this space. We will start to post once we have some interesting things to share, but if you have ideas, opinions, companies or investments in this space: tell us about them, as we are all ears: danny@techcrunch.com and Arman.tabatabai@techcrunch.com.
Open-source analysis at TechCrunch
Since I launched this daily “column” last week, I have included the text near the top that “We are experimenting with new content forms at TechCrunch.” One of those forms is what might be called open-source journalism. Definitions are fuzzy, but I take it to mean working “in the open”: allowing you, the audience of this column, to engage in not just feedback around finalized and published posts, but to actually affect the entire process of analysis, from sourcing and ideation to data science and writing.
I am thankful to work at a publication like TechCrunch where my readers are often working in the exact sectors that I am writing about. When I wrote about Form Ds last week, a number of startup attorneys reached out with their own thoughts and analysis, and also explained key aspects of how the law is changing around SEC disclosure for startups. That’s really powerful, and I want to apply it to as many fields as possible.
This thesis is ultimately intentional — now I have to operationalize it. There aren’t good tools (yet!) that I know of that allows for easy sharing of data and notes that doesn’t rely on a hacked together set of Google Docs and Github. But I’m exploring the stack, and will publish more things publicly as we have them.
Amazon HQ2 – the future of corporate relations with cities
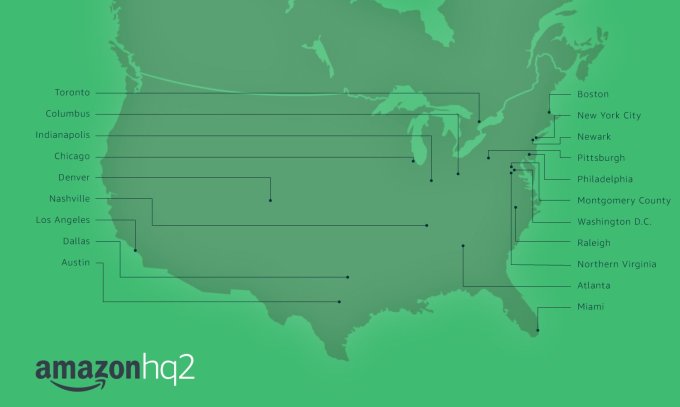
Amazon’s long process for selecting an HQ2 is finally over, and the official answer is two: Northern Virginia and NYC. Tons of words have been spilled about the search, and I am sure even more analysis will strike today about what put those two locations over the top.
To me, the key for mayors is to start using these reverse searches (where a company seeks a city and not vice versa) as leverage to actually get resources to fund infrastructure and other critical services.
This is a theme that I discussed about a year ago:
Take Boston’s bid for GE’s new headquarters. Yes, the city offered property tax rebates of about $25 million , but GE’s move also pushed the state to fund a variety of infrastructure improvements, including the Northern Avenue bridge and new bike lanes. That bridge adds a critical path for vehicles and pedestrians in Boston’s central business district, yet has gone unfunded for years.
Ideally, governments could debate, vote, and then fund these sorts of infrastructure projects and community improvements. The reality is that without a time-sensitive forcing function like a reverse RFP process, there is little hope that cities and states will make progress on these sorts of projects. The debates can literally go on forever in American democracy.
So if you are a mayor or economic planning official, use these processes as tools to get stuff done. Use the allure of new jobs and tax revenues to spur infrastructure spending and get a rezoning through a recalcitrant city council. Use that “prosperity bomb” to upgrade old parts of the urban landscape and prepare the city for the future. A healthier, more humane city can be just around the corner.
Take DC. The city has seen one of the best-run Metro systems deteriorate to abysmal levels over the past few years due to a complete dumpster fire of organizational design (the DC transit agency WMATA is funded by inconsistent revenue sources that ensure it will never be sustainable). Here is an opportunity to use Amazon’s announcement to get the tax framework and operations figured out to ensure that real estate, transportation, and other critical urban infrastructure are designed effectively.
China’s mobile internationalization

Timothy Allen/Getty Images
Talking about second headquarters, the technology industry clearly has separated into poles, one based around the United States and the other based around China. Two articles I read recently gave good insights of the benefits and challenges for China in this world.
The first is from Sam Byford writing at The Verge, who investigates the native OS options that Chinese consumers receive from companies like Xiaomi, Huawei, Oppo, and others. The headline is much more shrill than the text, so don’t let that frighten you.
Byford provides an overview of the lineage of Chinese mobile OSes, and also notes that what might look like design gaffes in Western consumer eyes might be critical needs for Chinese buyers:
But what is true today is that not all Chinese phone software is bad. And when it is bad from a Western perspective, it’s often bad for very different reasons than the bad Android skins of the past. Yes, many of these phones make similar mistakes with overbearing UI decisions — hello, Huawei — and yes, it’s easy to mock some designs for their obvious thrall to iOS. But these are phones created in a very different context to Android devices as we’ve previously understood them.
The article is perhaps a tad long for what it is, but Byford’s key viewpoint should be repeated as a mantra by any person connected to the technology sector today: “The Chinese phone market is a spiraling behemoth of innovation and audacity, unlike anything we’ve ever seen. If you want to be on board with the already exciting hardware, it’s worth trying to understand the software.”
Of course, while China may be a huge country, its leading technology companies do want to globalize and expand their user bases outside of the Middle Kingdom’s borders. That may well be a challenging proposition.
Writing at Factor Daily, Shadma Shaikh dives into the failure of WeChat to break into the Indian market. The product lessons learned by WeChat’s owner Tencent could be applied to any Silicon Valley company — cultural knowledge and appropriate product design are key to entering overseas markets.
Shaikh gives a couple of examples:
Another design feature in the app allowed users to look up and send add-friend requests to WeChat users nearby. During initial onboarding when users were just checking app’s features, many would tap the “people nearby” feature, which would switch on location sharing by default – including with strangers. Once location sharing with strangers was switched on, it wasn’t very intuitive to turn it off.
“Women used to get a lot of unwarranted messages from men, which was a major turn off and many of them left the platform,” Gupta says. “China probably didn’t have this stalking problem.”
And
In China, where the internet was cheaper than in India in 2012, sending video files of, say, 4 MB was not a challenge. WhatsApp compresses a 5 MB photo to 40 kilobytes. WeChat did not compress the files and took many minutes and data to send and receive media files.
Internationalization will never be easy, but the lessons that Silicon Valley has slowly learned over the past two decades will need to be learned again by Chinese companies if they want to export their software to other countries.
Reading Docket
- Eliot Peper’s new science fiction novel Borderless
- Daniel J Hopkins’ The Increasingly United States (about how U.S. elections are more national and less local than ever before).
Read Full Article
No comments:
Post a Comment