A blog about how-to, internet, social-networks, windows, linux, blogging, tips and tricks.
28 September 2018
Block.Party raises $10M, will adapt Settlers of Catan to its blockchain game console
Blok.Party, the company the upcoming PlayTable game console, announced today raised $10 million in new funding. It’s also unveiling a big content partnership, where Blok.Party will create its own version of the popular board game Settlers of Catan.
I first wrote about Blok.Party and PlayTable earlier this year, when co-founder and CEO Jimmy Chen first laid out his vision to use blockchain technology to build a console that can recognize real-world objects (like figurines and cards), creating a hybrid between tabletop and video gaming.
The idea may have sounded a little abstract at the time, but it got a lot clearer when Chen dropped by the TechCrunch New York office to play a couple rounds of Catan with me.
I’ll admit that I hadn’t played in a while, but it was clear from the start that PlayTable saved us some setup time — instead of putting all the pieces of the physical board together, you play on a digital representation of the board. Most of the pieces are digitized too, and we used and traded our cards using smartphones. But there is a physical “robber” pieces, because Chen said this allows the robber’s movement to remain “a very visceral experience … that a digital version can’t ever capture.”
It may not be too long before you get to try this out for yourself, at least if you’re among the 100,000 pre-orders Blok.Party has received so far. Chen said the company will start shipping its first devices this fall.
He added that Catan, like many of the other games built for PlayTable, will be priced at around $20.
“For us, it’s not about trying to compete based on price,” Chen said. “We’re trying to compete based on experience.”
The new funding comes from crypto fund JRR Capital and other investors. Chen said the company will use the money to continue scaling the product, including further software development and building out the library of games.
At the same time, he emphasized that although Blok.Party is manufacturing the initial devices, his vision is to achieve real scale through partnerships with hardware manufacturers, who will build their own PlayTable consoles. Apparently, some of those discussions are already underway.
“Our strategy is to always have [our own] hardware program running to continually do research,” Chen said. “What I’ve discovered is that keeping a hardware program running is not that expensive. The expensive part is when you try to scale the program.”
Read Full Article
Google Helps You Plan Your Next Vacation

Google is continuing on its mission to help us all plan our vacations more efficiently. Its latest efforts are designed to bring the various elements involved in planning a vacation together using the whole of Google, including Search, Maps, and Trips.
Vacations Can Be a Pain to Plan
In February 2018, Google aligned its vacation planning tools. The company realized that unless you pay a premium for a package holiday, there are so many elements involved that vacations can be a pain to plan. And now it’s improving its planning tools again.
Google explains the most recent changes in a post on The Keyword. The overarching theme is stitching your trip plans together across Google. And that’s the point. Google wants to be the one tool to rule them all when it comes to vacation planning.
Improving Your Vacation Planning Toolset
The first improvement allows you to resume planning where you left off. This means that even if you haven’t booked anything, when you search for a popular travel destination Google will show you relevant suggestions in Search.
As you start booking parts of your holiday Google will further customize your search results. For example, if you’ve already booked a hotel in Rome, the next time you search for Rome Google will show you flight prices, the weather, and any events taking place.
Google is also expanding your ability to track flight prices during the holidays. The company already offers this for Thanksgiving, but will now extend this through Christmas and New Year. This should save you paying over the odds for a flight.
Last but not least, Google wants to help you choose a hotel based on its location. To enable this Google is assigning each hotel a location score based on information pulled from Google Maps. You can then pick a hotel based on its proximity to your interests.
Making It Easier to Plan Your Vacation
Individually these changes are all fairly minor, but when combined they add up to a collection of tools almost guaranteed to make it easier to plan your next vacation. As long as you’re willing to give Google access to all of this information about your trip.
Read the full article: Google Helps You Plan Your Next Vacation
Read Full Article
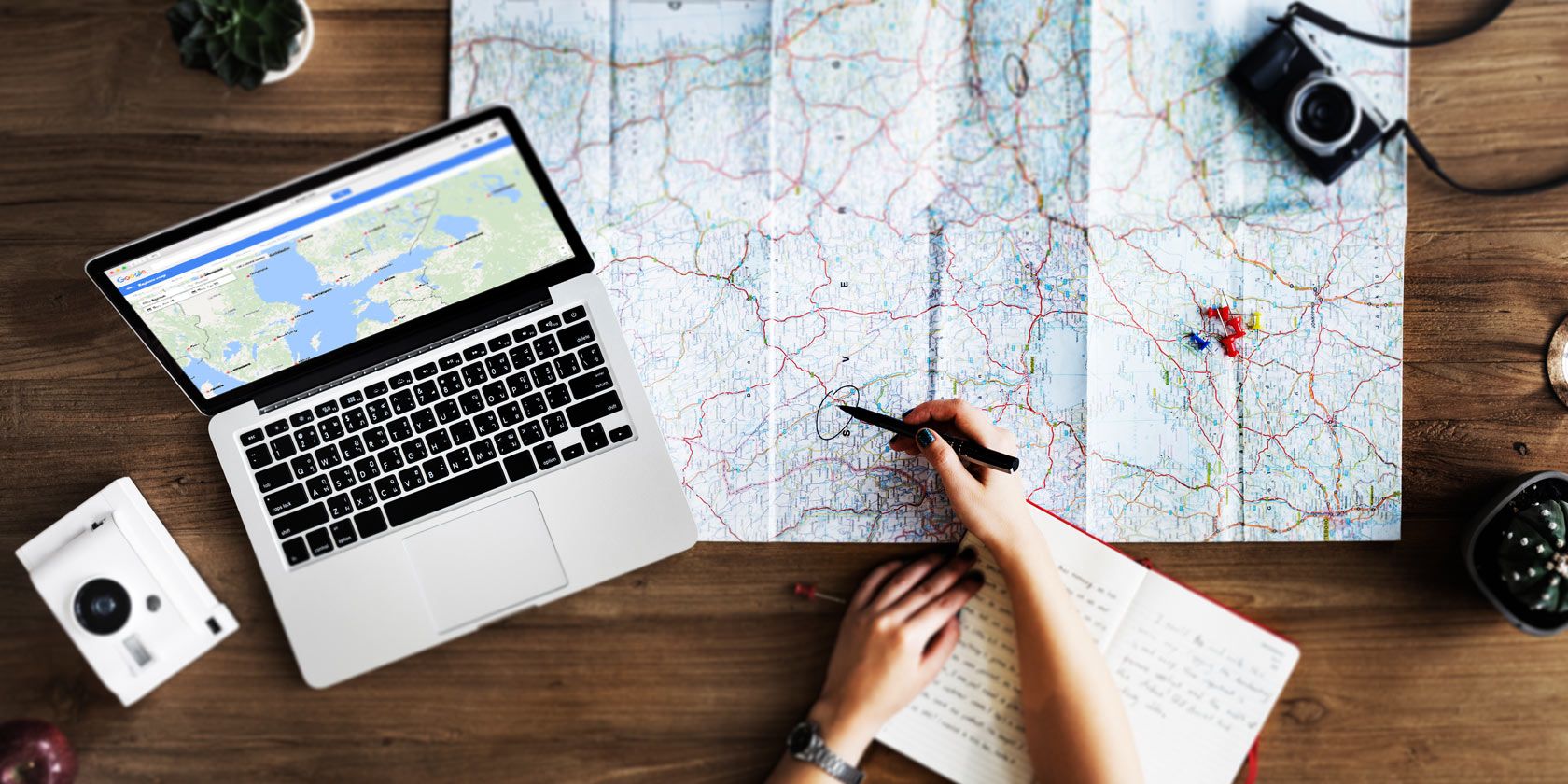
What Is “Five Eyes” Surveillance? VPN Users, Beware!

If you’ve ever used a VPN, or are concerned about online privacy, you’ve probably stumbled across references to “Five Eyes,” “Nine Eyes,” and “14 Eyes.”
But what exactly do these surveillance alliances do? And can they affect the security of your VPN service?
What Is Five Eyes?
Five Eyes is a nickname for the United Kingdom–United States of America Agreement (UKUSA).
Despite the official name, UKUSA agreement consists of five countries. They are the UK, US, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. The deal has its origins in a World War II intelligence-sharing agreement between Britain and America.
Five Eyes has given birth to many of the most notable privacy scandals in recent years, including PRISM, XKeyscore, and Tempora.
Today, its powers are scarily wide-ranging. According to the Electronic Frontier Foundation, the five governments can force any “communications service provider” (including ISPs, social media platforms, email providers, cell phone networks, and more) to:
- Insert malware on its users’ devices.
- Ignore existing laws in pursuit of Five Eyes directives.
- Interfere with people’s user experience.
- Provide governments with new product designs in advance.
- Provide user information as requested in secret warrants.
What Is Nine Eyes?
Nine Eyes is another intelligence sharing agreement. It’s grown out of the original Five Eyes alliance. It includes all the Five Eyes members, plus Denmark, France, the Netherlands, and Norway.
Its powers and dedication to information sharing is broadly the same as the Five Eyes agreement.
What Is 14 Eyes?
The 14 Eyes agreement adds a further five countries to the list: Germany, Belgium, Italy, Spain, and Sweden.
Interestingly, both France and Germany have been close to becoming full Five Eyes members in 2009 and 2013 respectively. The two agreements both fell through for various reasons.
Lastly, it’s important to mention Israel and Singapore. Israel reportedly enjoys observer status with the main Five Eyes group, while Singapore has partnered with the group but is not an official member.
What Does This Mean for VPNs?
Given the sweeping powers granted by the three agreements, what impact does it have on your VPN service?
It’s all a question of jurisdiction. When talking about a VPN provider’s jurisdiction, there are three things to consider:
- Local laws: Some countries outright ban VPN usage.
- Company location: The state in which the VPN provider is registered and has its physical offices.
- Server location: VPN providers typically offer servers in many different countries.
From a surveillance perspective, the two things you need to worry about are the company location and the company servers.
A VPN provider with either a physical address, or servers in the countries listed, could be compelled to hand over any information it has, including connection logs and browser traffic. The country might even monitor a VPN server’s inbound and outbound traffic. Worse still, the governments can forbid the provider from even notifying the affected customers; you lose the chance to respond to the invasion of privacy.
And, of course, due to the very nature of the agreements, once your information has been acquired by one country, it’s in the system. Ultimately, it could be shared with the other countries if they request it.
TFW you bank hates freedom and puts a hold on your card the SECOND you renew your vpn service for another year because it is (intelligently) based outside of Five Eyes countries.
— Jessica K (@Renessa47) March 29, 2018
If security is your main priority, you shouldn’t use a VPN that’s domiciled in one of the Five, Nine, or 14 Eyes countries. Nor should you connect to servers in one of those countries using a VPN provider from a non-14 Eyes member.
If you really need to use a VPN provider from one of the Five, Nine, or 14 Eyes member countries (for example, due to a unique feature), make sure you select one that explicitly does not keep logs. However, not even that can adequately protect you.
For example, you don’t need to look any further than the once-popular US-based email provider, Lavabit.
When the FBI found out Edward Snowden had used the service, it requested the company’s logs. The company did not keep logs, so the FBI instead issued a subpoena for the SSL keys. The keys would have given the FBI access to metadata and unencrypted content for all Lavabit users.
To its credit, rather than hand over the information, Lavabit opted to shut down. You cannot be so confident that your VPN provider would be equally willing to fall on its sword.
VPNs in Surveillance Countries: Which to Avoid
A surprising number of mainstream VPN providers have their headquarters in one of the participating countries. Here are a few popular ones to watch out for:
- Hotspot Shield
- StrongVPN
- Private Internet Access
- LiquidVPN
- IPVanish
- HideMyAss
- SaferVPN
- VPNSecure
- Getflix
- UnoTelly
- Mullvad
- PrivateVPN
To reiterate, these services aren’t necessarily bad. If your main reason for using a VPN is to circumvent geo-blocking on Netflix and other online services, you might have no choice but to sign up.
However, if you want a VPN for its security benefits, you should look elsewhere.
Which VPNs Do We Recommend?
If you want to avoid a VPN company that’s located in either a Five, Nine, or 14 Eyes territory, MakeUseOf recommends either ExpressVPN or CyberGhost.
ExpressVPN
Express VPN is based in the British Virgin Islands and thus is not subject to any of the three surveillance sharing agreements.
Other key features include an automatic kill switch (to prevent VPN leaks), split tunneling, service-wide encryption, zero-knowledge DNS, and 148 server locations across 94 countries.
Use this link to get up to 49% off of ExpressVPN!
CyberGhost
CyberGhost is a Romanian company and, therefore, is also not subject to the 14 Eyes information sharing requirements.
You’ll have access to unlimited bandwidth and traffic, DNS and IP leak protection, 256-bit AES encryption, support for OpenVPN, L2TP-IPsec, and PPTP protocols, and simultaneous connections on up to seven devices at the same time.
Both providers have servers in the US and UK, meaning you can still use them to access localized websites and services. Just remember to switch back to a non-14 Eyes country as soon as you no longer need access to the geo-blocked content.
Use this link to get a special discount for CyberGhost!
Learn More About VPNs
If you take away one thing from this article, learn to value the importance of thorough research. Many VPN providers are quick to profess how wonderful they are; if you look at each provider’s homepage, you will find it difficult to unearth the differences. However, dig a little deeper, and you’ll soon discover that some providers are much more secure than others.
If you’d like to learn more before signing up for a VPN provider, check out our articles on the best VPNs for Kodi, the best VPNs according to Reddit, and the best VPNs for Chrome.
Image Credit: antonprado/Depositphotos
Read the full article: What Is “Five Eyes” Surveillance? VPN Users, Beware!
Read Full Article
Spotify ends test that required family plan subscribers to share their GPS location
Spotify has ended a test that required its family plan subscribers to verify their location, or risk losing accessing to its music streaming service. According to recent reports, the company had sent out emails to its “Premium for Family” customers which asked them to confirm their locations using GPS. The idea here is that some customers may have been sharing Family Plans, even though they’re not related, as a means of paying less for Spotify by splitting the plan’s support for multiple users. And Spotify wanted to bust them.
Spiegel Online and Quartz first reported this news on Thursday.
Of course, as these reports pointed out, asking users to confirm a GPS location is a poor means of verification. Families often have members who live or work outside the home – they may live abroad, have divorced or separated parents, have kids in college, they may travel for work, or any other number of reasons.
But technically, these sorts of situations are prohibited by Spotify’s family plan terms – the rules require all members to share a physical address. That rule hadn’t really been as strictly enforced before, so many didn’t realize they had broken it when they added members who don’t live at home.
Customers were also uncomfortable with how Spotify wanted to verify their location – instead of entering a mailing address for the main account, for instance, they were asked for their exact (GPS) location.
The emails also threatened that failure to verify the account this way could cause them to lose access to the service.
Family plans are often abused by those who use them as a loophole for paying full price. For example, a few years ago, Amazon decided to cut down on Prime members sharing their benefits, because they found these were being broadly shared outside immediate families. In its case, it limited sharing to two adults who could both authorize and use the payment cards on file, and allowed them to create other, more limited profiles for the kids.
Spotify could have done something similar. It could have asked Family Plan adult subscribers to re-enter their payment card information to confirm their account, or it could have designated select slots for child members with a different set of privileges to make sharing less appealing.
Maybe it will now reconsider how verification works, given the customer backlash.
We understand the verification emails were only a small-scale test of a new system, not something Spotify is rolling out to all users. The emails were sent out in only four of Spotify’s markets, including the U.S.
And the test only ran for a short time before Spotify shut it down.
Reached for comment, a Spotify spokesperson confirmed this, saying:
“Spotify is currently testing improvements to the user experience of Premium for Family with small user groups in select markets. We are always testing new products and experiences at Spotify, but have no further news to share regarding this particular feature test at this time.”
Read Full Article
How to Play MP3 and Other Audio Files on a Raspberry Pi
Costing as little as $5, you can turn any Raspberry Pi into a whole host of useful devices: a Minecraft server, a retro gaming station, a desktop PC, or even a homemade laptop.
But how useful is it for playing music and audio files?
The Raspberry Pi as a Media Player
Not only can you use a Raspberry Pi as a Kodi media center, a Raspberry Pi can also play music. Thanks to the audio out port (see below), you can pipe music through to a dedicated speaker or simple headphones. With HDMI, you can even send audio to your TV (which you probably already knew).
But how do you play MP3s on Raspberry Pi without installing Kodi first?
Several tools can be installed on Raspbian (or whatever Raspberry Pi operating system you’re using) to play MP3, FLAC, OGG, even WAV files on your Raspberry Pi. With the right software, you might even be able to set up playlists and subscribe to podcasts!
Copying MP3 Files to Your Raspberry Pi
To get started playing MP3 or other audio files on your Raspberry Pi, you’ll need to either download some (via the browser), or copy them across.
You have several options for copying data to your Pi:
- Transfer files with a USB stick
- Upload files to your cloud account and download to the Pi
- Transfer using an external hard disk drive
- Copy data to the /boot/partition on your Pi’s microSD card
- Transfer data via SSH using a desktop SFTP app (such as FileZilla)
Find full details on all of these methods using our guide to transferring data between a Raspberry Pi and desktop PC.
Outputting Sound From Your Raspberry Pi
While HDMI is probably adequate, you might want to use the A/V socket on your Raspberry Pi. This might be the case if your HDMI cable doesn’t carry sound, for example, or the monitor speakers are faulty.
The Raspberry Pi 2 and later has a 3.5mm A/V port for use with audio and video TRRS compatible RCA cables. While the colors may not match those on your TV (some swapping around is required), the results are good. It’s thanks to this connector that the Raspberry Pi can be hooked up to old TVs for authentic retro gaming experiences.
In addition to video and audio, the port can also output audio only. A standard headphone jack can be connected, for example, as can a speaker. (For the best results, use a powered loudspeaker.)
Playing Audio in the Command Line With omxplayer
You should find omxplayer is already bundled with your Raspberry Pi. If not, use:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install omxplayer
Run from the terminal, omxplayer has a help file that you can check using:
omxplayer -h
However, to get started, all you need to know is the file path and filename of the audio file you wish to play.
In this example, I’ve copied an MP3 file (Led Zeppelin’s “In My Time of Dying”) to my Raspberry Pi and play it with omxplayer:
omxplayer inmytimeofdying.mp3
It’s really as simple as that:
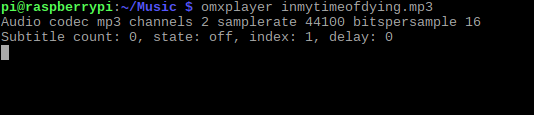
However, as you’ll discover when checking the help notes for omxplayer, you can do so much more, such as specify a particular route for the audio. To send the file through your HDMI cable, for example, use the audio pass-through switch, -o:
omxplayer -o hdmi [AUDIO_FILENAME]
You could also use the both command to play the audio through HDMI and the local output. The possibilities for audio (and video) playback with omxplayer are considerable, so once you get to grips with it you’ll find it a great tool to have to hand.
Playing Audio on a Desktop PC With VLC
If you would rather use a desktop computer to enjoy audio on your Raspberry Pi, the best option is VLC Player. Capable of playing all manner of media, VLC Player will play audio in virtually any format.
To install VLC, open a terminal and use:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install vlc
Wait for the software to download and agree to installation:
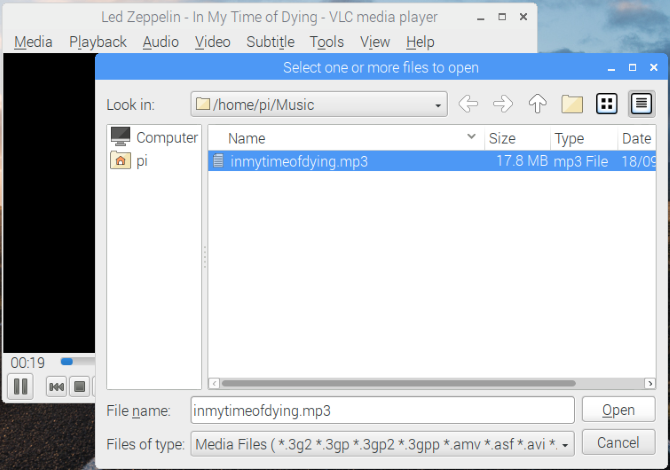
Note: VLC Player on the Raspberry Pi comes in two flavors. There is the main version, for easy installation, and the source version that can be compiled with hardware acceleration for better performance. You probably won’t need hardware acceleration for playing audio, although it might come in useful for high-definition video.
That’s all you need to do. The app will be added to a new menu subfolder called Sound & Video. Launch VLC from the desktop when you’re ready to playback your favorite audio tracks. (By the way, check out our tips on the best hidden VLC features.)
Enjoy Music With Your Raspberry Pi
It doesn’t take long to get music and audio playing on your Raspberry Pi. In fact, the main problem you’ll face is organization. So when you’re migrating your audiobooks or albums to your Pi’s storage, make sure everything is sorted correctly.
Believe us, having multiple directories labeled “Disc 2” is going to cause a lot of problems when you’re searching for a particular song!
Of course, you have other options to play music with your Raspberry Pi. Installing Plex will turn the Raspberry Pi into a media server and player for your home network.
Read the full article: How to Play MP3 and Other Audio Files on a Raspberry Pi
Read Full Article
The new Wear OS starts hitting smartwatches
Google’s in a tough spot with Wear OS. It’s been four and half years since the operating system arrived as Android Wear, and while plenty of manufacturers have tried their hand at devices, the operating system has failed to make a large dent on the smart watch category. Apple continues to dominate the space, while top competitors Samsung and Fitbit have opted to go in-house with their operating systems.
In February, Android Wear got a modest 2.0 update, and the following month, the operating system got a full on rebrand. “We’re now Wear OS by Google, a wearables operating system for everyone,” the company said at the time. Even with all of that movement over the past year, Wear OS is still in need of an upgrade. By a number of early accounts, the 2.1 update, which is starting to roll out to user, is a strong step in that direction.
This latest version brings new swipe gestures, prioritizing notifications, settings, Google Fit and Assistant. Those last two are also getting some key upgrades, helping bring the company’s health and AI offerings up to speed with the competition.
While the smartwatch play has appeared fairly stagnant at times, it’s important to remember as Android celebrates its 10th anniversary, that the smartphone OS wasn’t exactly a rousing success out of the gate. In the meantime, Apple, Fitbit and the like have proven that smartwatches do have some staying power, and once again analysts are bullish on the category.
Earlier this month, meanwhile, Qualcomm reaffirmed its commitment to Wear OS by showcasing its chip architecture promising extended battery life. It seems as if enough players are involved and hopeful in Wear OS to keep it going, but there’s still a lot of work to be done if it’s going to break out of the looming shadow of the Apple Watch.
Read Full Article
Nielsen: U.S. smart speaker adoption grew to 24% in Q2 2018, 4 in 10 own more than one
In the second quarter, the adoption of smart speakers – like Amazon Echo and Google Home devices – grew to 24% in the U.S., up from 22% the prior quarter, according to new data from Nielsen, released this week. The measurement firm took a look at how consumers were using their speakers, when, as well as how many were buying multiple devices.
The firm found that 4 out of 10 smart speaker owners have more than one device – a sizable percentage that points to consumers finding enough value in their first device to add more throughout the home.
The living room is the most popular location for smart speaker placement (63%), followed by the bedroom (35%), and then the kitchen (28%).
This is not surprising, given that the primary use case for the devices is music streaming, with 90% of smart speaker owners saying that stream music at least once per week.
Searching for real-time information like weather or traffic, followed by searches for historical facts were the next most popular activities, at 81% and 75%, respectively. News was tied for fourth place, with 68% listening in a typical week.
68% also said they chatted with their assistant for fun and used alarms and timers.
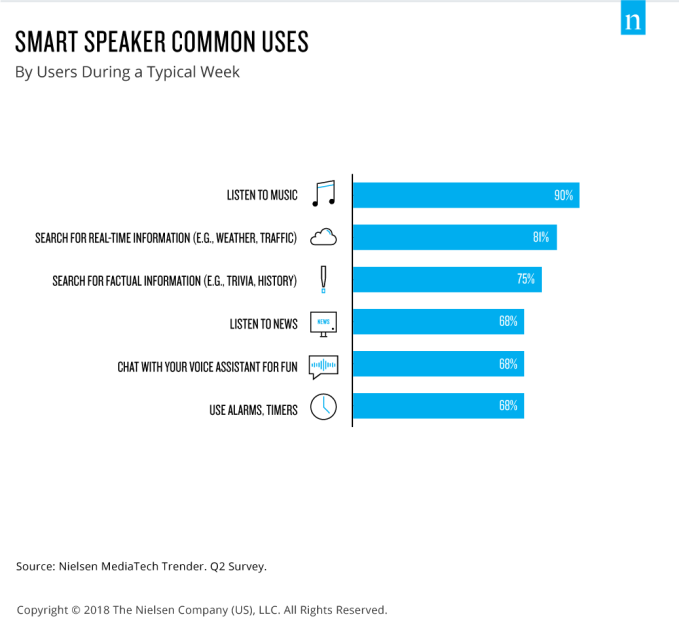
That so many people are chatting with their smart assistants, like Alexa and Google Assistant, in a more playful capacity is worth noting here. It’s not enough for these voice platforms to be good and finding and retrieving information and taking actions, they have to do that with some personality, too. Amazon has even gone so far as to give Alexa her own opinions on things like pets, beer, movies, colors, and more, which change from time to time.
Smart speakers are also acting as a bit of an extension of our mobile devices, the report said. Nielsen found that consumers were syncing data from their phones to the voice-based devices for things like audio streaming (53%) and shopping apps (52%), and more. This latter figure seems to indicate that many are, in fact, using their smart devices for shopping-related activities, despite earlier reports that downplayed shopping’s connection with smart speaker devices.
A recent report from The Information, citing leaked Amazon data, claimed that consumers were not making purchases through Echo devices. However, it seems that consumers are taking a first step towards purchase – list making – through Alexa. When the sale later goes through, however, it’s on the web, mobile web, or in the native app, not directly from the speaker. Whether or not that’s actually impacting sales, or just offering consumers a different way to create their purchase reminders, still remains to be seen. But there is a connection between the devices and the shopping app, this data shows.
Consumers were also found to use their smart speakers more often on weekends, and in the afternoons increasing as it got later in the evening, the survey said.
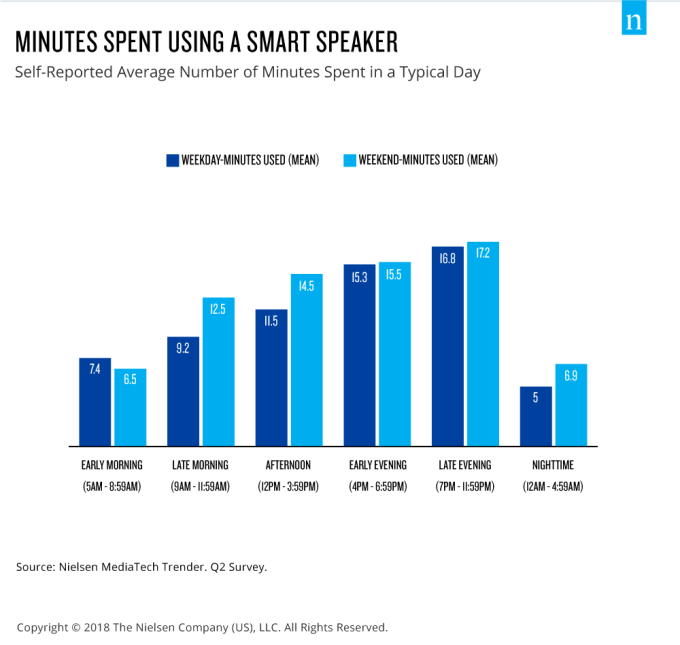
Also notable is that consumer sentiment towards their smart speakers is highly positive.
75% said they’d like to learn how to do more with the devices, and 72% said they would recommend them or purchase them as a gift for family and friends.
The data in the report comes from a new Nielsen consumer tracking survey called MediaTech Trender, which aims to understand consumer sentiment and behavior around emerging technologies, like smart speakers, VR, and other platforms. This particular survey was conducted among 2,000 U.S. consumers, and will continue to be done on a quarterly basis.
Read Full Article
Lyft unveils second annual diversity report
Lyft has released its second annual diversity report outlining the gender and racial breakdown of its 4,000-person workforce.
At a glance, little has changed from last year’s report, which was the first time the $15 billion ride-hailing company disclosed its diversity stats. Forty percent of Lyft’s workforce is female, a slight decrease from last year’s 42 percent, and about 33 percent of its leadership is female, a 3 percent decrease year-over-year. Fifty-two percent of its employees are white, down from 63 percent. Its leadership team remains mostly white and male.
It’s worth noting that Lyft roughly doubled in size in the last 12 months, according to Nilka Thomas, its vice president of talent and inclusion. The company is growing rapidly as it prepares for a 2019 initial public offering. This week, reports emerged that it was in talks with J.P. Morgan to lead its IPO and that it had more than doubled revenue in the first six months of 2018 to $909 million on a net loss of $373 million.
[gallery ids="1722278,1722279,1722280,1722281,1722282,1722283"]
The company has made several notable hires this year, too, including a whole bunch of former Tesla employees. Thomas, for her part, joined Lyft in March just months before the company brought in another $600 million and continued its hiring craze. She’s responsible for global hiring, diversity and inclusion, workplace policy and employee relations.
Thomas told TechCrunch that considering such immense growth at Lyft this past year, she’s pleased with the latest report.
“In hypergrowth, what tends to happen is you have a bias toward speed and diversity can suffer,” Thomas said.
Before joining Lyft, Thomas spent 13 years at Google, most recently as its director of global diversity, integrity and governance. In the six months since she was hired, Thomas has helped launch an internal database that gives employees access to the racial and gender diversity data of different teams across the company, a sort of diversity report card updated in real time. Thomas says the goal is to make sure a manager’s numbers don’t get lost in the bigger picture and to keep them accountable as Lyft continues to hire.
Thomas has also maintained a focus on Lyft’s culture. Though it’s great for companies like Lyft or Uber to disclose diversity data, it means nothing if they aren’t providing employees from underrepresented backgrounds resources to succeed. With that in mind, Thomas has piloted a program called R.I.C.H. — Race, Identity, Culture and Heritage — a group for Lyft employees to learn how to have difficult conversations surrounding race in the workplace.
“In the era of #MeToo, we want to make sure that we’ve gone beyond what our compliance obligations are,” she said. “We are really sensitive to what can happen to marginalized and vulnerable groups.”
Last year, Lyft was recognized by the Human Rights Campaign for its work on corporate equality. The company has implemented a Gender Inclusion and Affirmation Policy that promises to provide an inclusive environment for transgender people and supports various nonprofits through its Round Up & Donate program. Last month, Girls Who Code, an organization focused on closing the gender gap in tech, announced it had raised $1 million from Lyft rider donations.
Uber, for its part, hired its first-ever chief diversity officer, Bo Young Lee, earlier this year under chief executive Dara Khosrowshahi’s lead. In its first diversity report since both Khosrowshahi and Lee were hired, Uber showed slight progress, though the company still has no black and brown people in tech leadership roles.
At TechCrunch Disrupt SF in September, TechCrunch’s Megan Rose Dickey spoke to both Khosrowshahi and Lee. Khosrowshahi, in a wide-ranging discussion, said Uber is “really trying to shift the culture of the company going forward.” Lee, for her part, told Dickey she’s working tirelessly to integrate Uber’s new cultural norms.
Both Uber and Lyft — in fact, most of the highly valued unicorn companies in Silicon Valley and the Fortune 500 powerhouses — have a long way to go before establishing equitable cultures and hiring practices.
“This challenge expands across the entire industry, in part because we’ve normalized the problem,” Thomas said. “We have a pretty dire status quo.”
Read Full Article
Can You Trust Your Browser With Credit Card Information?

You’re shopping online; you find the perfect item, proceed to checkout, and pay. Your browser remembers your username. It might even remember your password, based on what you’ve entered in the past.
But then it asks whether you want it to save your credit card information. Can you trust your browser with keeping that secure? Should you avoid Autofill altogether? And how can your browser keep your financial data safe when you’re visiting websites?
What Exactly Is Autofill?
We trust our browsers with a huge amount of data, mostly because we feel we have to. You must have confidence that your browsing history, for instance, won’t be leaked en masse. Yet many of us are wary of the private information collected and used for advertising.
Nonetheless, we become complacent and let Autofill (a feature in web browsers like Google Chrome) and Autocomplete do the hard work for us.
No one likes filling in forms, and so Autofill will add in your email, phone number, and address for you if you want. You have to have this function turned on, of course—we’ll come back to this later on because you’ll need to know how toggle settings. Most mainstream browsers do this, notably Google Chrome, Safari, and Microsoft Edge, which boast the lion’s share of the market.
You can also use Autocomplete on Opera and Mozilla Firefox, both of which are especially well-known for their focus on maintaining your privacy.
You might think this is all done through cookies stored automatically, but implementation is more complex than that. It’s not simply a case of storing information: it’s also about presenting it in the appropriate fields.
There’s a section devoted to Autofill on your browser, so you can add in your credit or debit card information and rely on that in future. On Chrome, all you need to do is visit chrome://settings/autofill and enter payment methods.
But wait. Before you do that, you should know the dangers…
Should You Use Autofill for Payment Methods?
The problem with using Autofill for credit card information isn’t about trusting your browser. It’s about hackers gaining access to this through phishing sites.
Phishing is simply a fraudulent means of obtaining personal information. Websites set up by cybercriminals may have text boxes for basic information which we regularly give up anyway. Despite the value of personal data, we often submit our names and email addresses. They don’t feel like a valuable commodity anymore because we use them to sign up for social networks, online shops, and newsletters.
If you’ve got Autofill turned on, these text boxes will be automatically filled in. But some phishing sites have hidden elements. These won’t be seen by users, but dig into a page’s script, and malicious code reveals secret intents. These trick your Autofill function into adding private data which you’ve not approved of on the site but have within your browser.
Not all browsers do this. Chrome and Firefox only add credit card details into boxes you specifically click on. If a form element isn’t visible, then you don’t click in the box, so Autofill doesn’t relinquish any further data.
That’s not the only concern, though. Your main worry should be: what happens if someone else gets access to your browser?
This is possible in a couple of notable ways. The first is simple. Someone uses the same device. You probably trust the people you share a computer with, but junked or recycled hardware can be a serious security threat. Ideally, you’ll clean all data from any devices you’re passing on.
Another means is, once more, through phishing. Take Vega Stealer for example. This malware was spread through an email campaign primarily targeted at the marketing and PR sector. Vega Stealer’s main purpose was to collect details stored within Chrome and Firefox, i.e. cookies and credentials stored for Autofill.
Essentially, you store data locally, but that doesn’t mean a third-party can’t access it.
Can You Trust Your Browser to Transmit Data?
If you can’t entirely trust your browser to Autocomplete your financial details, how can you trust it with payment details at all?
Browsers recognize that they have a duty of care. If they don’t look after users, those disgruntled customers will switch to one of their competitors.
Data sent between your device and a site’s server should be encrypted. This means private information is rendered unreadable to anyone without the correct decryption key, i.e. your password. Check a site is secure by looking at the URL; if it reads “HTTPS”, that extra “S” stands for “Secure”.
You could also use a Virtual Private Network (VPN), which acts as a tunnel between two destinations. Picture a tunnel between your PC and the website you’re using. No other parties can look at what’s going through that tunnel unless they’re at either end-point. VPNs even protect your data when your device is connected to a public network.
As VPNs go, we highly recommend ExpressVPN (save up to 49% off using this link) and CyberGhost.
VPNs are typically a regular expense, but Opera has one already built-in. It’s not turned on by default, so you’ll need to go to the browser settings, then Privacy and security > Enable VPN.
Sadly, other browsers don’t boast this same feature. This is partly because VPNs stop the collection of cookies, which many consider enhance your online experience—though, as Vega Stealer demonstrates, they can also be exploited.
And let’s not forget that you don’t have a choice but to trust your browser to some degree. If you shop online, you must have confidence that your browser takes the necessary security measures. Otherwise, you’re reduced to solely visiting bricks-and-mortar stores.
How Do You Turn Off Autofill?
The process is different depending on the browser you use. Still, it’s typically very easy to do. On Chrome, for example, click on the vertical ellipsis in the top right-hand corner then go on Settings. Or take a shortcut by going to chrome://settings/autofill.
From there, you can turn Autofill off completely, or just instruct Chrome not to collect payment methods. Our look at Autofill’s privacy implications explains how to disable this feature in all mainstream browsers.
Read the full article: Can You Trust Your Browser With Credit Card Information?
Read Full Article
The 12 Best Udemy Courses for Blockchain and Cryptocurrency

It doesn’t matter whether you’re a cryptocurrency newbie or a blockchain expert, there’s always something new to learn.
Udemy courses are one of the best ways to grow your knowledge in any area, and crypto is no different. If you’d like to expand your horizons, check out these 12 Udemy courses for blockchain and cryptocurrency.
1. Blockchain and Bitcoin Fundamentals
Price: PAID
Level: Beginner
Length: 2.5 hours
This introductory course is an excellent launchpad for anyone who’s just starting their blockchain and cryptocurrency journey.
The bulk of the content is divided into 29 short lectures that last no more than five minutes. The videos cover simple topics such as what is a blockchain, Bitcoin’s history and value, smart contracts, SegWit, and hashes.
The course concludes with a guide for buying your first Bitcoins, including advice on wallets, storage, and performing transactions.
2. Blockchain A-Z: Learn How to Build Your First Blockchain
Price: PAID
Level: Expert
Length: 14.5 hours
One of the beautiful aspects of decentralized blockchains is that anyone can make one. This course teaches you how with a complete step-by-step guide. The three modules are How to Build a Blockchain, How to Create a Cryptocurrency, and How to Create a Smart Contract.
The course also includes a great guide to five of the most popular altcoins: Litecoin, Neo, Ripple, Cardano, and Stellar.
3. Blockchain for Business 2018: The New Industrial Revolution
Price: PAID
Level: Intermediate
Length: 6 hours
As the many real-world examples of blockchain prove, there are very few companies that won’t benefit from using the technology in some part of their business model.
If you already have a solid understanding of how a blockchain works, but you’re not sure how that translates to your own enterprise, this is the course for you.
The videos focus on four business sectors: industrial, tech, consumer goods, and finance.
4. The Basics of Blockchain: Ethereum, Bitcoin, and More
Price: PAID
Level: Beginner
Length: 3.5 hours
Targeted at beginners, The Basics of Blockchain: Ethereum, Bitcoin, and More course introduces you to the key features of blockchains.
The course begins with an overview of blockchains, then progresses into looking at blockchains’ economics, underlying technology, and business viability.
Each of the four modules ends with an exam so you can check you’ve understood the content.
5. Build and Deploy Your First Decentralized App with Ethereum
Price: FREE
Level: Beginner/Intermediate
Length: 1.5 hours
Decentralized apps—DApps for short—are like regular apps, except they are built on a blockchain. Anyone can create a DApp using smart contracts.
This course explains the process. It assumes you have no prior knowledge; it describes the basics in a simple and clear way.
As you progress through the course, the complexity of the content goes up a notch. Videos cover topics such as solidity events, function modifiers, mappings and structs, and inheritance and deployment.
6. Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Course 101 for Absolute Beginners
Price: FREE
Level: Beginner
Length: 1 hour
This short one-hour long free course is perfect for anyone who wants to educate themselves in the basics of blockchain and cryptocurrency but who has no interest in digging down into the nitty-gritty of the topic.
The eight videos explain the core concepts in simple terms. They tick off the key things you need to know, including mining, how smart contracts work, decentralized autonomous organizations, and cryptocurrencies.
7. Cryptocurrency Wealth: How to Trade & Invest Like the Pros
Price: PAID
Level: Intermediate/Expert
Length: 4 hours
Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you’ll know that investor interest in cryptocurrencies has exploded over the last couple of years.
In some ways, trading cryptocurrencies is like trading on traditional Forex exchanges. In other ways, it’s like night and day. This course introduces you to everything you need to get going, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis, using exchanges, and buying ICOs.
Warning: Trading cryptocurrencies is extremely risky! The markets are highly volatile. Do not invest more than you can afford to lose.
8. Blockchain Development on Hyperledger Fabric Using Composer
Price: PAID
Level: Expert
Length: 8 hours
This course is aimed squarely at expert-level programmers, coders, and developers.
If you don’t have a solid understanding of JavaScript, Java, or NodeJS, as well as a working knowledge of HTTP and REST, this isn’t the course for you. Ideally, you also need to be comfortable using Docker and Unix commands.
The course itself explains how to use the Hyperledger Fabric framework to create enterprise-grade blockchains and applications.
9. The Cryptocurrency Bible
Price: PAID
Level: Beginner
Length: 3.5 hours
The Cryptocurrency Bible is one of the cheapest courses on this list. The other beginner courses we’ve introduced you to have focused on the blockchain side of things. This course looks at beginner-level topics in the cryptocurrency sphere.
Lectures cover information such as the history of Bitcoin, how to create a trading account, how to start mining coins, and the importance of cryptography.
10. Cryptocurrency Investment Fundamentals
Price: PAID
Level: Beginner/Intermediate
Length: 4 hours
With a 4.9-star rating, the Cryptocurrency Investment Fundamentals is the highest-rated crypto trading course on Udemy.
It offers a fantastic holistic overview of all aspects of the trading process. In our opinion, the best module is Cryptocurrency as an Investment. It discusses the differences between crypto and stocks, the relationship between Bitcoin value and altcoins’ value, the economics of crypto supply and demand, and much more.
The course closes with some investment strategies, including a special section on Warren Buffet’s approach to wealth accumulation.
11. Cryptocurrency Investing: How to Find Undervalued Altcoins
Price: PAID
Level: Intermediate
Length: 1 hour
As you’re probably aware by now, there’s a lot more to crypto than just Bitcoin. The altcoin sector has also exploded; estimates suggest there are between 1,600 and 2,000 in existence.
This course teaches you to spot the small handful of those 2,000 altcoins that are undervalued. It covers how to perform altcoin research, how to spot ICO scams, and more.
12. Ardor Blockchain Bootcamp
Price: FREE
Level: Intermediate/Expert
Length: 3.5 hours
We end with the Ardor Blockchain Bootcamp course. Ardor is a cryptocurrency and a blockchain that sells itself as a scalable blockchain-as-a-service solution for businesses.
The first part of the course discusses Ardor wallets, buying Ardor, and using Ardor. The second part looks in more detail at the advanced functions of the Ardor blockchain, including accessing the TestNet, and using Ardor as a monetary system, voting system, and data cloud, and marketplace.
Learn More About Blockchains and Cryptocurrency
Udemy courses can help you learn, but so can we!
If you’re a novice and would like to learn more about blockchain and cryptocurrency, check out our introduction to cryptocurrency terms you need to know.
Read the full article: The 12 Best Udemy Courses for Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
Read Full Article
How to Extract Pages From a PDF in Windows 10

PDF is a multi-platform document format. So there’s no shortage of PDF apps and software to manage all your PDF needs. One such need is the ability to extract a specific page or a set of pages from a larger PDF document.
Third-party tools can do it easily, but did you know that Windows 10 has a native tool that does the same job? It’s called Microsoft Print to PDF, and here’s how to use it.
How to Extract Pages From a PDF in Windows 10
The Print to PDF feature is baked into Windows 10 and is available to any app that has a print feature. You can find it in the Print dialog of the applications. Also note that “extracting a page from a PDF” keeps the original PDF document intact. The extracted pages are “copied” as a separate PDF and saved in your desired location.
The process is simple. We are using Google Chrome to open and extract the PDF pages:
- Open the PDF file you want to extract pages from with a program that supports PDF. Browsers like Chrome and Microsoft Edge are ideal candidates. Even Microsoft Word can do the job.
- Go to the Print dialog or hit the universal shortcut key Ctrl + P. You can also right-click and select Print from the context menu.
- In the Print dialog, set your printer to Microsoft Print to PDF.
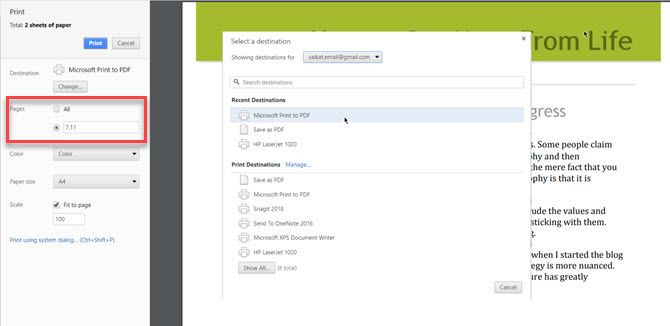
- In the Pages section, select the option for entering a page range and enter the page number which you want to extract. For instance, if you want to extract Page 7 of a PDF file, enter 7 in the box. If you want to extract a few non-consecutive pages like page 7 and 11, enter 7, 11 in the box.
- Click Print and browse to the location where you want to save the file.
Multiple extracted pages are saved as a single PDF document. To separate them as different documents you need to extract them one by one.
The ability to extract PDF pages is useful in many everyday scenarios, just like these free tools that help you edit PDF files anywhere.
Read the full article: How to Extract Pages From a PDF in Windows 10
Read Full Article
Browse the Best Gaming Easter Eggs and Deleted Content on This Site

With all the work that goes into developing video games, do you ever wonder what gets left behind? It’s a common occurrence for developers to leave all sorts of graphics, music, secret messages, and other tidbits in their games.
As it turns out, there’s a website that’s completely dedicated to finding unused content in games. It’s called The Cutting Room Floor (TCRF), and it’s definitely worth a look if you’re into games.
The Best Gaming Easter Eggs and Deleted Content
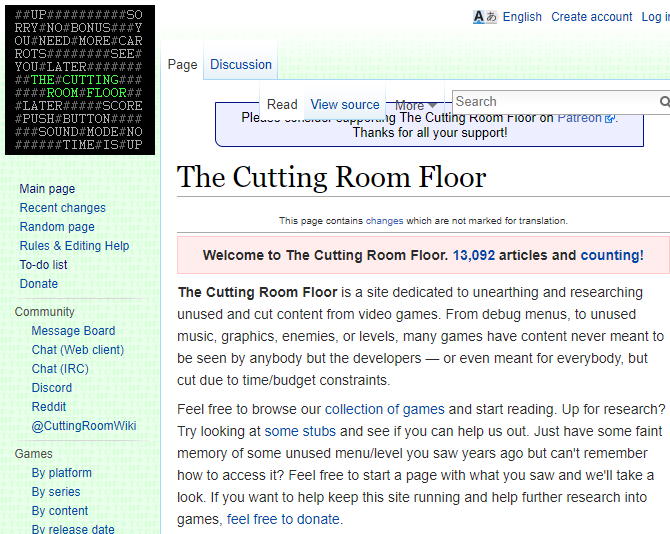
TCRF is set up like other wikis you may have visited. The homepage provides a featured articles, trivia, and even links to contribute if you’re interested.
Use the Search box in the top-right to look for a game, or browse by various criteria using the links on the left. Start with the best platformers of all time if you need some inspiration.
Once you land on a game’s page, you’ll see a breakdown of all the neat content inside. Common types of deleted content on TCRF include:
- Debug modes: Many games feature a mode that allows you to manipulate the game for testing purposes.
- Unused graphics: Find sprites, fonts, items, enemies, and more that didn’t make it into the game.
- Unused music: Here you’ll find tunes that weren’t used in the final game for whatever reason.
- Revisional differences: This section shows what changed between revisions (often quite interesting for older games).
- Regional differences: Similar to the above, this collects differences between the game in different countries.
More than the content alone, what makes this site great is the commentary on the items and thinking about what it implies. It’s interesting to speculate on what an unused music track was for, or why a certain expression for a character was cut.
Overall, if you want to go deeper into your favorite games, The Cutting Room Floor is a great place to do so. It’s fun to explore what was leftover and what could have been.
For more, check out other awesome game sites you’ve probably never heard of.
Read the full article: Browse the Best Gaming Easter Eggs and Deleted Content on This Site
Read Full Article
How to Delete Cookies on Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari

HTTP cookies have both positive and negative traits. Yes, third-party cookies can follow you around the web and record your actions, but cookies can also be used for authentication, personalizing websites, and automatically filling in forms.
If you delete them, you’ll lose all that stored information and will have to enter it again.
However, if you still want to press ahead and delete your browser’s cookies, we’ve got you covered. Here’s how to clear cookies on four popular browsers.
How to Delete Cookies on Google Chrome
If you’re running Google Chrome, use these instructions to clear your cookies:
- Open Chrome and click on the More menu in the top right-hand corner.
- Go to Settings > Advanced > Clear Browsing Data.
- Click the checkbox next to Cookies and other site data.
- Select Clear data.
How to Delete Cookies on Mozilla Firefox
If you’re a Firefox user, you need to follow these instructions instead:
- Open Firefox and click on the Menu button (three horizontal lines).
- From the menu, choose Options.
- Select Privacy and Security in the left-hand menu.
- Click on the Manage Data link.
- Choose Remove All Shown.
How to Delete Cookies on Microsoft Edge
Edge is still a relative newcomer in the world of browsers, but it’s becoming increasingly popular among Windows users. Here’s how to clear cookies on Edge:
- Open Edge and click on the More button.
- Go to Settings > Clear Browsing Data > Choose what to clear.
- Mark the checkbox next to Cookies and saved website data.
- Click Clear.
How to Delete Cookies on Apple Safari
Lastly, let’s look at how to delete cookies on Safari.
- Go to Safari > Preferences.
- Click on Privacy.
- Select Manage Website Data.
- Click on Remove All.
To learn more about other non-mainstream browsers, check out our article about open-source web browsers you should check out.
Image Credit: Faithie/Depositphotos
Read the full article: How to Delete Cookies on Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari
Read Full Article
California cops bust crime ring that nabbed $1M worth of devices from Apple Stores
Fear not, citizens — the law enforcement apparatus of California has apprehended or is hot on the trail of more than a dozen hardened criminals who boldly stole from the state’s favorite local business: Apple. Their unconscionable larceny amounted to more than a million dollars worth of devices stolen from Apple Stores — the equivalent of hundreds of iPhones.
The alleged thieves would wear hoodies into Apple stores — already suspicious, I know — and there they would snatch products on display and hide them in the ample pockets of those garments. Truly cunning.
These crimes took place in 19 different counties in California, the police forces of which all collaborated to bring the perpetrators to justice, though the San Luis Obispo and Oakland departments led the charge. So far seven of the thieves have been arrested, and nine more have warrants out.
In a press release, California Attorney General Xavier Becerra harangued his state regarding the dangers of the criminal element.
Organized retail thefts cost California business owners millions and expose them to copycat criminals. Ultimately, consumers pay the cost of this merchandise hijacking. We will continue our work with local law enforcement authorities to extinguish this mob mentality and prosecute these criminals to hold them accountable.
You hear that, would-be copycats? You hear that, assembling mob? Xavier’s gonna give it to you… if you don’t fly straight and stop trying to stick ordinary consumers with the costs of your crimes. Not to mention California businesses. With Apple paying that $15 billion in back taxes, it doesn’t have a lot of cash to spare for these shenanigans.
Well, I suppose it’s doing okay.
I’ve asked Apple for comment on this case and whether they participated or cooperated in it. Perhaps Face ID helped.
Read Full Article
Facebook policy head makes a surprising cameo at the Kavanaugh hearing
Facebook might be doing its best to stay out of political scandals in the latter half of 2018, but the company had a presence, front and center, at one of the most contentious Senate hearings in modern history.
Facebook’s Vice President of Global Public Policy at Facebook, Joel Kaplan, was spotted sitting prominently near his wife, Laura Cox Kaplan, in the section for Brett Kavanaugh’s supporters. He is pictured on the left side of the header image, second row, in a blue tie.
For reference, below is an image of Kaplan to the immediate right of Mark Zuckerberg during a Senate Judiciary joint hearing in April of this year.

WASHINGTON, DC – APRIL 10: Facebook co-founder, Chairman and CEO Mark Zuckerberg concludes his testimony before a combined Senate Judiciary and Commerce committee hearing in the Hart Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill April 10, 2018 in Washington, DC. (Photo by Win McNamee/Getty Images)
Kaplan has not made any public commentary on Twitter or Facebook about his support for the Supreme Court nominee, though through retweets, Kaplan’s wife appears to be of the mind that the hearing is part of a “smear campaign” against the family friend.
Kaplan is also featured in this viral image, making the rounds on Twitter.
What a photo… pic.twitter.com/OIW5700U8C
— Sam Altman (@sama) September 27, 2018
His appearance during the hearing is a show of personal support, though it still turns heads for such a prominent Facebook employee to make a visible statement during such a politically divisive event. Kaplan is not representing Facebook in a formal capacity.
Kaplan served as a policy adviser on George W. Bush’s 2000 election campaign and went on to serve as a policy assistant to the president and as the deputy director of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and a deputy chief of staff. Kavanaugh worked for the Bush administration during the same period, joining the former president’s legal team and going on to work on the nomination of Chief Justice John Roberts to the Supreme Court.
Kaplan joined Facebook in 2011 as its VP of U.S. public policy. Kaplan continues to serve in a heavily influential political role with the company today, leading its Washington D.C. office which serves as the company’s lobbying arm.
Read Full Article
Amazon Launches a New 4-Star Retail Store

Amazon is continuing its push into bricks-and-mortar retail. This time with a new store in New York. Called Amazon 4-star, the new store will sell a selection of bestselling products, all of which have a rating of 4 stars or above on Amazon.com.
In December 2016, Amazon announced Amazon Go, a grocery store with no checkouts. There are now four Amazon Go stores in the U.S., with more due to be opened soon. However, Amazon’s bricks-and-mortar ambitions don’t end there…
Amazon Launches a 4-Star Store
The first Amazon 4-star store opened today in New York. As the name suggests, everything sold in store is “rated 4 stars and above, is a top seller, or is new and trending on Amazon.com”. This is, in essence Amazon.com curated for a smaller retail space.
The products on sale include “devices, consumer electronics, kitchen, home, toys, books, and games”. In a post on the Amazon Blog, Amazon suggests the selection is “a direct reflection of our customers—what they’re buying and what they’re loving”.
Amazon 4-star opens tomorrow in the SoHo neighborhood of #NYC – check out a sneak peek of the store here: https://t.co/tA2G8zI5OK pic.twitter.com/UYD0UeEkA5
— Amazon News (@amazonnews) September 26, 2018
Amazon has tried to bring some elements of the website through to its retail space. So there are products grouped as “Most-Wished-For” and “Frequently Bought Together”. There are also review cards with actual quotes from Amazon customers.
Interestingly, each product has two price tags; the list price and the Prime price. The latter is the same price you’d pay buying online, but it’s only available to Prime subscribers. So even in its retail spaces Amazon is giving people a reason to sign up for Prime.
Amazon Likes Bricks and Mortar
This is Amazon pushing hard into the physical retail space. Like it or not, Amazon has forced many retailers out of business, and now Amazon is literally moving into the stores those retailers have abandoned. As Alanis Morissette once sang, “Isn’t it ironic”.
While Amazon stores are clearly destined to become a common sight in cities, for the time being at least most of us will continue to shop on Amazon’s websites. So, with that in mind, you should check out our exhaustive guide to shopping on Amazon.
Read the full article: Amazon Launches a New 4-Star Retail Store
Read Full Article
Google adds creator credit to Images
Google’s attempting to smooth out its relationship with photo rights holders by bringing some additional contextual data to its Image Search. In a blog post today, Product Manager Ashutosh Agarwal highlighted the company’s plan to associate Creator and Credit metadata with images served up via search.
The company notes that finding out who created a given image — and who owns the rights — has traditionally been tricky online. Google Images hasn’t been particularly useful in this manner, forcing users to hunt down that information themselves.
The information will start showing up on images today, when available, and in the next few weeks, Google will also be adding a copyright notice. Users can find all this by clicking the “Image Credits” link on a given shot.
Google’s partnering with CEPIC (Center of the Picture Industry) and IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council) to create best practices for attribution, moving forward. The company has received pushback regarding Images of late. Back in February, Google dropped the View Images link as part of a settlement with Getty.
Read Full Article
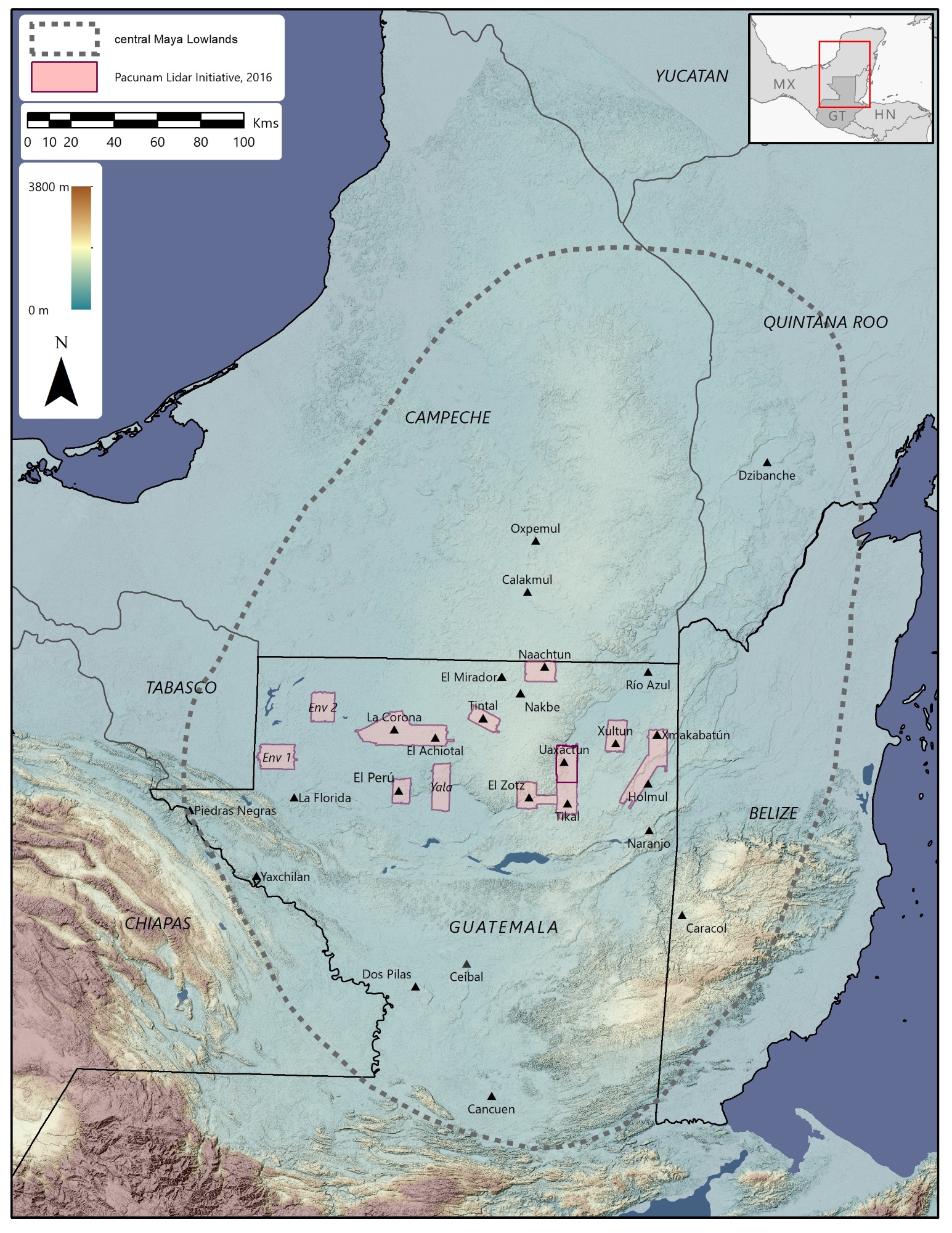
How aerial lidar illuminated a Mayan megalopolis
Archaeology may not be the most likely place to find the latest in technology — AI and robots are of dubious utility in the painstaking fieldwork involved — but lidar has proven transformative. The latest accomplishment using laser-based imaging maps thousands of square kilometers of an ancient Mayan city once millions strong, but the researchers make it clear that there’s no technological substitute for experience and a good eye.
The Pacunam Lidar Initiative began two years ago, bringing together a group of scholars and local authorities to undertake the largest-yet survey of a protected and long-studied region in Guatemala. Some 2,144 square kilometers of the Maya Biosphere Reserve in Petén were scanned, inclusive of and around areas known to be settled, developed or otherwise of importance.
Preliminary imagery and data illustrating the success of the project were announced earlier this year, but the researchers have now performed their actual analyses on the data, and the resulting paper summarizing their wide-ranging results has been published in the journal Science.
“We’ve never been able to see an ancient landscape at this scale all at once. We’ve never had a data set like this. But in February really we hadn’t done any analysis, really, in a quantitative sense,” co-author Francisco Estrada-Belli, of Tulane University, told me. He worked on the project with numerous others, including his colleagues Marcello Canuto and Stephen Houston. “Basically we announced we had found a huge urban sprawl, that we had found agricultural features on a grand scale. After another nine months of work we were able to quantify all that and to get some numerical confirmations for the impressions we’d gotten.”
“It’s nice to be able to confirm all our claims,” he said. “They may have seemed exaggerated to some.”
The lidar data was collected not by self-driving cars, which seem to be the only vehicles bearing lidar we ever hear about, nor even by drones, but by traditional airplane. That may sound cumbersome, but the distances and landscapes involved permitted nothing else.
“A drone would never have worked — it could never have covered that area,” Estrada-Belli explained. “In our case it was actually a twin-engine plane flown down from Texas.”
The plane made dozens of passes over a given area, a chosen “polygon” perhaps 30 kilometers long and 20 wide. Mounted underneath was “a Teledyne Optech Titan MultiWave multichannel, multi-spectral, narrow-pulse width lidar system,” which pretty much says it all: this is a heavy-duty instrument, the size of a refrigerator. But you need that kind of system to pierce the canopy and image the underlying landscape.
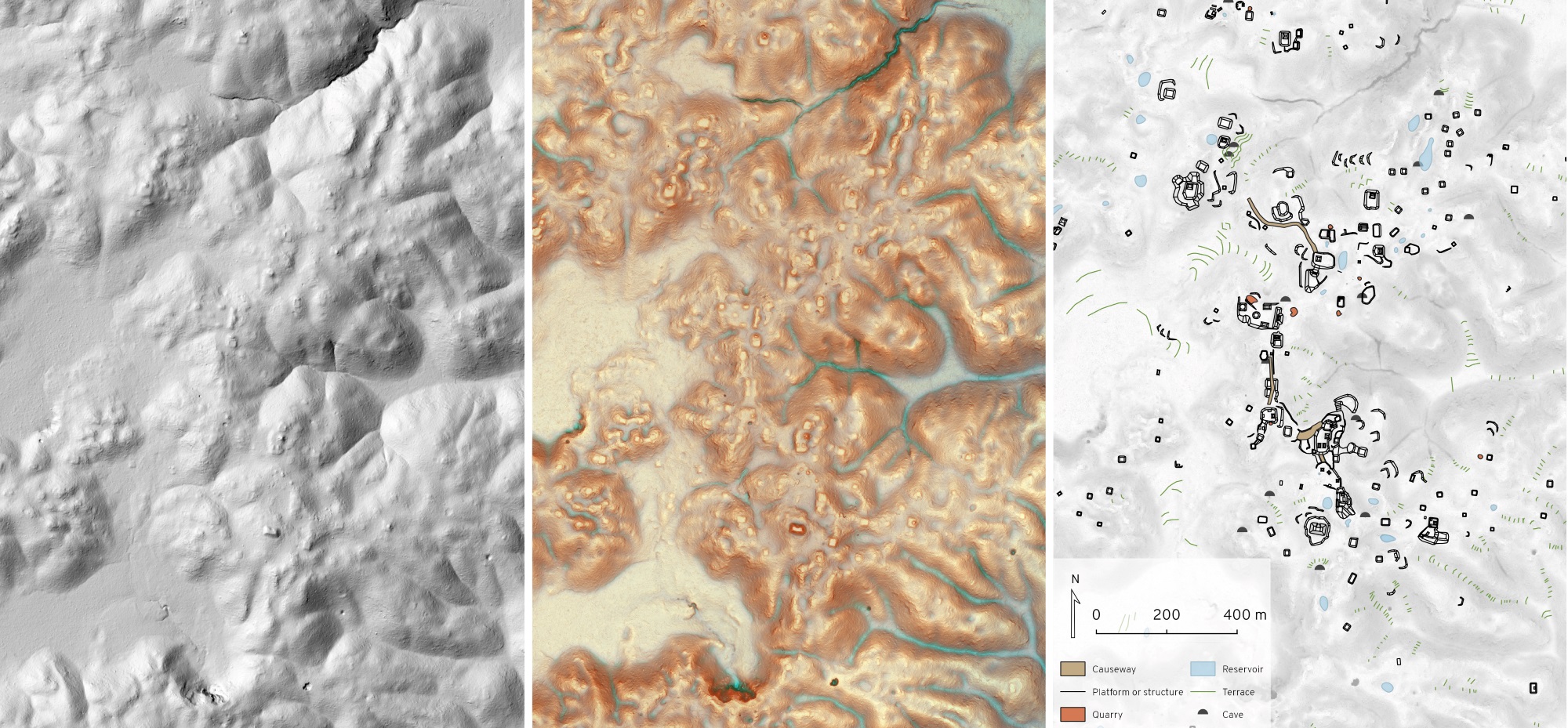
The many overlapping passes were then collated and calibrated into a single digital landscape of remarkable detail.
“It identified features that I had walked over — a hundred times!” he laughed. “Like a major causeway, I walked over it, but it was so subtle, and it was covered by huge vegetation, underbrush, trees, you know, jungle — I’m sure that in another 20 years I wouldn’t have noticed it.”
But these structures don’t identify themselves. There’s no computer labeling system that looks at the 3D model and says, “this is a pyramid, this is a wall,” and so on. That’s a job that only archaeologists can do.
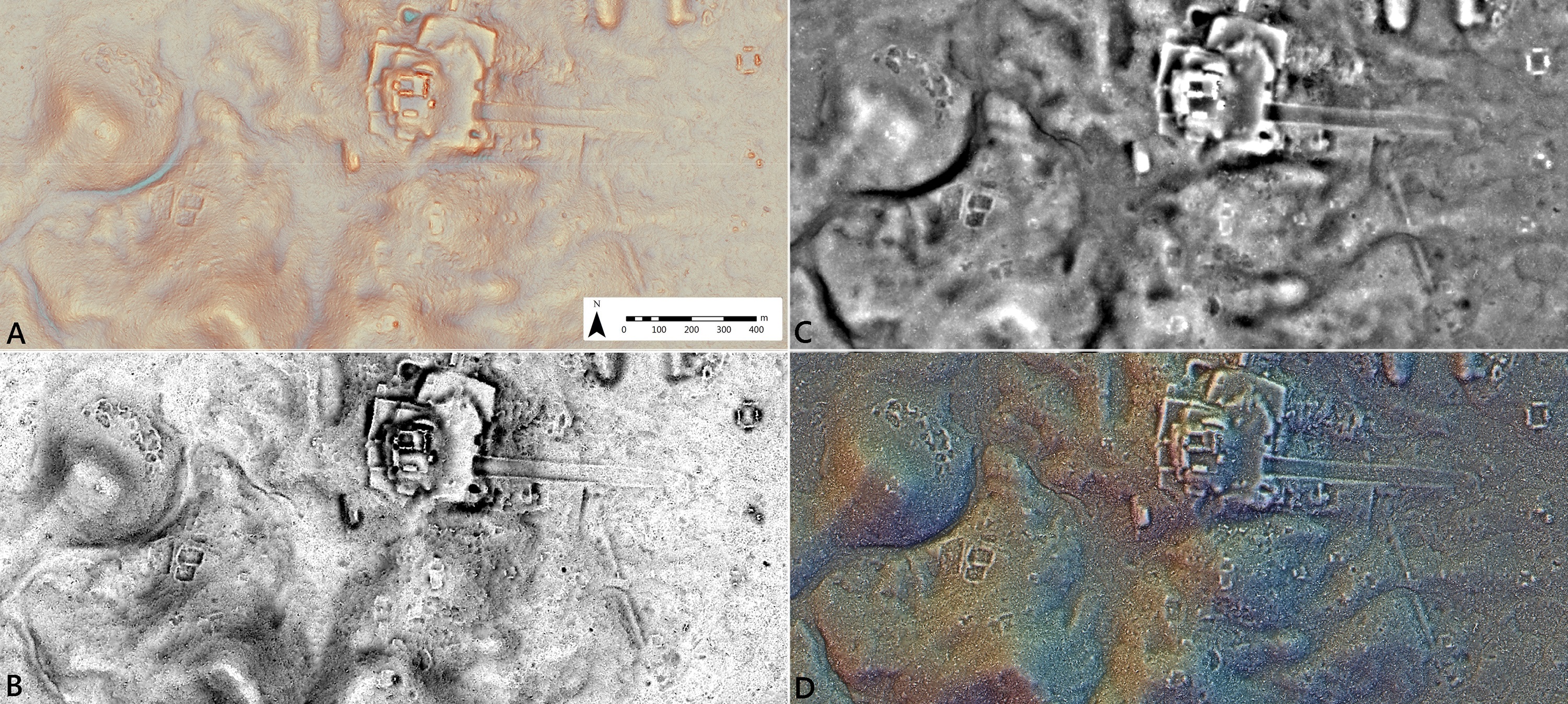
“It actually begins with manipulating the surface data,” Estrada-Belli said. “We get these surface models of the natural landscape; each pixel in the image is basically the elevation. Then we do a series of filters to simulate light being projected on it from various angles to enhance the relief, and we combine these visualizations with transparencies and different ways of sharpening or enhancing them. After all this process, basically looking at the computer screen for a long time, then we can start digitizing it.”
“The first step is to visually identify features. Of course, pyramids are easy, but there are subtler features that, even once you identify them, it’s hard to figure out what they are.”
The lidar imagery revealed, for example, lots of low linear features that could be man-made or natural. It’s not always easy to tell the difference, but context and existing scholarship fill in the gaps.
“Then we proceeded to digitize all these features… there were 61,000 structures, and everything had to be done manually,” Estrada-Belli said — in case you were wondering why it took nine months. “There’s really no automation because the digitizing has to be done based on experience. We looked into AI, and we hope that maybe in the near future we’ll be able to apply that, but for now an experienced archaeologist’s eye can discern the features better than a computer.”
You can see the density of the annotations on the maps. It should be noted that many of these features had by this point been verified by field expeditions. By consulting existing maps and getting ground truth in person, they had made sure that these weren’t phantom structures or wishful thinking. “We’re confident that they’re all there,” he told me.
[gallery ids="1721959,1721960,1721957,1721961,1721958"]“Next is the quantitative step,” he continued. “You measure the length and the areas and you put it all together, and you start analyzing them like you’d analyze other data set: the structure density of some area, the size of urban sprawl or agricultural fields. Finally we even figured a way to quantify the potential production of agriculture.”
This is the point where the imagery starts to go from point cloud to academic study. After all, it’s well known that the Maya had a large city in this area; it’s been intensely studied for decades. But the Pacunam (which stands for Patrimonio Cultural y Natural Maya) study was meant to advance beyond the traditional methods employed previously.
“It’s a huge data set. It’s a huge cross-section of the Maya lowlands,” Estrada-Belli said. “Big data is the buzzword now, right? You truly can see things that you would never see if you only looked at one site at a time. We could never have put together these grand patterns without lidar.”
“For example, in my area, I was able to map 47 square kilometers over the course of 15 years,” he said, slightly wistfully. “And in two weeks the lidar produced 308 square kilometers, to a level of detail that I could never match.”
As a result the paper includes all kinds of new theories and conclusions, from population and economy estimates, to cultural and engineering knowledge, to the timing and nature of conflicts with neighbors.
The resulting report doesn’t just advance the knowledge of Mayan culture and technology, but the science of archaeology itself. It’s iterative, of course, like everything else — Estrada-Belli noted that they were inspired by work done by colleagues in Belize and Cambodia; their contribution, however, exemplifies new approaches to handling large areas and large data sets.
The more experiments and field work, the more established these methods will become, and the greater they will be accepted and replicated. Already they have proven themselves invaluable, and this study is perhaps the best example of lidar’s potential in the field.
“We simply would not have seen these massive fortifications. Even on the ground, many of their details remain unclear. Lidar makes most human-made features clear, coherent, understandable,” explained co-author Stephen Houston (also from Tulane) in an email. “AI and pattern recognition may help to refine the detection of features, and drones may, we hope, bring down the cost of this technology.”
“These technologies are important not only for discovery, but also for conservation,” pointed out co-author Thomas Garrison in an email. “3D scanning of monuments and artifacts provide detailed records and also allow for the creation of replicas via 3D printing.”
Lidar imagery can also show the extent of looting, he wrote, and help cultural authorities provide against it by being aware of relics and sites before the looters are.
The researchers are already planning a second, even larger set of flyovers, founded on the success of the first experiment. Perhaps by the time the initial physical work is done the trendier tools of the last few years will make themselves applicable.
“I doubt the airplanes are going to get less expensive but the instruments will be more powerful,” Estrada-Belli suggested. “The other line is the development of artificial intelligence that can speed up the project; at least it can rule out areas, so we don’t waste any time, and we can zero in on the areas with the greatest potential.”
He’s also excited by the idea of putting the data online so citizen archaeologists can help pore over it. “Maybe they don’t have the same experience we do, but like artificial intelligence they can certainly generate a lot of good data in a short time,” he said.
But as his colleagues point out, even years in this line of work are necessarily preliminary.
“We have to emphasize: it’s a first step, leading to innumerable ideas to test. Dozens of doctoral dissertations,” wrote Houston. “Yet there must always be excavation to look under the surface and to extract clear dates from the ruins.”
“Like many disciplines in the social sciences and humanities, archaeology is embracing digital technologies. Lidar is just one example,” wrote Garrison. “At the same time, we need to be conscious of issues in digital archiving (particularly the problem of obsolete file formatting) and be sure to use technology as a complement to, and not a replacement for methods of documentation that have proven tried and true for over a century.”
The researchers’ paper was published today in Science; you can learn about their conclusions (which are of more interest to the archaeologists and anthropologists among our readers) there, and follow other work being undertaken by the Fundación Pacunam at its website.
Read Full Article
How to Automatically Send Monthly Invoices From Google Sheets

If you work from home or run your own business, it’s not always easy to remember to send your invoices out on time.
In this article you’ll see how to write a Google Script (VERY simple, don’t worry).
We’ll also show you how to do the same with a macro. A macro can nicely packages up your invoice and emails it out to any email address (or addresses) you like.
Step 1: Prep Your Monthly Invoice
If you don’t currently track your invoices using Google Sheets, you really should. Even if you’ve never programmed anything in your life.
Google Sheets is stored on the cloud, where you also have the power of Google scripts at your fingertips. Because of this, Google Sheets is far more “internet-enabled” than Excel is.
It doesn’t really matter how you format your invoice for this solution to work. Let’s take a few things that you should get organized before tackling your Google Script.
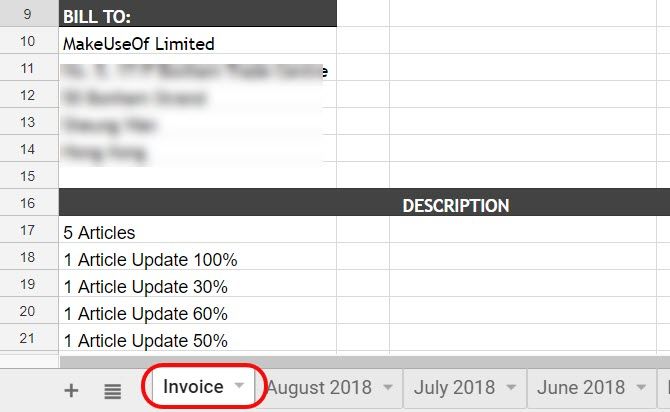
This isn’t complicated. All you need to do is make sure your current month’s sheet is always named the same. In my case I call it “Invoice”.
On the 1st of the month, the invoice is automatically sent. Then some time later during the first week, I just rename it to that month and year.
Then recreate the “Invoice” sheet and start logging for the current month again.
Step 2: Create the Google Script
To get into the Google Script editor from Google Sheets, just click on Tools in the menu. Then click Script editor.
It’s smart to rename the Project name to something you’ll remember later if you ever need to go back through your scripts and tweak it.
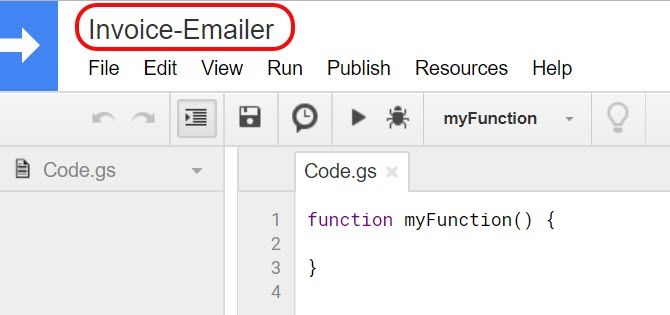
Next, paste in the following script.
function myFunction() {
var ss = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSpreadsheet();
var filename = "Current Month " + ss.getName();
var SendBook = ss.copy(filename);
var ToUser = "xxxxx@gmail.com"
MailApp.sendEmail({
to: ToUser,
subject: 'Here is my invoice for last month!',
body: 'Hi! I have attached my invoice for this month. Thanks for the work, really appreciate it! -Ryan',
attachments: [SendBook.getBlob().setName(filename)]
});
}
We’ve covered the sendEmail function in the past if you’re interested in how that works.
Edit the right parts of that script so that it’s going to the correct email address. Make sure it uses the right name of the person you’re sending it to in the body as well.
To test that your script is working, fill out the “ToUser” text with your own email address.
Click on the Save disk icon in the menu to save the script. Next click on the Play icon (looks like a right arrow).
![]()
It’ll ask you to confirm authorization for the script to access your other Google data (like Gmail and Sheets).
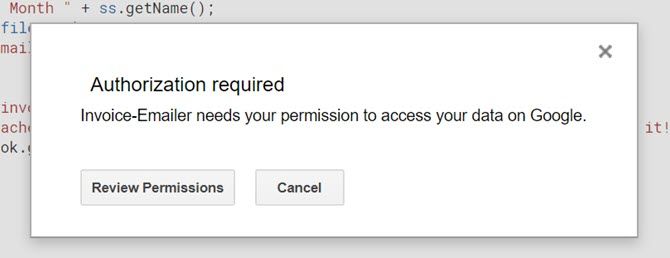
You might get a warning that the script is unsafe. This is only because you’re writing a custom script that Google hasn’t reviewed or authorized for wider use.
You can ignore this warning since you created the script and you know it’s safe.
If it runs properly, you should have received an email that looks like this:
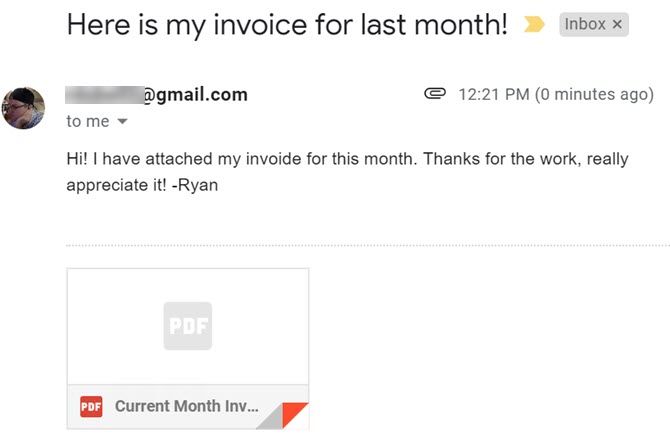
As you can see, the spreadsheet gets attached to the email as a PDF. This makes it really easy for the recipient to open and view it even if they don’t use Google Sheets.
Now we need to automate this so it runs on the 1st of every month.
Step 3: Automate Your Invoice Script
To automate your script, you need to create what’s called a “trigger”.
Go back to your Google Script, click Edit in the Menu, and choose Current project’s triggers.
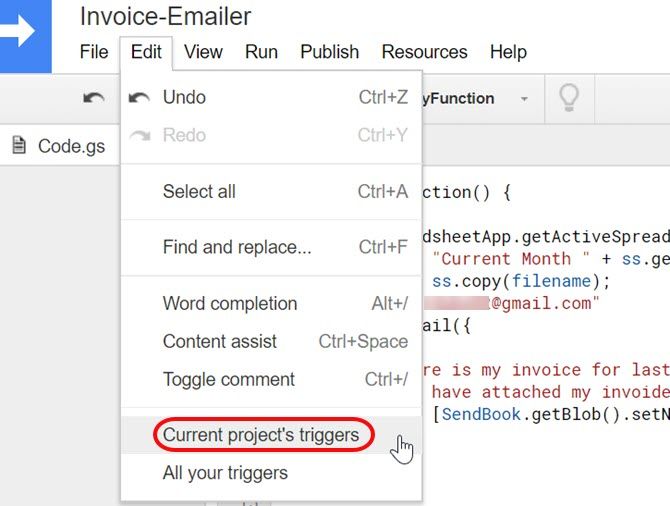
Since you haven’t created any triggers yet for this project, this will be blank.
You’ll see a blue link that reads “No triggers set up.” Click it.
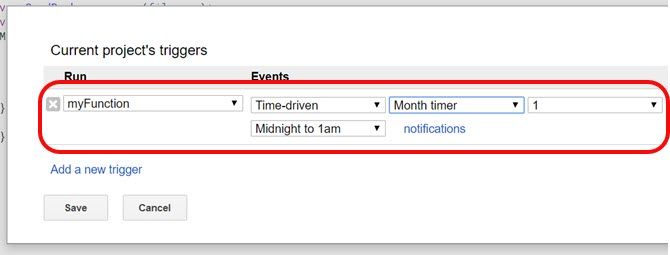
Choose Time-driven events, set the timer to Month timer, and leave the number at 1.
Once you click Save, Google Scripts will send off the PDF format of your invoice, via email, on the 1st of every month.
That’s all there is to it!
The important thing is just to make sure you keep your invoice well updated during the month. Make sure it’s finished and ready to go on the first day of the next month.
Step 4: Create a Macro
There is another non-programming approach you can take to accomplish the same thing as the script above: Google Sheets now includes a macros feature. Macros let you record a series of actions to accomplish a task. In this case, you’d first create the macro, and then trigger it the same way you triggered your Google Script.
First, in your Invoice Sheet, go to Tools > Macros, and select Record Macro.
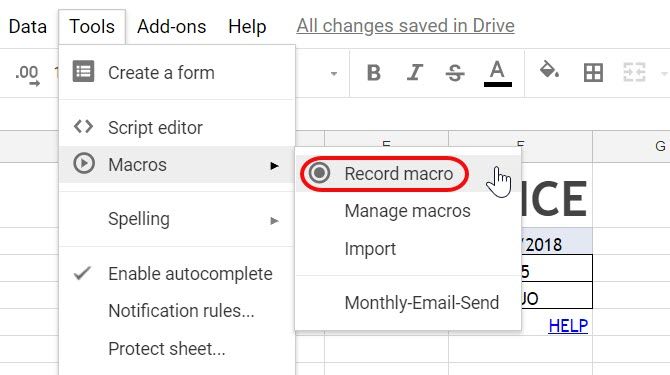
Next, just go through the normal steps of sending someone the sheet as a PDF attachment.
Go to File, and click Email as attachment.
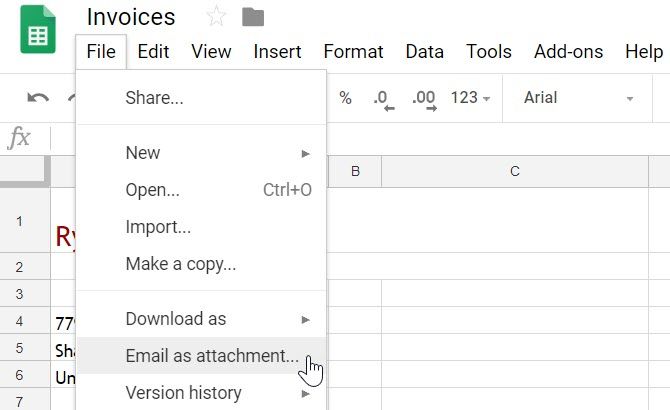
Then, fill out all of the form fields so the subject and body looks natural.
Then click Send.
On the “Recording new macro” pop-up, click on Save. This finishes the macro recording process. Give the macro a name you’ll remember, and click Save again.
You should have seen your test email arrive with the PDF attached.
Step 5: Automate the Macro
Now it’s time to automate the macro. You can trigger macros just like you trigger Google Scripts.
Go back into Tools and Script editor. Click on the macros.gs code.
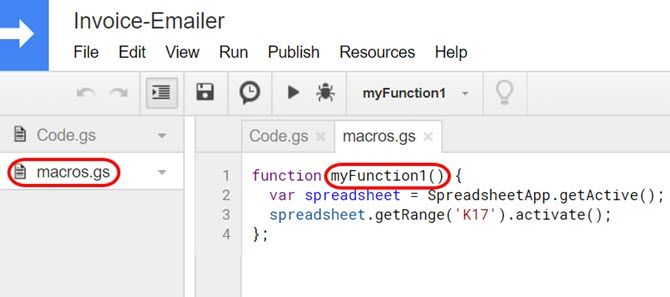
Make note of the name of the macro function. In the example above, the macro function name is myFunction1.
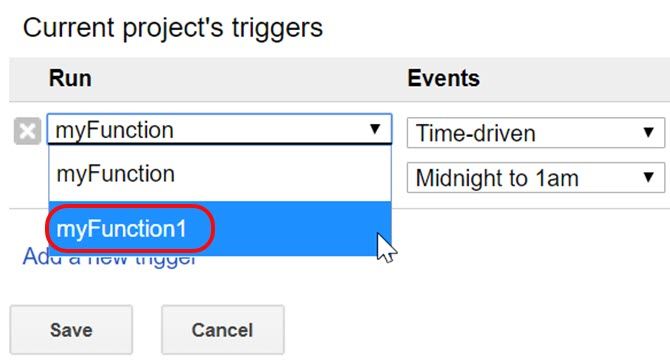
Now go into Edit, and Current project’s triggers.
This time, in the functions dropdown box, you’ll see the macro function in the list. Select it.
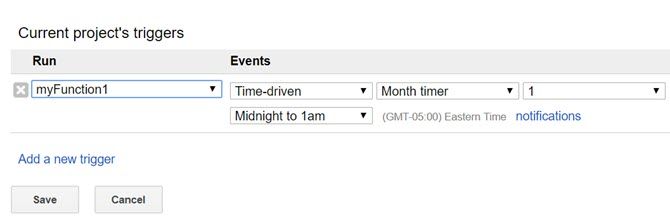
Then, just set up the rest of the trigger like you did above for the Google Script trigger.
Set Events to Time-driven. Choose Month timer. Leave the number at 1.
Now your recorded macro will run every month.
It will send out the Invoice sheet as a PDF to whatever email addresses you defined when you recorded the macro.
Automated Google Sheets Can Save Time
The triggers feature in Google Sheets is really the power behind this automation. It lets you automate all of those mundane tasks you do frequently, so that you can focus on more important things.
If you’re just getting started with Google Scripts, and you’d like to learn more, we’ve covered other examples of useful Google Scripts you can try right now.
Read the full article: How to Automatically Send Monthly Invoices From Google Sheets
Read Full Article