Facebook will soon be the latest tech giant to enter the world of cloud gaming. Their approach is different than what Microsoft or Google has built but Facebook highlights a shared central challenge: dealing with Apple.
Facebook is not building a console gaming competitor to compete with Stadia or xCloud, instead the focus is wholly on mobile games. Why cloud stream mobile games that your device is already capable of running locally? Facebook is aiming to get users into games more quickly and put less friction between a user seeing an advertisement for a game and actually playing it themselves. Users can quickly tap into the title without downloading anything and if they eventually opt to download the title from a mobile app store, they’ll be able to pick up where they left off.
Facebook’s service will launch on the desktop web and Android, but not iOS due to what Facebook frames as usability restrictions outlined in Apple’s App Store terms and conditions.
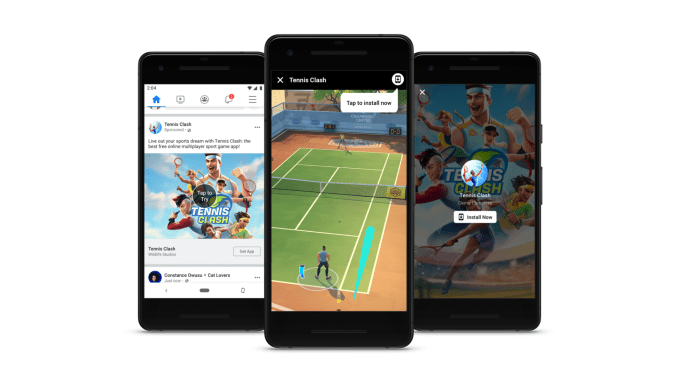
With the new platform, users will be able to start playing mobile games directly from Facebook ads. Image via Facebook.
While Apple has suffered an onslaught of criticism in 2020 from developers of major apps like Spotify, Tinder and Fortnite for how much money they take as a cut from revenues of apps downloaded from the App Store, the plights of companies aiming to build cloud gaming platforms have been more nuanced and are tied to how those platforms are fundamentally allowed to operate on Apple devices.
Apple was initially slow to provide a path forward for cloud gaming apps from Google and Microsoft, which had previously been outlawed on the App Store. The iPhone maker recently updated its policies to allow these apps to exist, but in a more convoluted capacity than the platform makers had hoped, forcing them to first send users to the App Store before being able to cloud stream a gaming title on their platform.
For a user downloading a lengthy single-player console epic, the short pitstop is an inconvenience, but long-time Facebook gaming exec Jason Rubin says that the stipulations are a non-starter for what Facebook’s platform envisions, a way to start playing mobile games immediately without downloading anything.
“It’s a sequence of hurdles that altogether make a bad consumer experience,” Rubin tells TechCrunch.
Apple tells TechCrunch that they have continued to engage with Facebook on bringing its gaming efforts under its guidelines and that platforms can reach iOS by either submitting each individual game to the App Store for review or operating their service on Safari.
In terms of building the new platform onto the mobile web, Rubin says that without being able to point users of their iOS app to browser-based experiences, as current rules forbid, Facebook doesn’t see pushing its billions of users to accessing the service primarily from a browser as a reasonable alternative. In a Zoom call, Rubin demoes how this could operate on iOS, with users tapping an advertisement inside the app and being redirected to a game experience in mobile Safari.
“But if I click on that, I can’t go to the web. Apple says, ‘No, no, no, no, no, you can’t do that,’ Rubin tells us. “Apple may say that it’s a free and open web, but what you can actually build on that web is dictated by what they decide to put in their core functionality.”
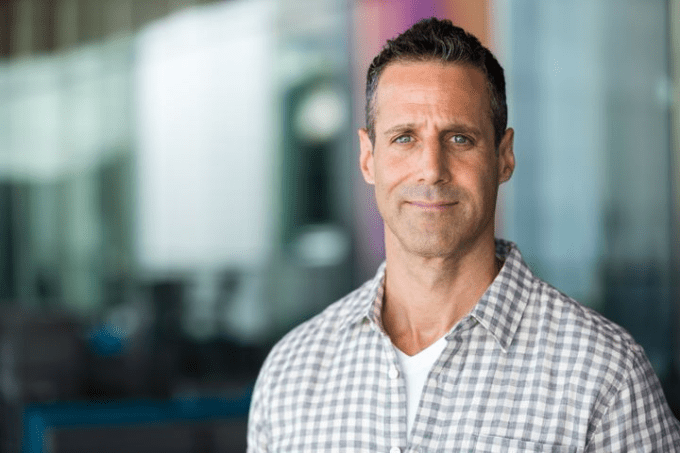

Facebook VP of Play Jason Rubin. Image via Facebook.
Rubin, who co-founded the game development studio Naughty Dog in 1994 before it was acquired by Sony in 2001, has been at Facebook since he joined Oculus months after its 2014 acquisition was announced. Rubin had previously been tasked with managing the games ecosystem for its virtual reality headsets, this year he was put in charge of the company’s gaming initiatives across their core family of apps as the company’s VP of Play.
Rubin, well familiar with game developer/platform skirmishes, was quick to distinguish the bone Facebook had to pick with Apple and complaints from those like Epic Games which sued Apple this summer.
“I do want to put a pin in the fact that we’re giving Google 30% [on Android]. The Apple issue is not about money,” Rubin tells TechCrunch. “We can talk about whether or not it’s fair that Google takes that 30%. But we would be willing to give Apple the 30% right now, if they would just let consumers have the opportunity to do what we’re offering here.”
Facebook is notably also taking a 30% cut of transaction within these games, even as Facebook’s executive team has taken its own shots at Apple’s steep revenue fee in the past, most recently criticizing how Apple’s App Store model was hurting small businesses during the pandemic. This saga eventually led to Apple announcing that it would withhold its cut through the end of the year for ticket sales of small businesses hosting online events.
Apple’s reticence to allow major gaming platforms a path towards independently serving up games to consumers underscores the significant portion of App Store revenues that could be eliminated by a consumer shift towards these cloud platforms. Apple earned around $50 billion from the App Store last year, CNBC estimates, and gaming has long been their most profitable vertical.
Though Facebook is framing this as an uphill battle against a major platform for the good of the gamer, this is hardly a battle between two underdogs. Facebook pulled in nearly $70 billion in ad revenues last year and improving their offerings for mobile game studios could be a meaningful step towards increasing that number, something Apple’s App Store rules threaten.
For the time being, Facebook is keeping this launch pretty conservative. There are just 5-10 titles that are going to be available at launch, Rubin says. Facebook is rolling out access to the new service, which is free, this week across a handful of states in America, including California, Texas, Massachusetts, New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Delaware, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Washington, D.C., Virginia and West Virginia. The hodge-podge nature of the geographic rollout is owed to the technical limitations of cloud-gaming– people have to be close to data centers where the service has rolled out in order to have a usable experience. Facebook is aiming to scale to the rest of the U.S. in the coming months, they say.
 Read Full Article
Read Full Article