With just under a year until U.S. Election Day, Twitter is bringing back its Election Labels, which provide information about political candidates — including what office they’re running for and their state and district number. The labels will also have a small ballot box icon to accompany this information. The feature was first launched during the 2018 U.S. midterms, where the labels were seen 100 million times per day by Twitter users in the week before Election Day.
In addition, 13% of U.S. election-related conversations on Twitter included a tweet with an Election Label, the company says.
Now the labels are making a return ahead of the 2020 U.S. elections.
The labels will appear on accounts of candidates who are running for the U.S. House of Representatives, U.S. Senate, or Governor in the 2020 election who have qualified for the general election ballot, says Twitter. And they will begin to appear on candidates’ Twitter accounts after they qualify, which will happen on a rolling basis as states have different caucus and election dates, the company notes. The first takes place on March 3rd.
To enable the feature, Twitter has again partnered with Ballotpedia, a civic nonprofit that publishes non-partisan information about federal, state and local politics. The organization will help Twitter to identify which candidates have qualified for the general election ballot so their accounts can be appropriately labeled.
The Election Label will appear on the profile page of a candidate’s Twitter account and on every tweet and retweet they post to their account, even when embedded on sites off of Twitter.
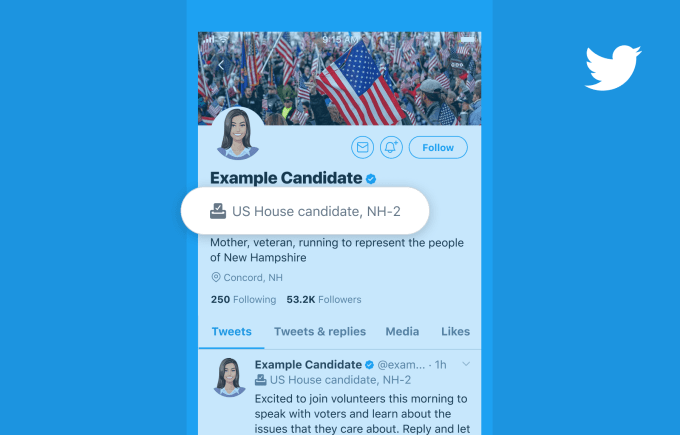
Ahead of this, Twitter today will also start to verify the campaign Twitter accounts of those who have qualified for primary elections for the U.S. House, Senate or Governor. This is different from how Twitter handled candidate verification during the 2018 midterms. Back then, it only verified candidates after they qualified for the general election ballot. This time around, Twitter says it will proactively verify the primary candidates.
This verification is the same checkmark other high-profile accounts receive — like those belonging to celebrities or other public figures. These verifications will start today and will continue on a rolling basis as states have different filing deadlines. Ballotpedia is also assisting on this effort as well, by helping Twitter identify the candidates.
Twitter, like other social platforms, had been heavily impacted by foreign interference with the U.S. 2016 presidential election. Last year, Twitter said that 1.4 million people had interacted with Russian trolls during the presidential campaign, which is more than double the 677,775 that Twitter originally believed had either seen, followed, or retweeted one of those accounts. These interference issues have been ongoing, as thousands of Twitter accounts spreading false information remained active in the weeks ahead of the U.S. midterms.
Bots continue today to infect the platform, in an effort to sway public opinion. For example, in April, Twitter removed over 5,000 bots with ties to a social media operation that previously promoted messages sympathetic to Saudi Arabia’s government. The bots had more recently been promoting the “Russiagate” hoax.
Disinformation efforts like this are not just impacting social platforms in the U.S. nor are they only associated with Russian bots. In a report released at the beginning of 2019, Twitter said it had banned more than 4,000 disinformation accounts originating in Russia, 3,300 from Iran, and more than 750 from Venezuela.
When Twitter first introduced the Election Labels for the U.S. midterms, it stressed how important it is for people using its platform to be able to identify the original sources and authentic information.
Today, Twitter’s system to label and verify politicians and candidates’ campaigns is now a part of a number of efforts Twitter has underway to make sure conversations taking place on its platform are authentic. The company says it will later release more tools to help better find quality news and have more informative conversations on Twitter.
Read Full Article