Is there any space on kids’ homescreens for another social sharing app to poke in? Y Combinator backed Splish wants to have a splash at it ( ) — with a super-short-form video and photo sharing app aimed at the under-25s.
) — with a super-short-form video and photo sharing app aimed at the under-25s.
The SF-based startup began bootstrapping out of their college dorm rooms last July, playing around with app ideas before settling on goofy video loops to be their social sharing steed of choice.
The Splish app pops content into video loops of between 1-5 seconds. Photos can be uploaded too but motion must be added in the form of an animated effect of your choice. So basically nothing on Splish stays still. (Hence its watery name.) But while wobbly, content on Splish is intended to stick around — rather than ephemerally pass away (a la snaps).
Here are a few examples of Splishes (embedded below as GIFs… but you can see them on its platform here, here and here):



It’s the first startup for the four college buddy co-founders: Drake Rehfeld, Alex Pareto, Jackson Berry and Zac Denham, though between them they’ve also clocked up engineering hours working for Snapchat, Facebook and Team 10.
Their initial web product went up in March and they landed a place on YC’s program at the start of May — when they also released their iOS app. An Android app is pending, and they’ll be on the hunt for funding come YC demo day.
The gap in the social sharing market this young team reckons it’s spotted is a sort of ‘anti-Instagram’ — offering a playful contrast to the photo sharing platform’s polished (and at times preening) performances.
The idea is that sharing stuff on Splish is a bonding experience; part of an ongoing smartphone-enabled conversation between mates, rather than a selectively manicured photoshoot which also has to be carefully packaged for public ‘gram consumption.
Splish does have a public feed, though, so it’s not a pure messaging app — but the co-founders say the focus is friend group sharing rather than public grandstanding.
“Splish is a social app for sharing casual looping videos with close friends,” says Rehfeld, giving the team’s elevator pitch. “It came out of our own experience, and we’re building for ourselves because we noticed that the way you socialize right now in real life is you do activities with your friends. You go to the beach, you go to the bar, the bowling alley. We’re working to bring this same type of experience online using Splish through photo and video. So it’s more about interaction and hanging out with your friends online.”
“When you use Instagram you really feel like you’re looking at a magazine. It’s just the highlights of people’s lives,” he adds. “And so we’re trying to make a place where you’re getting to know your friends better and meeting new people as well. And then on the other side, on Snapchat, you’re really sharing interesting moments of your lives but it’s not really pushing the boundaries or creating with your friends. It’s more just a communication messaging tool.
“So it’s kind of the space in between broadcast and chat — talking and interacting with your close friends through Splish, through photo and video.”
Users of the Splish app can apply low-fi GIF(ish) retro filters and other photographic effects (such as a reverse negative look) to the video snippets and photos they want to send to friends or share more widely — with the effects intended to strip away at reality, rather than gloss it over. Which means content on Splish tends to look and feel grungy and/or goofy. Much like an animated GIF in fact. And much less like Instagram.
The team’s hope is the format adds a bit of everyday grit and/or wit to the standard smartphone visual record, and that swapping Splishes gets taken up as a more fun and casual way of communicating vs other types of messaging or social sharing.
And also that people will want to use Splish to capture and store fun times with friends because they can be checked out again later, having been conveniently packaged for GIF-style repeat lols.
“Part of the power here in Splish is that relationships are built on shared experiences and nostalgia and so while [Snapchat-style] ephemerality reduced a lot of the barriers for posting what it didn’t do is strengthen relationships long term or over time because the chats and the photos disappeared,” says Rehfeld.
The idea is a content format to gives people “shared experience that lasts”, he adds.
They’re also directly nudging users to get creative via a little gamification, adding a new feature (called Jams) that lets users prompt each other to make a Splish in response to a specific content creation challenge.
And filming actual (playful) physical shoulder pokes has apparently been an early thing on Splish. That’s the merry-go-round of social for ya.

Being a fair march north of Splish’s target age-range, I have to confess the app’s loopy effects end up triggering something closer to motion sickness/vertigo/puking up for me. But words are my firm social currency of choice. Whereas Rehfeld argues the teenager-plus target for Splish is most comfortable with a smartphone in its hand, and letting a lens tell the tale of what they’re up to or how they’re feeling.
“We started with that niche first because there’s a population in that age range that really enjoys this creative challenge of expressing yourself in pretty intuitive ways, and they understand how to do that. And they’re pretty excited about it,” he tells TechCrunch.
“There’s also been a little bit of a shift here where users no longer just capture what they have in real-life using the camera, but the camera’s used as an extension of communication — especially in that age range, where people use the camera as part of their relationship, rather than just capturing what happens offline.”
As with other social video apps, vertical full screen is the preferred Splish frame — for a more “immersive experience” and, well, because that’s how the kids do it.
“It’s the way users, especially in this age range, hold and use their phones. It’s pretty natural to this age range just because it’s what they do everyday,” he says, adding: “It’s just the best way to consume on the phone because it fills the whole screen, it’s how you were already using the phone before you clicked into the video.”
Notably, as part of the team’s soft-edged stance against social media influencer culture, Rehfeld says Splish is choosing not to bake “viral components” into the app — ergo: “Nobody’s rewarded for likes or ‘re-vines’. There’s no reblog, retweet.”
Although, pressed on how firm that anti-social features stance is, he concedes they’re not abandoning the usual social suite entirely — but rather implementing that sort of stuff in relative moderation.
“We have likes and we have a concept of friends or follows but the difference is we’re building those with the intention of not incentivizing virality or ‘influencership’,” he says. “So we always release them with some sort of limit, so with likes you can’t see a list of everybody who’s liked a post for example. So that’s one example of how we’ve, kind of, brought in a feature that people feel comfortable with and love but with our own spin that’s a little bit less geared towards building a following.”
Asked if they’re trying to respond to the criticism that’s been leveled at a lot of consumer technology lately — i.e. that it’s engineered to be highly and even mindlessly addictive — Rehfeld says yes, the team wants to try and take a less viral path, less well travelled, adding: “We’re building as much as possible for user experience. And a lot of the big brands build and optimize towards engagement metrics… and so we’re focused on this reduction of virality so that we can promote personal connections.”
Though it will be interesting to see if they can stick to medium-powered stun guns as they fight to carve out a niche in the shadow of social tech’s attention-sapping giants.
Of course Splish’s public feed is a bit of a digital shop window. But, again, the idea is to make sure it’s a casual space, and not such a perfectionist hothouse as Instagram.
“The way the product is built allows people to feel pretty comfortable even in the more public feeds, the more featured feeds,” adds Rehfeld. “They post still very casual moments, with a creative spin of course. So it’s stayed pretty similar content, private and public.”
Short and long
It’s fair to say that short form video for social sharing has a long but choppy history online. Today’s smartphone users aren’t exactly short of apps and online spaces to share moving pictures publicly or with followers or friends. And animated GIFs have had incredible staying power as the marathon runner of the short loop social sharing format.
On the super-short form video side, the most notable app player of recent years — Twitter’s Vine — sprouted and spread virally in 2013, amassing a sizable community of fans. Although Instagram soon rained on its video party, albeit with a slightly less super-short form. The Facebook-owned behemoth has gatecrashed other social sharing parties in recent years too. Most notably by cloning Snapchat’s ‘video-ish’ social sharing slideshow Stories format, and using its long reach and deep resources to sap momentum from the rival product.
Twitter voluntarily threw in the towel with Vine in 2016, focusing instead on its livestreaming video product, Periscope, which is certainly a better fit for its core business of being a real-time social information network, and its ambition to also become a mainstream entertainment network.
Meanwhile Google’s focus in the social video space has long been on longer form content, via YouTube, and longer videos mesh better with the needs of its ad network (at least when YouTube content isn’t being accused of being toxic). Though Mountain View also of course plays in messaging, including the rich media sharing messaging space.
Apple too has been adding more powerful and personalized visual effects for its iMessage users — such as face-mapping animoji. So smartphone users are indeed very, very spoiled for sharing choice.
Vine’s success in building a community did show that super-short loops can win a new generation of fans, though. But in May its original co-founder, Dom Hofmann, indefinitely postponed the idea of reviving the app by building Vine 2 — citing financial and legal roadblocks, plus other commitments on his time.
Though he did urge those “missing the original Vine experience” to check out some of the apps he said had “sprung up lately” (albeit, without namechecking any of the newbs). So perhaps a Splish or two had caught his eye.
There’s no doubt the space will be a tough one to sustain. Plenty of apps have cracked in and had a moment but very few go the distance. Overly distinctive filters can also feel faddish and fall out of fashion as quickly as they blew up. Witness, for example, the viral rise of art effect photo app Prisma. (And now try and remember the last time you saw one of its art filtered photos in the wild… )
So sustaining a novel look and feel can be tough. Not least because social’s big beast, Facebook, has the resources and inclination to clone any innovations that look like they might be threatening. Add in network effects and the story of the space has been defined by a shrinking handful of dominant apps and platforms.
And yet — there’s still always the chance that a new generation of smartphone users will shake things up because they see things differently and want to find new ways and new spaces to share their personal stuff.
That’s the splash that Splish’s team is hoping to make.
 Read Full Article
Read Full Article
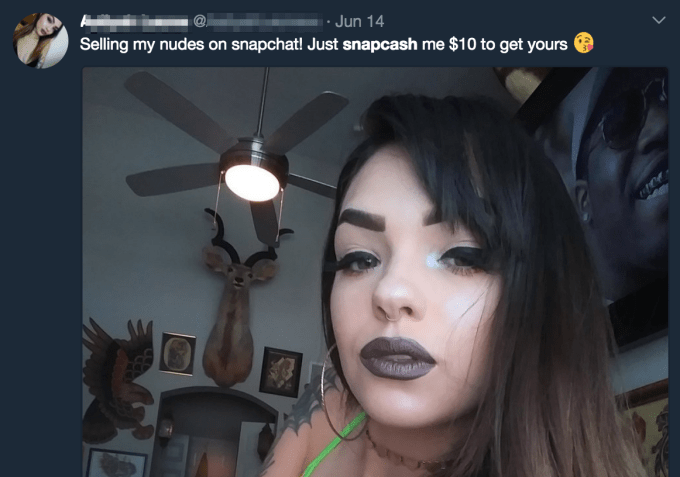
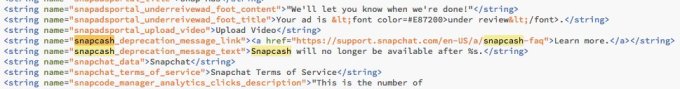
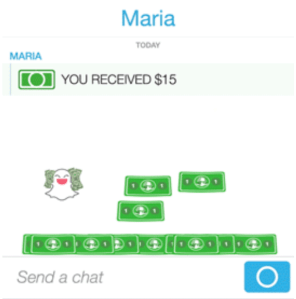 We’ll see how Snapchat plans evolve its commerce strategy without this driver. Earlier this month, TechCrunch revealed that Snapchat’s code contained mentions of a project codenamed “eagle” that’s a camera search feature. It was designed to allow users to scan an object or barcode with their Snapchat camera and see product results in Amazon. But since our report, mentions of Amazon have disappeared from the code. It’s unclear what will happen in the future, but camera search could give Snapchat new utility and monetization options.
We’ll see how Snapchat plans evolve its commerce strategy without this driver. Earlier this month, TechCrunch revealed that Snapchat’s code contained mentions of a project codenamed “eagle” that’s a camera search feature. It was designed to allow users to scan an object or barcode with their Snapchat camera and see product results in Amazon. But since our report, mentions of Amazon have disappeared from the code. It’s unclear what will happen in the future, but camera search could give Snapchat new utility and monetization options.

 ) — with a super-short-form video and photo sharing app aimed at the under-25s.
) — with a super-short-form video and photo sharing app aimed at the under-25s.


