Interested in building a home web server? The simplest way is to install Linux on a spare computer. Thanks to the simplicity of Linux, this is straightforward, giving you an affordable way to host a website or blog.
Here’s how to set up a Linux web server.
How to Make Your Own Web Server With Linux
To build a Linux web server that can be run from home, you’ll need the hardware and an operating system. In addition, web server software should be installed, and a means of accessing the server from the internet se up.
We can break that down into four easy steps you can follow to build your own Linux webserver.
- Find an old/unwanted computer
- Install a Linux operating system
- Set up the application web server software (Apache, PHP, MySQL)
- Reach the server from the internet
Let’s get started.
1. Find an Old Computer for Your Linux Web Server
Before choosing a computer to use as a web server, you’ll need to know the minimum requirements of the OS. While Ubuntu is popular, it isn’t lightweight enough. Instead, Lubuntu 19.04 is a stronger option. This is a lighter alternative to Ubuntu, built on the same code.
Download: Lubuntu 19.04
Lubuntu System Requirements
Lubuntu 19.04 has a minimum requirement of:
- 512MHz dual core processor or better (1GHz recommended, as opposed to 2GHz for Ubuntu)
- 4GB system memory
- 25GB of free hard drive space
- Choice of 32-bit (for older PCs) and 64-bit versions
You might have a suitable old PC at the back of a drawer or picked one up at a thrift store. It’s worth noting that you can install a Linux web server on a Raspberry Pi. This little computer costs under $30 and is a smart option if you run into trouble with old hardware.
Also, don’t be limited to old Windows PCs. Apple Macs and MacBooks from the pre-2006 era with PowerPC processors can run Linux.
Like Ubuntu, Lubuntu supports a wide variety of video cards, hard drives, and other hardware. To check if the distro will work on your chosen hardware, run the Live CD.
If you plan on running the server 24/7, make sure it is in a well-ventilated area. It is better to place it in an air-conditioned room during the summer when heat will be your server’s enemy.
2. Install a Linux Operating System
![Set up a Linux web server with Lubuntu]()
Installing Lubuntu is straightforward. Simply grab the ISO file and write it to DVD or a USB flash device, to begin.
Download: Lubuntu
These disk images have the latest versions of software, so only a small upgrade should be required after installation. Use the 64-bit version if your computer supports it or the 32-bit version otherwise.
When you’re ready, insert the installation media in your computer and reboot. If you need to change the BIOS settings to boot from the optical drive or USB, then do so. In some cases, a boot media selection menu can be opened.
With the installation media booted, select Install Lubuntu. When prompted, select Download updates while installing and Install 3rd Party Software and then Erase and Use the Entire Disk.
Note that this will erase any other operating systems you have on this computer. Follow through the other options per your desired settings. Encrypting your home folder isn’t wise for a web server project. Reboot after the installation is complete.
Upon reboot, check for updates. Go to System > Administration > Update Manager > Install Updates. You may need to reboot after installing any updates it has found.
3. Install Linux Web Server Software
While alteratives are available, most websites run on a combination of Apache, MySQL, and PHP (known as LAMP). This is similar to what we recommended installing on Windows.
All three tools can be installed via the Software Center. Launch this via System > Administration > Synaptic Package Manager. This is where we install the software we need.
Search for and install the following package names, each of which will include various prerequisites: apache2, php5, php5-mysql, and mysql-server. Apply the changes to install the packages.
The packages will download and install shortly. The installer will prompt you for the MySQL “root” password. No reboot is necessary.
You can alternatively install these tools in the command line. Open a Terminal then:
sudo apt install lamp-server^ -y
![Set up a Linux web server on an old PC]()
Test Your Web Server!
You can test the installation by opening the Firefox browser on your server and heading to the URL http://127.0.0.1/. Alternatively, input http://localhost/.
You should see an “It works!” message meaning that your web server is running! Both Apache and MySQL will be running in the background and will start on bootup. With the web server now working you can edit the files in /var/www. Simply refresh the browser to see the changes live on your website.
Finding the Server’s Local IP Address
While the server is functional, it needs to be visible to the outside world. As such, it is important to keep the server up to date with all regular patches.
First, find the server’s local IP address and set it to something you will later be able to reference. You’ll find the current IP address—assigned by your router—in the Network Information box.
Find this by clicking on your network connection, then selecting Connection Information. This will pop up a box with your current IP address, network adapter card, broadcast address, gateway, and DNS server. Make a note of the IP address.
Next, edit your connection information to give you a static IP address on your local network. Right click again, but this time go to Edit Connections. Select the appropriate adapter name (e.g. eth1) and edit those settings.
Select the IPv4 tab and switch the Method to Manual. Click Add then enter the information from your connection settings. Note, however, the IP address will need to be entered differently. Retain the first three octets (the numbers between the dots) but change the last to a high number under 254.
It is important that the manually assigned IP address is not already in use on your network. If you are unsure, pick a high IP address like 250. This will be your static, local IP address.
Sharing the Web Folder
Several options are available to access and upload files onto your server. To illustrate the importance of folder permissions, consider sharing the web folder as an option.
It is important to only use this method if your server is on a private network. Be certain no one can connect to it and access your shared folder.
Start by relaxing permissions on the web folder. Open a terminal by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T, then enter:
sudo chmod 777 /var/www
You will be prompted your for your password. If correct, the permissions will be updated.
Now go to the file browser and find /var/. Right click the www folder and then select Sharing options and uncheck it. For security options, you can share it with or without a password. Select Guest access to share the folder without requiring a username and password.
Now, you or anyone else will be able to access the files without a password. For this reason, sharing with a password is recommended for security purposes. Also take a moment to check Allow others to create and delete files in this folder. This allows write access from the shared directory.
To view your files, go to the network location //localhost/www.
![Set up a Linux web server]()
It will either prompt for your password or allow you access straight to your files, depending on your security settings. These are the same files accessible in your web browser via http://localhost/ (or whatever static IP address you set).
Get Your Linux Server Online With Port Forwarding
Now you have an IP address, an important concept to understand is port forwarding. Every single person connected to the internet is behind an IP address. For most home connections (and many business connections) your computer’s IP is not actually exposed to the internet. –
So how do visitors to your website contact your server? We do this with port forwarding.
Ports on a server are like doors or windows on a house and as such have security implications. Each port will give you access to a different service running on the server. Web servers use port 80 by default.
To enable this, you’ll need to log into your router’s administrator page. Check the device’s documentation for details of this (some routers have the IP address printed on the back). Here, you should find a section called Port Forwarding, or Applications which will allow you to forward ports properly.
Forward TCP port 80 to inside your network to the static IP address you set earlier. Each router is different, so refer to your router’s operations manual on how to set this up properly.
Give Your Linux Web Server a Static Hostname
Most home routers connect to an ISP via what is called a dynamic IP. This means the public-facing IP address for your router will change after a set period, usually a week or so.
A way around this is the fantastic DynDNS server which lets you set a DynDNS URL for your site. Thanks to a client app, whenever your public IP address changes, the URL will still point to your Linux server.
So, visitors should be able to visit your web server from the outside world by going to https://ift.tt/38rUfUb. Some ISPs will block port 80 to your router. In this case, forward something like port 8080 to port 80. This will allow you to visit your website by going to https://ift.tt/36pG2Fz.
You Built a Linux Web Server!
Now that your web server is set up, you can focus on programming or installing your own software!
Perhaps you’ll run blog software or host a forum or bulletin board. You might be more interested in hosting a social network like Mastodon, a portfolio, whatever. It’s up to you.
These days, you can host a website on just about anything. Here’s how to turn your Android device into a web server to prove it.
Read the full article: How to Build a Linux Web Server With an Old Computer
Read Full Article
 Ready joined PayPal in 2013 when it
Ready joined PayPal in 2013 when it 





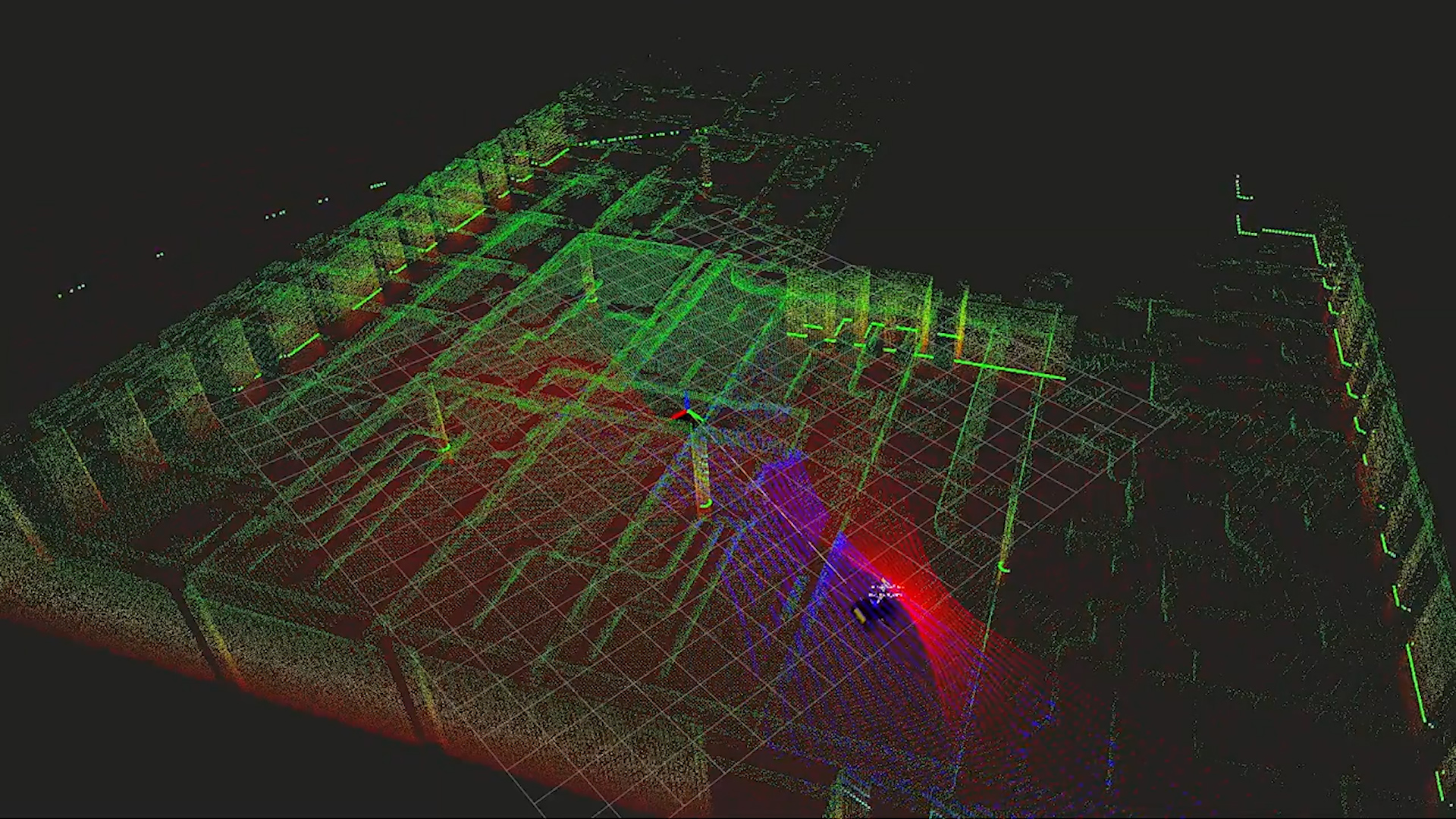
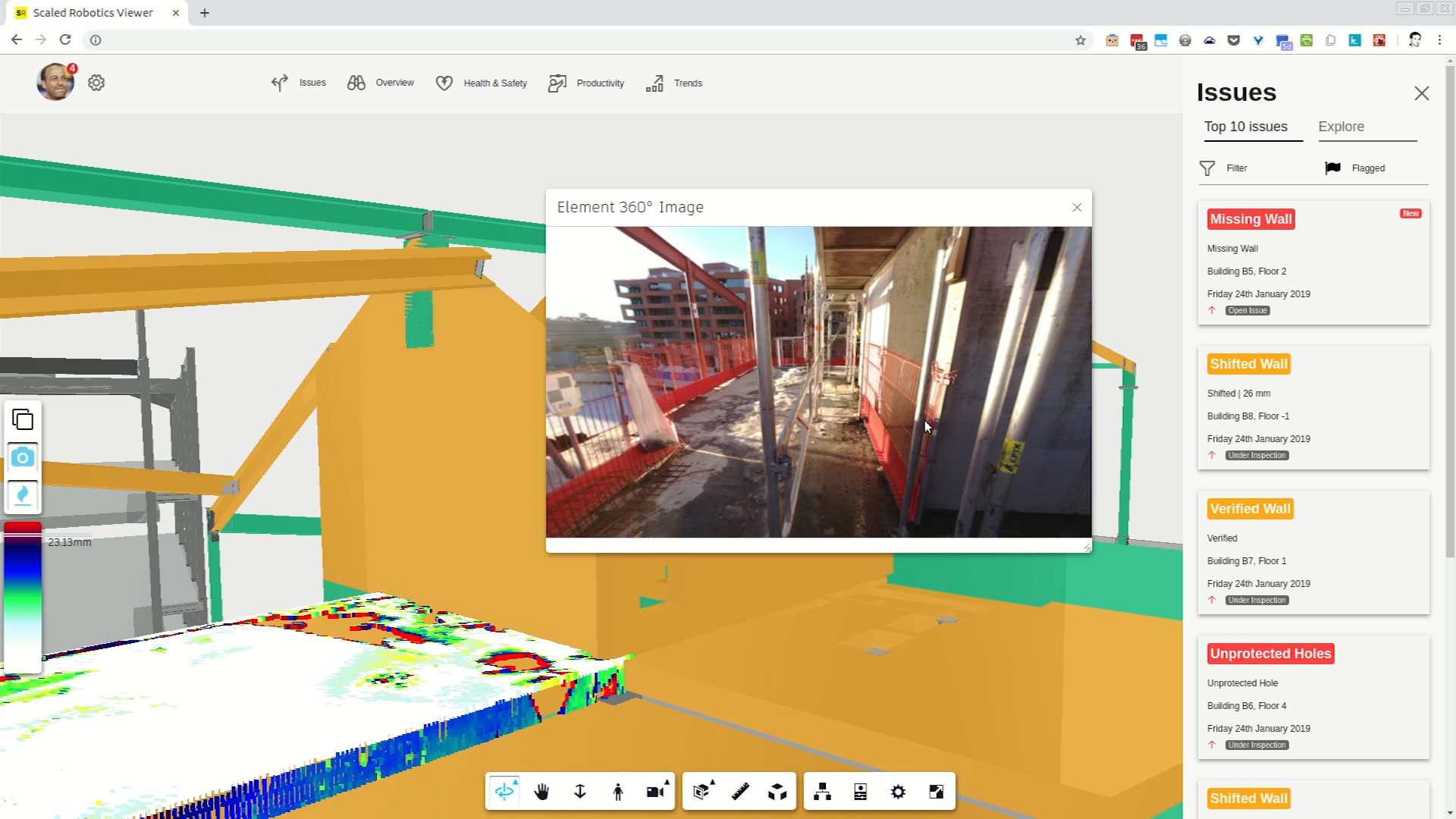
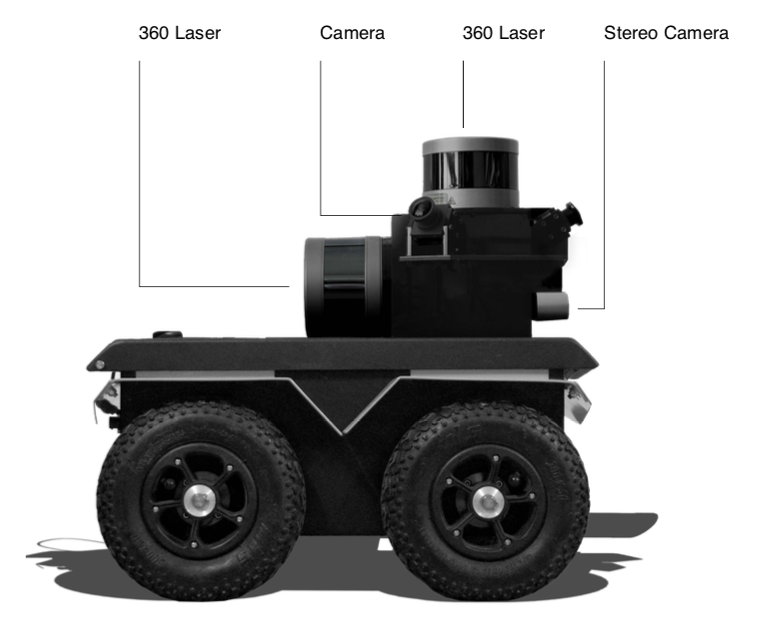 The data is assembled automatically but the robot can be either autonomous or manually controlled — in developing it, they’ve brought the weight down from about 70 kilograms to 20, meaning it can be carried easily from floor to floor if necessary (or take the elevator); and simple joystick controls mean anyone can drive it.
The data is assembled automatically but the robot can be either autonomous or manually controlled — in developing it, they’ve brought the weight down from about 70 kilograms to 20, meaning it can be carried easily from floor to floor if necessary (or take the elevator); and simple joystick controls mean anyone can drive it.