A blog about how-to, internet, social-networks, windows, linux, blogging, tips and tricks.
22 June 2018
A look back at the best tech ads of the last 35 years
Last week the Association of Independent Commercial Producers announced the winners of its annual awards honoring the best moving image marketing of the year and Apple’s “Welcome Home” ad took home the prize for Advertising Excellence in the single commercial category. Directed by Spike Jonze, the person behind movies like Her and Being John Malkovich, the musical short film follows the journey of a young woman, FKA Twigs, as she returns home from a challenging work day to an empty apartment. After asking Siri to “play something [she’d] like” her world is literally transformed as the music of Anderson .Paak’s “Til It’s Over” spills out of her HomePod.
With stunning visuals (most of which were not CGI) and captivating choreography, Jonze breathes life into a product that got mixed reviews after its release in February. This made us think, what other tech commercials have grabbed our attention in the last 35 years and transformed how we think about technology? Here’s a few of our favorites.
It’s hard to talk about transformative tech ads without mentioning this one first. This Super Bowl ad from 1984 was directed by Ridley Scott (who directed Alien in 1979) and was the world’s introduction to the Macintosh personal computer. The ad draws some not-so-subtle connections between PC consumerism and soulless corporate office spaces of the 80s to George Orwell’s dystopian ‘1984.’
In the commercial, a depiction of Big Brother speaks hypnotically to a mass of identical workers as woman in bright colors streaks through the crowd, mallet in hand. With Olympian effort, she sends it flying into the screen, disrupting the status quo of personal computing and promising the world that with the Macintosh “1984 won’t be like ‘1984′.”
Noticeably less high-concept than the introduction of the Macintosh, this 26 commercial campaign still captured a lot of attention in the earlier 2000s. The spots feature a character named Steven – a stereotypical easy-going, cool teenager who has a particular knack for charming parents into buying Dell computers for their families. A popular spot for Dell, the commercials even launched the star Ben Curtis into a little bit of fame himself. The actor recently appeared in a 2017 off-Broadway show ‘The Crusade of Connor Stephens.’
Confession time: I loved these commercials as a kid. Like, binge-watched-them-on-Apple.com loved them. This campaign ran for four years between 2006 and 2009 and featured suit-clad John Hodgman as a PC and hoodie-toting Justin Long as a Mac. The commercials put these two computers in direct conversation with each other (quite literally) and highlighted different features of Mac computers (e.g. iMovie, Time Machine and being dual compatible with Windows) against its PC counterparts.
Not biting or hostile, Mac came across as laid-back and creative — everything Apple was telling its customers they could be — and left PC flustered in its wake. In 2010 Adweek declared this campaign the best in the first decade of a new century.
Stepping outside the world of personal computing, we can’t fail to mention this famous Verizon campaign. These spots ran between 2002 and 2011 and featured a character named Test Man, decked out in a Verizon jacket and large glasses, who traveled around to test the strength of Verizon’s network. Ever thorough, he consistently asks the tech on the other side of the line “can you hear me now?” In 2002 Test Man won an award from Entertainment Weekly for “Most Mysterious Pitchman.”
While the Verizon campaign ended a little under ten years ago, the character has been recently revived — for Sprint. As another campaign of my childhood, this betrayal still stings.
You might want to get some tissues ready for this one. This minimalist commercial aired during the Super Bowl in 2010 and follows the love story of a couple from first their first meeting, to marriage and starting a family; all within the window of a Google search. The ad was one of the most popular aired during the game and was actually designed by a handful of ad and design students known as ‘Google 5.’ According to AdAge, the commercial concept was sparked by a comment in a Google brief to “remind people what they love about Google search” and a maxim by Google Creative Lab VP Robert Wong that “the best results don’t show up in a search engine, they show up in your life.”
Did we miss any ads that changed how you thought about technology? Let us know in the comments!
Read Full Article
Facebook mistakenly leaked developer analytics reports to testers
Set the “days without a Facebook’s privacy problem” counter to zero. This week, an alarmed developer contacted TechCrunch, informing us that their Facebook App Analytics weekly summary email had been delivered to someone outside their company. It contains sensitive business information including weekly average users, page views, and new users.
After two days of Facebook investigating, the social network now confirms to TechCrunch that 3 percent of apps using Facebook Analytics had their weekly summary reports sent to their app’s testers, instead of only the app’s developers, admins, and analysts.
Testers are often people outside of a developer’s company. If the leaked info got to an app’s competitors, it could provide them an advantage. At least they weren’t allowed to click through to view more extensive historical analytics data on Facebook’s site.
Facebook tells us it plans to notify all impacted developers about the leak today. Below you can find the email the company will send:
Subject line: We recently resolved an error with your weekly summary email
We wanted to let you know about a recent error where a summary e-mail from Facebook Analytics about your app was sent to testers of your app ‘[APP NAME WILL BE DYNAMICALLY INSERTED HERE]’. As you know, we send weekly summary emails to keep you up to date with some of your top-level metrics — these emails go to people you’ve identified as Admins, Analysts and Developers. You can also add Testers to your account, people designated by you to help test your apps when they’re in development.
We mistakenly sent the last weekly email summary to your Testers, in addition to the usual group of Admins, Analysts and Developers who get updates. Testers were only able to see the high-level summary information in the email, and were not able to access any other account information; if they clicked “View Dashboard” they did not have access to any of your Facebook Analytics information.
We apologize for the error and have made updates to prevent this from happening again.
One affected developer told TechCrunch “Not sure why it would ever be appropriate to send business metrics to an app user. When I created my app (in beta) I added dozens of people as testers as it only meant they could login to the app…not access info!” They’re still waiting for the disclosure from Facebook.

The privacy mistake comes just weeks after a bug caused 14 million users’ Facebook status update composers to change their default privacy setting to public. And Facebook has had problems with misdelivering business information before. In 2014, Facebook accidentally sent advertisers receipts for other business’ ad campaigns, causing significant confusion. The company has also misreported metrics about Page reach and more on several occasions.
While Facebook has been working diligently to patch app platform privacy holes since the Cambridge Analytica scandal, removing access to many APIs and strengthening human reviews of apps, issues like today’s make it hard to believe Facebook has a proper handle on the data of its 2 billion users.
Read Full Article
Facebook mistakenly leaked developer analytics reports to testers
Set the “days without a Facebook’s privacy problem” counter to zero. This week, an alarmed developer contacted TechCrunch, informing us that their Facebook App Analytics weekly summary email had been delivered to someone outside their company. It contains sensitive business information including weekly average users, page views, and new users.
After two days of Facebook investigating, the social network now confirms to TechCrunch that 3 percent of apps using Facebook Analytics had their weekly summary reports sent to their app’s testers, instead of only the app’s developers, admins, and analysts.
Testers are often people outside of a developer’s company. If the leaked info got to an app’s competitors, it could provide them an advantage. At least they weren’t allowed to click through to view more extensive historical analytics data on Facebook’s site.
Facebook tells us it plans to notify all impacted developers about the leak today. Below you can find the email the company will send:
Subject line: We recently resolved an error with your weekly summary email
We wanted to let you know about a recent error where a summary e-mail from Facebook Analytics about your app was sent to testers of your app ‘[APP NAME WILL BE DYNAMICALLY INSERTED HERE]’. As you know, we send weekly summary emails to keep you up to date with some of your top-level metrics — these emails go to people you’ve identified as Admins, Analysts and Developers. You can also add Testers to your account, people designated by you to help test your apps when they’re in development.
We mistakenly sent the last weekly email summary to your Testers, in addition to the usual group of Admins, Analysts and Developers who get updates. Testers were only able to see the high-level summary information in the email, and were not able to access any other account information; if they clicked “View Dashboard” they did not have access to any of your Facebook Analytics information.
We apologize for the error and have made updates to prevent this from happening again.
One affected developer told TechCrunch “Not sure why it would ever be appropriate to send business metrics to an app user. When I created my app (in beta) I added dozens of people as testers as it only meant they could login to the app…not access info!” They’re still waiting for the disclosure from Facebook.

The privacy mistake comes just weeks after a bug caused 14 million users’ Facebook status update composers to change their default privacy setting to public. And Facebook has had problems with misdelivering business information before. In 2014, Facebook accidentally sent advertisers receipts for other business’ ad campaigns, causing significant confusion. The company has also misreported metrics about Page reach and more on several occasions.
While Facebook has been working diligently to patch app platform privacy holes since the Cambridge Analytica scandal, removing access to many APIs and strengthening human reviews of apps, issues like today’s make it hard to believe Facebook has a proper handle on the data of its 2 billion users.
Read Full Article
How to Network Boot a Raspberry Pi Without a MicroSD Card

Setting up a Raspberry Pi usually means writing the disk image to a microSD card, then using it to boot the operating system.
It’s a good flow that works in most cases… but it’s not the only option. Now you can use network boot to run your Raspberry Pi, and forget about microSD cards completely!
MicroSD, USB, or Ethernet? For Raspberry Pi
Traditionally, running a Raspberry Pi has meant writing the disk image of your preferred distro to microSD. This is usually done using a tool like Etcher (although Linux and macOS users can access command line tools for writing data).
Having a fast, resilient microSD card is important, but even the best devices suffer performance degradation, and eventually fail. Keeping a backup of the microSD card is a good idea, so that you can instantly copy the image to a new card.

One alternative is to boot from a USB device instead, but with the release of the Raspberry Pi 3 B+, things have improved. Now you can boot multiple Raspberry Pi’s over Ethernet, from a central server. This uses Preboot eXecution Environment (or PXE, pronounced “pixie”) and is known as network booting (or “netboot”). It’s made possible thanks to a new feature in Raspbian, PiServer.
PXE has been a common feature in desktops and servers for years, although it’s usually used in corporations and public institutions. For Raspberry Pis in schools or businesses, using piServer, there’s no need to install the operating system on each Pi—instead, a single server runs the Raspbian x86 distribution as a server, and each Raspberry Pi acts as a client (a zero, or ultra-thin client, specifically) booting from the OS on the server. This is an excellent way to control what is installed on each Raspberry Pi (it’s all hosted on the server), and monitor how they’re used.
What You’ll Need to Use NetBoot on Raspberry Pi
Setting this up is pretty straightforward. However, PXE doesn’t work on older Raspberry Pi’s, only the 2018 model, the Raspberry Pi 3 B+.
Along with this, you’ll need a desktop computer or laptop, or some other suitable device to run Raspbian x86. You’ll also require:
- Raspbian Lite
- MicroSD card
Both of these are required for configuration of PXE, but once this is done, the microSD card can be repurposed.
How to Set Up a Raspberry Pi Server
With Debian Stretch with Raspberry Pi Desktop (the official name for Raspbian x86) downloaded, you have several options. It can be run as a live disc from DVD-ROM or USB; alternatively, you could install it as a virtual machine using VirtualBox. If you’re planning on using a dedicated machine, meanwhile, then a full installation will be appropriate.
While it is possible to use a Raspberry Pi running Raspbian as the server, this will result in slower performance.
Regardless of which solution you choose, ensure there is enough HDD capacity for each Raspberry Pi on the network. With the system set up, boot Raspbian x86.
How to Configure a Raspberry Pi Client
You should now be ready to configure your Raspberry Pi 3 B+. You should have written the OS to your microSD card already, so ensure this is inserted in the Raspberry Pi and boot the computer.
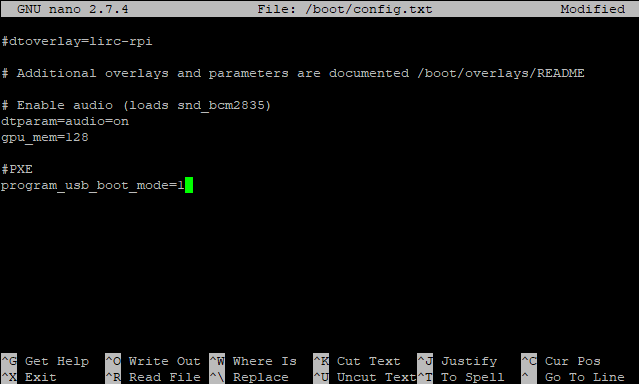
Open a command line (or connect via SSH) and input:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
With the file open in the text editor, add the following to the end of the file:
program_usb_boot_mode=1
Save the file and exit with Ctrl+X, then power down the Raspberry Pi:
sudo shutdown
You can now remove the microSD card.
Note: You can save time with the above process using this all-in-one command:
echo program_usb_boot_mode=1 | sudo tee -a /boot/config.txt
However, you will still need to switch off the computer.
How to Boot Your Raspberry Pi Over PXE
With an Ethernet cable connected to your Raspberry Pi 3 B+, you’re ready to connect the power supply and boot. At this stage, nothing much will happen, other than the power LED lighting up.
Put this to one side and configure PiServer. On the server computer launch PiServer from the Preferences menu. Follow the instructions in the wizard to set up the network. You should see the MAC address of each Raspberry Pi 3 B+ on the network in the Add clients screen; proceed to the Add users screen to create one or more user accounts and passwords.
Note: More can be added later. Also, the accounts are portable, and not locked to specific Raspberry Pis.
Click next to Add software, and select the operating system you wish each client to use. Currently, Raspbian and Raspbian Lite are available. Click Next to complete the procedure, install the client operating systems, and finish.
Simple Raspberry Pi Servers Without MicroSD Cards
By now, you should have at least one Raspberry Pi 3 B+ running as a zero client, and a PC running the Debian Stretch distro for 32-bit computers. The end result is a simplified, networked, Raspberry Pi environment that is centrally controlled and doesn’t require a microSD card.
It may not be ideal for offline projects, or many online projects, but as a solution to many computing tasks, network booting a Raspberry Pi 3 B+ is ideal. You might have a home server to connect your Raspberry Pi to, or use PiServer as a central server in a classroom scenario. PiServer might even control a bunch of Raspberry Pis using Power over Ethernet (PoE) in an industrial scenario. It’s all pretty exciting, isn’t it?
Want more Raspberry Pi server solutions? This little computer is capable of so much, from Raspberry Pi media servers to Raspberry Pi web hosting servers!
Read the full article: How to Network Boot a Raspberry Pi Without a MicroSD Card
Read Full Article
Teaching Uncalibrated Robots to Visually Self-Adapt
Posted by Fereshteh Sadeghi, Student Researcher, Google Brain Team
People are remarkably proficient at manipulating objects without needing to adjust their viewpoint to a fixed or specific pose. This capability (referred to as visual motor integration) is learned during childhood from manipulating objects in various situations, and governed by a self-adaptation and mistake correction mechanism that uses rich sensory cues and vision as feedback. However, this capability is quite difficult for vision-based controllers in robotics, which until now have been built on a rigid setup for reading visual input data from a fixed mounted camera which should not be moved or repositioned at train and test time. The ability to quickly acquire visual motor control skills under large viewpoint variation would have substantial implications for autonomous robotic systems — for example, this capability would be particularly desirable for robots that can help rescue efforts in emergency or disaster zones.
In “Sim2Real Viewpoint Invariant Visual Servoing by Recurrent Control” presented at CVPR 2018 this week, we study a novel deep network architecture (consisting of two fully convolutional networks and a long short-term memory unit) that learns from a past history of actions and observations to self-calibrate. Using diverse simulated data consisting of demonstrated trajectories and reinforcement learning objectives, our visually-adaptive network is able to control a robotic arm to reach a diverse set of visually-indicated goals, from various viewpoints and independent of camera calibration.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The Challenge
Discovering how the controllable degrees of freedom (DoF) affect visual motion can be ambiguous and underspecified from a single image captured from an unknown viewpoint. Identifying the effect of actions on image-space motion and successfully performing the desired task requires a robust perception system augmented with the ability to maintain a memory of past actions. To be able to tackle this challenging problem, we had to address the following essential questions:
- How can we make it feasible to provide the right amount of experience for the robot to learn the self-adaptation behavior based on pure visual observations that simulate a lifelong learning paradigm?
- How can we design a model that integrates robust perception and self-adaptive control such that it can quickly transfer to unseen environments?
 |
| Visually indicated goal reaching task with a physical robotic arm and diverse camera viewpoints. |
Collecting robot experience data is difficult and time-consuming. In a previous post, we showed how to scale up learning skills by distributing the data collection and trials to multiple robots. Although this approach expedited learning, it is still not feasibly extendable to learning complex behaviors such as visual self-calibration, where we need to expose robots to a huge space of various viewpoints. Instead, we opt to learn such complex behavior in simulation where we can collect unlimited robot trials and easily move the camera to various random viewpoints. In addition to fast data collection in simulation, we can also surpass hardware limitations requiring the installation of multiple cameras around a robot.
 |
| We use domain randomization technique to learn generalizable policies in simulation. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disentangling Perception from Control
To enable fast transfer to unseen environments, we devised a deep neural network that combines perception and control trained end-to-end simultaneously, while also allowing each to be learned independently if needed. This disentanglement between perception and control eases transfer to unseen environments, and makes the model both flexible and efficient in that each of its parts (i.e. 'perception' or 'control') can be independently adapted to new environments with small amounts of data. Additionally, while the control portion of the network was entirely trained by the simulated data, the perception part of our network was complemented by collecting a small amount of static images with object bounding boxes without needing to collect the whole action sequence trajectory with a physical robot. In practice, we fine-tuned the perception part of our network with only 76 object bounding boxes coming from 22 images.
 |
| Real-world robot and moving camera setup. First row shows the scene arrangements and the second row shows the visual sensory input to the robot. |
We tested the visually-adapted version of our network on a physical robot and on real objects with drastically different appearances than the ones used in simulation. Experiments were performed with both one or two objects on a table — “seen objects” (as labeled in the figure below) were used for visual adaptation using small collection of real static images, while “unseen objects” had not been seen during visual adaptation. During the test, the robot arm was directed to reach a visually indicated object from various viewpoints. For the two object experiments the second object was to "fool" the robotic arm. While the simulation-only network has good generalization capability (due to being trained with domain randomization technique), the very small amount of static visual data to visually adapt the controller boosted the performance, due to the flexible architecture of our network.
 |
| After adapting the visual features with the small amount of real images, performance was boosted by more than 10%. All used real objects are drastically different from the objects seen in simulation. |
Acknowledgements
This research was conducted by Fereshteh Sadeghi, Alexander Toshev, Eric Jang and Sergey Levine. We would also like to thank Erwin Coumans and Yunfei Bai for providing pybullet, and Vincent Vanhoucke for insightful discussions.
Google Finally Launches a Podcasts App on Android

After years of ignoring the medium, Google is finally taking podcasting seriously. To that end, the company has released a standalone app called Google Podcasts. Which, as you may have guessed from the name, is an app dedicated to podcasts.
What Is Google Podcasts?
In a nutshell, Google Podcasts lets you listen to podcasts. You can search for the podcasts you already know and love, and subscribe to your heart’s content. Or, if you’re keen to hear more, you can let Google recommend podcasts based on your listening habits.
? Listen up! Today we're releasing the Google Podcasts app for Android, designed to make it easier than ever to discover and listen to podcasts ? https://t.co/JOT3Rb0XTG pic.twitter.com/bMyLspt4FQ
— Google (@Google) June 19, 2018
As detailed on The Keyword, Google Podcasts syncs across different Google products, including Google Assistant. Google will remember how far through an episode you are, meaning you can start listening on your smartphone but finish listening on Google Home.
Google Wants to Transform Podcasting
At launch, Google Podcasts is very similar to countless third-party alternatives. However, in the longterm, Google is hoping to use the Podcasts app to “transform podcasting for the better”. This will be achieved by utilizing AI and encouraging diversity.
In terms of AI, Google will be using it to “offer recommendations based on your listening habits,” whether you’re a fan of a particular genre or a network. And in the future Google has plans to offer automatic subtitling powered by Google Translate.
In terms of diversity, Google claims that “only about a quarter of the most popular podcasts tend to be hosted by women, and even fewer by people of color”. As a result, Google is hoping to “increase the diversity of voices and remove barriers to podcasting”.
Alternatives to Google Podcasts
Google Podcasts is currently only available on Android, but an iOS version is likely in the future. In the meantime iPhone owners should use Overcast. And for Android owners who want an alternative, these are the best podcast players for Android.
Read the full article: Google Finally Launches a Podcasts App on Android
Read Full Article
Facebook prototypes tool to show how many minutes you spend on it
Are you ready for some scary numbers? After months of Mark Zuckerberg talking about how “Protecting our community is more important than maximizing our profits”, Facebook is preparing to turn that commitment into a Time Well Spent product.
Buried in Facebook’s Android app is an unreleased “Your Time On Facebook” feature. It shows the tally of how much time you spent on the Facebook app on your phone on each of the last seven days, and your average time spent per day. It lets you set a daily reminder that alerts you when you’ve reached your self imposed limit, plus a shortcut to change your Facebook notification settings.
Facebook confirmed the feature development to TechCrunch, with a spokesperson telling us “We’re always working on new ways to help make sure people’s time on Facebook is time well spent.”
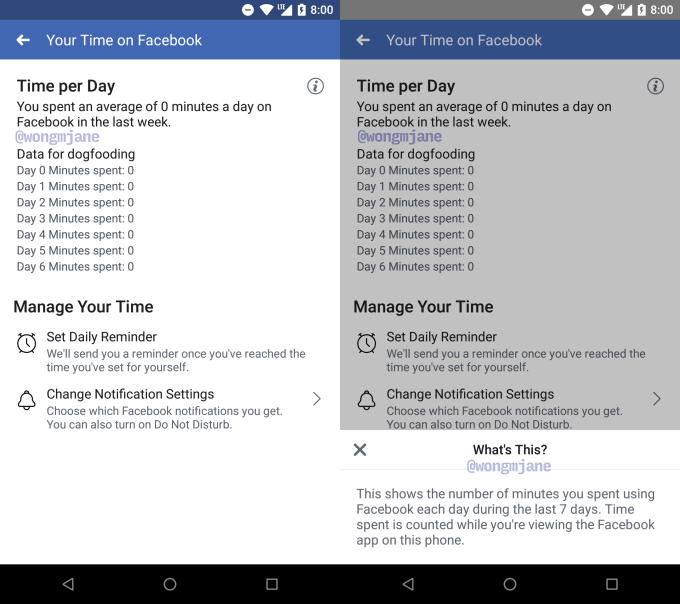
The feature could help Facebook users stay mindful of how long they’re staring at the social network. This self-policing could be important since both iOS and Android are launching their own screen time monitoring dashboards that reveal which apps are dominating your attention and can alert you or lock you out of apps when you hit your time limit. When Apple demoed the feature at WWDC, it used Facebook as an example of an app you might use too much.
Images of Facebook’s digital wellbeing tool come courtesy of our favorite tipster and app investigator Jane Manchun Wong. She previously helped TechCrunch scoop the development of features like Facebook Avatars, Twitter encrypted DMs, and Instagram Usage Insights — a Time Well Spent feature that looks very similar to this one on Facebook.
Our report on Instagram Usage Insights led the sub-company’s CEO Kevin Systrom to confirm the upcoming feature, saying ““It’s true . . . We’re building tools that will help the IG community know more about the time they spend on Instagram – any time should be positive and intentional . . . Understanding how time online impacts people is important, and it’s the responsibility of all companies to be honest about this. We want to be part of the solution. I take that responsibility seriously.”
Facebook has already made changes to its News Feed algorithm designed to reduce the presence of low-quality but eye-catching viral videos. That led to Facebook’s first ever usage decline in North America in Q4 2017, with a loss of 700,000 daily active users in the region. Zuckerberg said on the earnings call that this change “reduced time spent on Facebook by roughly 50 million hours every day.”
Zuckerberg has been adamant that all time spent on Facebook isn’t bad. Instead as we argued in our piece “The Difference Between Good And Bad Facebooking”, its asocial, zombie-like passive browsing and video watching that’s harmful to people’s wellbeing, while active sharing, commenting, and chatting can make users feel more connected and supported.
But that distinction isn’t visible in this prototype of the “Your Time On Facebook Tool” which appears to treat all time spent the same. If Facebook was able to measure our active vs passive time on its app and impress the health difference, it could start to encourage us to either put down the app, or use it to communicate directly with friends when we find ourselves mindlessly scrolling the feed or enviously viewing people’s photos.
Read Full Article
Facebook prototypes tool to show how many minutes you spend on it
Are you ready for some scary numbers? After months of Mark Zuckerberg talking about how “Protecting our community is more important than maximizing our profits”, Facebook is preparing to turn that commitment into a Time Well Spent product.
Buried in Facebook’s Android app is an unreleased “Your Time On Facebook” feature. It shows the tally of how much time you spent on the Facebook app on your phone on each of the last seven days, and your average time spent per day. It lets you set a daily reminder that alerts you when you’ve reached your self imposed limit, plus a shortcut to change your Facebook notification settings.
Facebook confirmed the feature development to TechCrunch, with a spokesperson telling us “We’re always working on new ways to help make sure people’s time on Facebook is time well spent.”

The feature could help Facebook users stay mindful of how long they’re staring at the social network. This self-policing could be important since both iOS and Android are launching their own screen time monitoring dashboards that reveal which apps are dominating your attention and can alert you or lock you out of apps when you hit your time limit. When Apple demoed the feature at WWDC, it used Facebook as an example of an app you might use too much.
Images of Facebook’s digital wellbeing tool come courtesy of our favorite tipster and app investigator Jane Manchun Wong. She previously helped TechCrunch scoop the development of features like Facebook Avatars, Twitter encrypted DMs, and Instagram Usage Insights — a Time Well Spent feature that looks very similar to this one on Facebook.
Our report on Instagram Usage Insights led the sub-company’s CEO Kevin Systrom to confirm the upcoming feature, saying ““It’s true . . . We’re building tools that will help the IG community know more about the time they spend on Instagram – any time should be positive and intentional . . . Understanding how time online impacts people is important, and it’s the responsibility of all companies to be honest about this. We want to be part of the solution. I take that responsibility seriously.”
Facebook has already made changes to its News Feed algorithm designed to reduce the presence of low-quality but eye-catching viral videos. That led to Facebook’s first ever usage decline in North America in Q4 2017, with a loss of 700,000 daily active users in the region. Zuckerberg said on the earnings call that this change “reduced time spent on Facebook by roughly 50 million hours every day.”
Zuckerberg has been adamant that all time spent on Facebook isn’t bad. Instead as we argued in our piece “The Difference Between Good And Bad Facebooking”, its asocial, zombie-like passive browsing and video watching that’s harmful to people’s wellbeing, while active sharing, commenting, and chatting can make users feel more connected and supported.
But that distinction isn’t visible in this prototype of the “Your Time On Facebook Tool” which appears to treat all time spent the same. If Facebook was able to measure our active vs passive time on its app and impress the health difference, it could start to encourage us to either put down the app, or use it to communicate directly with friends when we find ourselves mindlessly scrolling the feed or enviously viewing people’s photos.
Read Full Article
Citymapper lets you find Ofo, Mobike and scooters around you
Urban transportation app Citymapper quietly rolled out an app update that lets you find many alternative mobility services in the app. You can now find the nearest dockless bike or electric scooter around you (not the Bird and Lime kind, the motorcycle kind).
The integrations are already live in many cities. The company didn’t add new buttons for each service because it was already getting quite crowded with buses, subways and ride-sharing services.
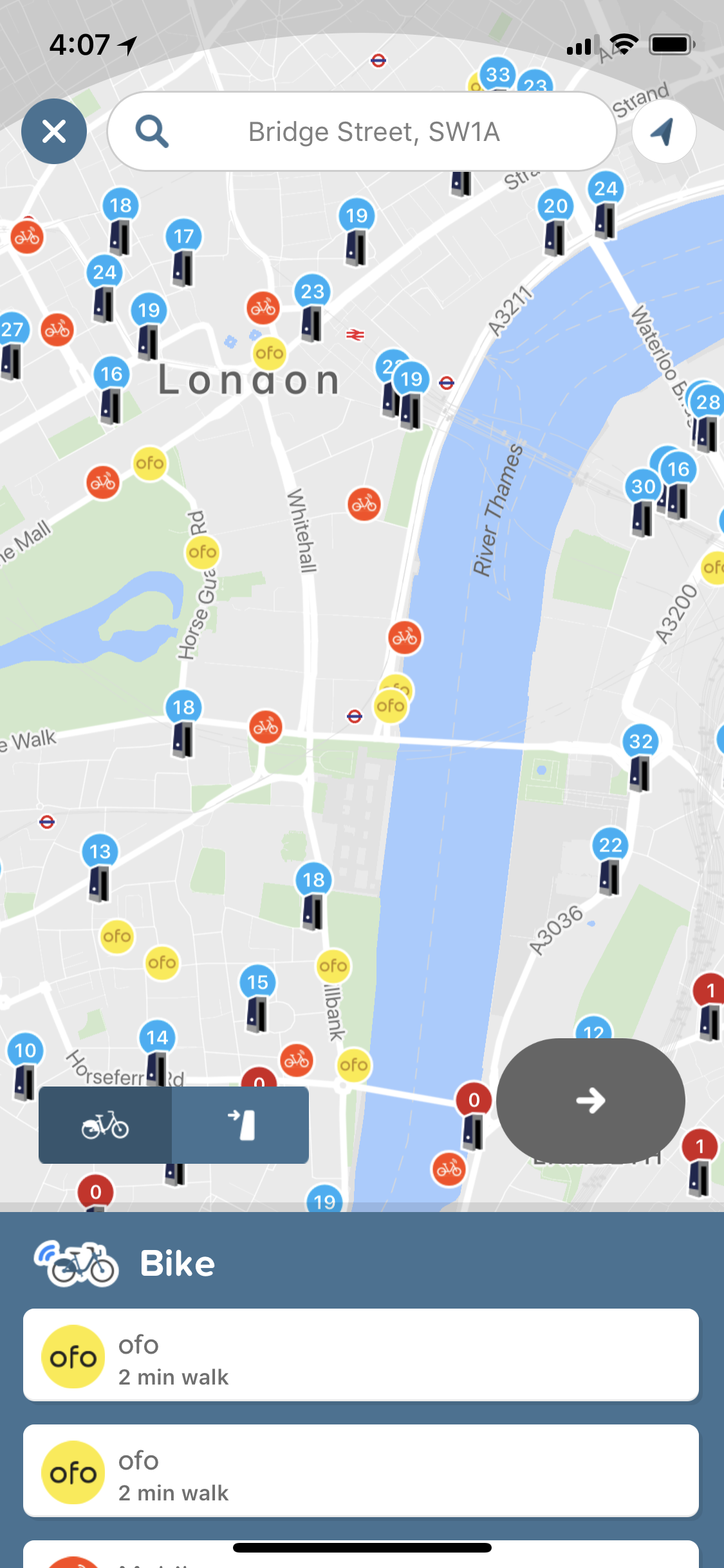
If you tap the bike button, you get a map view of the streets around you. In addition to traditional bike-sharing services, you’ll now find colored dots representing both Ofo and Mobike. TechCrunch’s Ingrid Lunden previously reported that the Mobike integration was coming soon. Below the map, you get a list of the closest bikes.
But Citymapper also added a new scooter button in multiple cities. As the name suggests, this button helps you locate the closest free-floating scooter that you can unlock with your phone.
In Paris, you’ll find Coup and Cityscoot scooters. In Berlin, you’ll find Coup scooters. In Madrid and Barcelona, you’ll find Muving, ioscoot, eCooltra and Yugo scooters… You get the idea. Chances are all your local options will be there.
Interestingly, electric scooters from Bird and Lime aren’t in there just yet. It might be what everybody is talking about, but you’ll only see Jump and Ford bikes in San Francisco.
For now, all you can do is locate the nearest bike or scooter. You still have to open each individual app to scan the QR code and unlock those vehicles.
But this is an interesting approach. Citymapper doesn’t operate any transportation service. It can be an agnostic player and provide a comprehensive view of what’s around you without any conflict of interest. It doesn’t have to recreate a transportation hub like Lyft or Uber as those two companies recently acquired Motivate and Jump to provide bike-sharing services.
And if you’re visiting a city for the first time, you can open the app to find out how you’ll be able to navigate that new city.
Read Full Article
Transfer.sh is an instant sharing tool for programmers
File sharing tools are a dime a dozen these days. There’s Dropbox, Google Drive, and iCloud. But what if you want to share something quickly and easily from the command line? That’s why programmer Remco Verhoef created Transfer.sh.
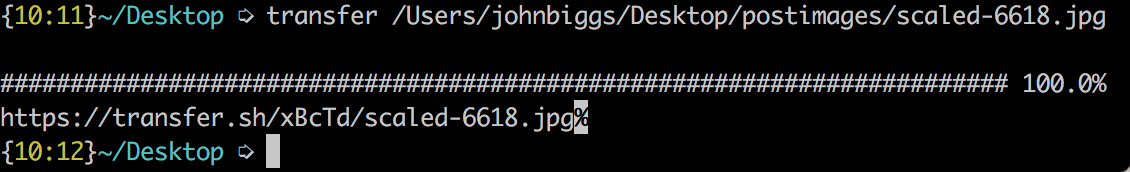
The service has basically a file dump. You send a file to transfer.sh via curl and it stays there for fourteen days until its automatically deleted. For example, I uploaded this picture by adding a bit of code to my .bashrc.
The system is one of those small, clever tools that just works. Verhoef created it because he needed to be able to upload files on the fly.
“I created this application when I needed to share log data from within a ssh shell with someone else,” he said. “So I created a web application where I can easily upload files using curl (which is available on almost every platform) just using the command line and modify the file on the fly, like encrypting the contents, applying grep etc. The application has been made open source because it could be usable for many other people and I’d encourage them to run their own server.”
“We don’t have a business model, and we are keeping the site running as courtesy. It is getting a bit difficult to keep it running, because of the popularity and usage,” he said. He also runs a dev shop and is releasing a number of other products including ICO security.
Verhoef doesn’t promise security on his platform, only convenience. He recommends piping files through gpg before uploading them.
Not everyone is using the product for good, however, which frustrates his team.
“It is being used by a lot of people,” he said. “Some are using it for uploading log files, others are exporting complete video surveillance to us. Sometimes it is being abused, by distributing malware, botnets and other malicious tools, but we try to stop it as soon as possible. One time a porn website was serving porn photos through us, and when we found out we had all photos replaced by dogs and kittens.”
Read Full Article
7 Hidden Calibre Features That’ll Help You Manage Your Ebooks Better

Calibre might not be the most polished app in the world, but it’s definitely the best software for managing your ebook collection.
It ticks all the right boxes: it’s free, there aren’t any ads, and it boasts a vast number of powerful features. Sadly, many of those features fly under the radar, which is a shame because they can elevate your ebook management to the next level.
So, without further ado, let’s take a look at some of the best hidden Calibre features.
Download: Calibre on Windows, Mac, and Linux
1. Merge and Split EPUB Ebooks
Some books come in multiple installments. Perhaps it’s a series of books like the Lord of the Rings trilogy, or maybe it’s a reference guide such as an encyclopedia.
Similarly, some books are exceptionally long; encyclopedias again spring to mind. A long book means a large file size, and that can be problematic when you’re waiting for a book to fully load in your e-reader.
The solution is to use two Calibre plugins called EpubSplit and EpubMerge. Combined, they let you collate multiple books or divide single books at your choosing.
To install the plugins, follow the instructions below:
- Open the Calibre app.
- Right-click on the Preferences icon in the upper right-hand corner.
- Select Get plugins to enhance Calibre from the drop-down menu.
- Locate EpubSplit and highlight the plugin.
- Click on Install in the lower right-hand corner.
- Choose the toolbars and menus where you want the plugin option to appear.
- Locate EpubMerge and highlight the plugin.
- Again, click on Install in the lower right-hand corner.
- And again, choose the toolbars and menus where you want the plugin option to appear.
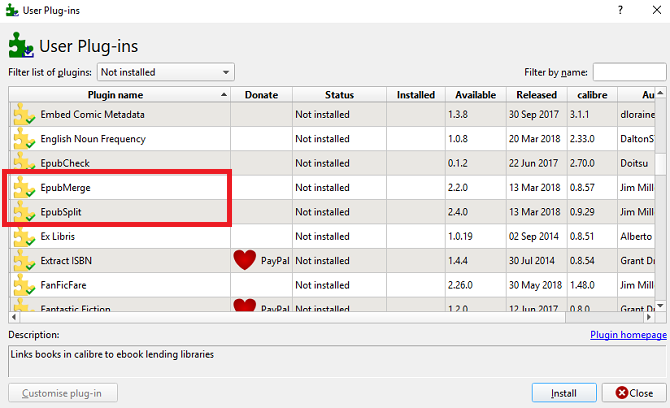
To use the plugins, click on the book you want to merge or split in your library, select the correct plugin in the menu bar, and choose the sections you either want to split or merge.
Note: The plugins only work with ebooks in the EPUB format. We’ll discuss how to convert books into different formats shortly.
2. Get Your Favorite Magazines on Your E-Reader
Online magazine subscriptions can be confusing. Some offer an online-only digital version, some offer a Kindle version, and some are only available as Android apps.
Wouldn’t it be great if you could cut through the fluff and download your favorite magazines onto your e-reader automatically?
Well, Calibre makes this possible.
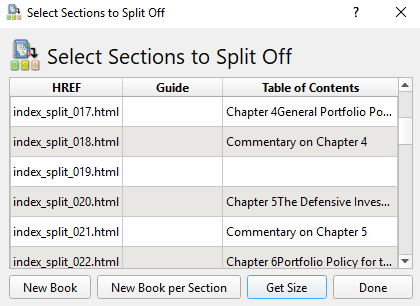
To get started, click on the Fetch News tab at the top of the app’s home screen. In the left-hand panel, you’ll see a list of languages. Click on your dialect of choice to see what’s available.
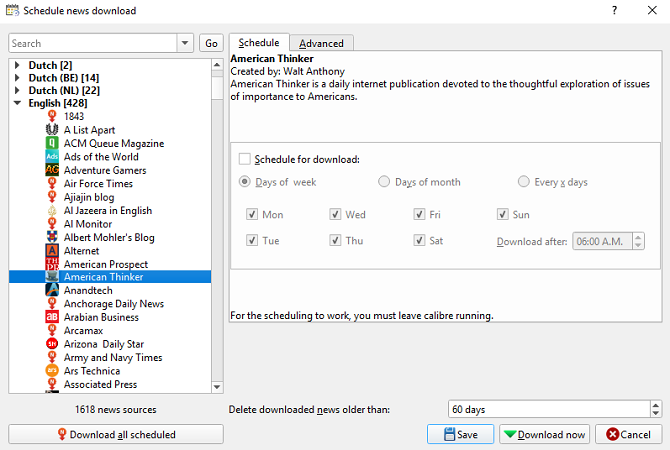
Find the title you want to read and—if required—enter your paywall login credentials. Next, in the right-hand panel, mark the checkbox next to Schedule for download and hit Download Now.
Lastly, you need to force Calibre to send your newly downloaded magazine issues to your e-reader. Go to Preferences > Behavior and mark the checkbox next to Automatically send downloaded news to ebook reader.
Note: For automatic downloading to work, Calibre needs to be running on your computer.
3. Turn Calibre Into a Sharing Server
If several members of your household have a Kindle, or if you own multiple Kindles, continually syncing your data manually quickly becomes tedious.
Instead, why not turn your Calibre app into a content server? By doing so, you can make your entire Calibre library available on all your devices. You can even upload new content to your Calibre library from those devices.
The process is remarkably straightforward. In Calibre’s menu bar, go to Connect/share > Start content server. Your computer might prompt you to allow the app through its firewall.
Next, click on the Connect/share tab for a second time. You’ll see your computer’s local IP address followed by the port number. Make a note of them.
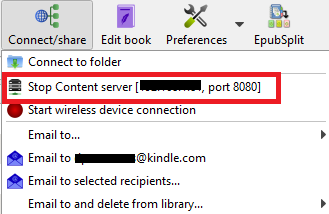
Now head to your Kindle’s browser (or any other browser) and type [IP address]:[port number] in the address bar. You should see all your Calibre books appear on your screen.
Click on a book’s title to open it or click on the + icon in the upper right-hand corner to add more content to your library.

Note: If you want to access your library when you’re away from your home network, you’ll need to allow port forwarding to Calibre’s port number on your router.
4. Convert Ebooks Into Different Formats
Sadly, the world of ebook file formats is a bit of a mess.
In theory, the standard format is the open-source EPUB. However, Amazon’s Kindle devices—which are the world’s most popular e-readers—can’t read it. Instead, they rely on the proprietary AZW format. And let’s not start on MOBI, LIT, AZW3, or the other dozen different formats you see out there.
Suffice to say, you need a way to convert ebooks into different formats.
Thankfully, Calibre delivers. To convert an ebook into a different file format, use the following instructions:
- Open Calibre.
- Right-click on the book you want to convert and go to Convert Books > Convert Individually.
- In the upper right-hand corner of the new window, choose your desired new format.
- Click on OK and give the conversion a minute or two to complete.
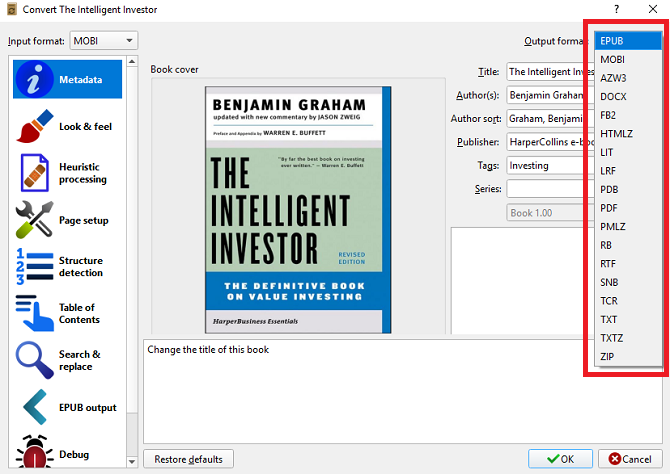
You can verify if the conversion has been successful by clicking on Jobs in the bottom right-hand corner of the app’s home screen. You can also check whether the new format is listed in the book’s information panel on the right-hand side of the screen.
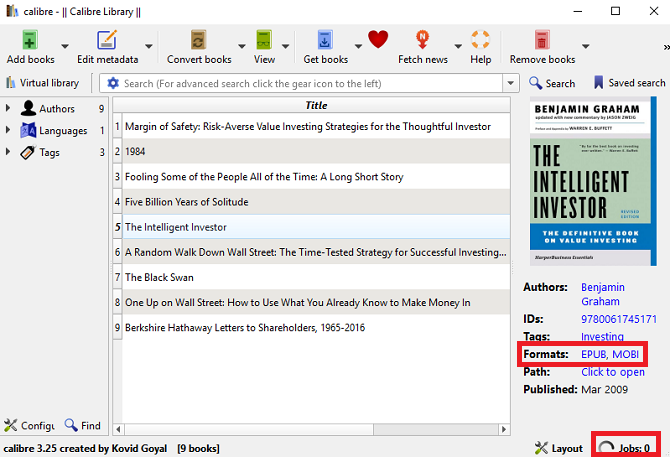
Note: You can also automatically convert new ebooks when you import them into your library for the first time.
5. Remove DRM From Ebooks
We now live in an age in which true ownership of digital media is becoming less common. Luckily for bookworms, Calibre lets your wrestle back control of your ebooks by offering a way to remove the DRM from titles you’ve bought from Amazon and other online stores.
We covered the process in detail when we explained how to remove the DRM on every ebook you own. So we recommend reading that article for the full scoop.
6. Automatically Download Ebook Metadata
Like any media library, you need to keep the metadata organized. Doing so will lead to a much smoother and more enjoyable experience, especially if you have a vast number of books.
But who has the time to enter all that information manually?
Calibre offers a little-used feature that lets you scan for your books’ metadata automatically. It can even find the correct book covers.
To scan for metadata, right-click on the book in question and go to Edit Metadata > Download metadata and covers. A new box will pop up on your screen. You need to select Download both.
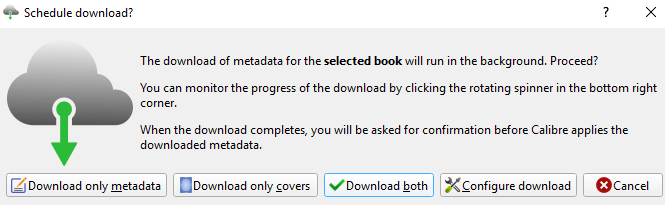
When the scan is finished, you’ll see a notification appear. Click on Review downloaded metadata and make any tweaks as appropriate.
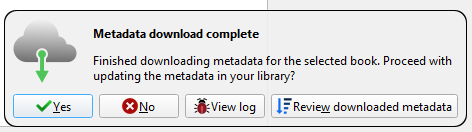
Calibre can pull metadata from Amazon, Google Images, Overdrive, Open Library, Edelweiss, Douban Books, and more.
7. Put Your Ebook Library in the Cloud
If using the content server method that we described earlier sounds too finicky, you can instead use Dropbox as an alternative.
By keeping your books in Dropbox rather than on your local machine, you’ll be able to access them from anywhere. However, if you set up the Calibre app correctly, you’ll also be able to use the app to manage your library locally.
Firstly, you need to download and install Dropbox on your computer.
Next, head to Calibre and move your library to the shared Dropbox folder on your machine. The fastest way of achieving this is to go to Preferences > Run Setup Wizard and point the Calibre app at the Dropbox folder.
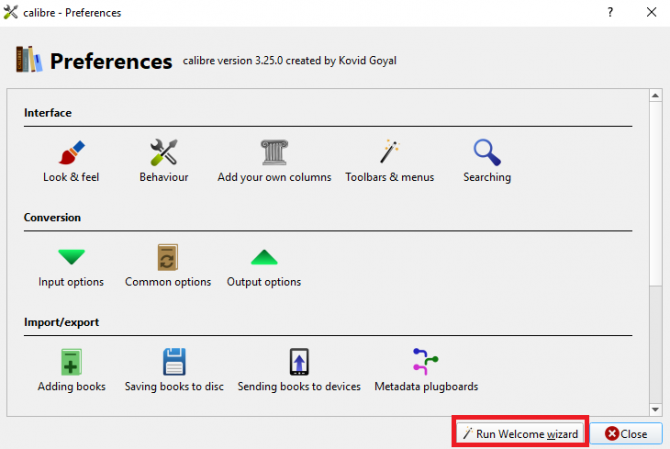
Lastly, drag-and-drop your ebooks from their current location into the Dropbox folder. Et voila, you now have a cloud-based ebook library that you can manage locally using Calibre.
Do You Need More Books to Read?
The seven features we have covered in this article are all great, but you won’t be able to enjoy them if you don’t have a library of ebooks to begin with.
But building a library doesn’t necessarily involve spending money. There are lots of sites to get free ebooks, and you can even download free books directly from Amazon.
Read the full article: 7 Hidden Calibre Features That’ll Help You Manage Your Ebooks Better
Read Full Article
