Device management can be extremely time-consuming for any team. Buying a new device, manually entering all the settings, and downloading all required apps can become tedious. Devices that are unmanaged can also pose a security threat to entire organizations.
Let’s take a closer look at how Jamf Now can streamline your organization’s Apple device management.
What Is Jamf Now?
Jamf Now is a management solution created exclusively for Apple devices. Jamf Now is ideal for small businesses and allows you to set up, protect and manage devices all from a single dashboard. Devices can be configured quickly and consistently, and apps can be centrally deployed.
Once a device is paired with your Jamf Now account you’re able to view details like its serial number, available storage, and model. You can send the latest OS updates to a single unit or manage a group of devices using Blueprints. Jamf Now also allows you to place restrictions on devices to prevent users from changing certain settings. This is a very powerful feature to ensure devices in your organization meet security and compliance needs.
Jamf Now can also be used to help employees retain their individual Apple IDs and request assistance. For example, if an employee loses their iOS device you’re able to lock the device and place a custom message on the screen. The lost device can also be remotely and securely erased all from within your Jamf Now account.
How Does Jamf Now Work?
Jamf Now works by first creating a trust between your Jamf Now account and Apple which we’ll cover in the upcoming steps. If you’re planning on using Jamf Now to manage your company devices, ensure you use a dedicated company Apple ID. If you change the Apple ID that is paired with Jamf Now, you will need to enroll all of your devices again.
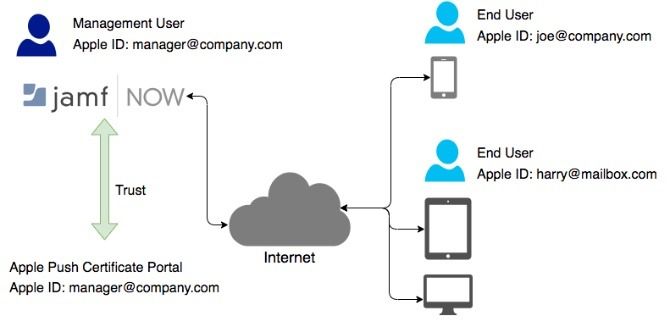
After a trust is established you need to add devices into your Jamf Now account in order for them to be managed. Jamf Now supports two levels of management: Supervised and Enrolled. Supervised devices can be controlled on a much deeper level than devices that are only enrolled. Company devices typically fall under the Supervision level of management.
Some of the most powerful Jamf Now features require Supervision such as:
- Restrictions (iOS)
- Lost Mode
- Activation Lock Bypass
- Wallpaper
Enrolled devices are typically used for organizations that have a Bring Your Own Device policy.
You may also be interested in some of the more business-oriented features such as Apple Business Manager, which allows you to buy hardware and apps in bulk and distribute them to your workforce. These are optional, but you will also require an Apple ID that is associated with Apple Business Manager. It’s free to sign up but you will need a registered company and an organization email account. Yahoo or Gmail accounts won’t work! If you require the Supervised level of management you must have connected DEP to your Jamf Now account.
This guide will cover setting up your Jamf Now account to easily manage your devices. To successfully deploy devices you will need:
- An email address for creating a Jamf Now account.
- The same email address for connecting to APNs.
Step 1: Setting Up Jamf Now
Setting up a Jamf Now account is really straightforward.
- Go to the Jamf Now website and create a free account.
- Check your inbox for and activation email and click on the Activate your account link to begin the setup procedure.
Step 2: Connecting to APNs Using Jamf Now
Apple Push Notification service (APNs) is the way Jamf Now securely stays in touch with all your Apple devices. Once you activate and log in to your Jamf Now account the first screen prompts you to connect to APNs.
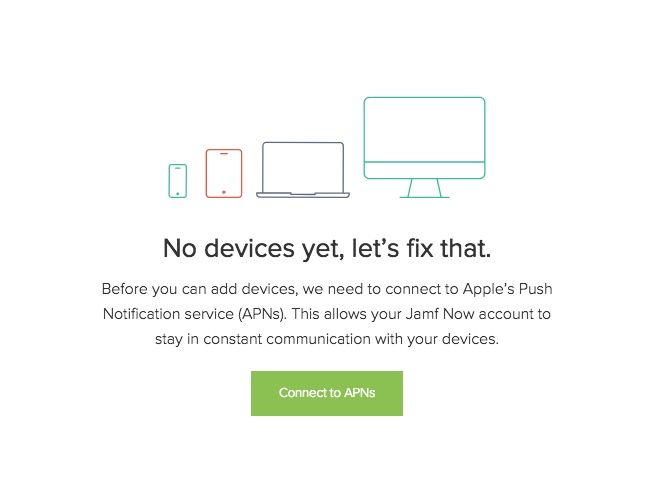
There are four steps which are required to pair your Jamf account to your Apple ID.
- Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from Jamf Now
- Create an Apple Push Certificate in the Apple Push Certificate Portal
- Upload your Apple Push Certificate to Jamf Now
- Save your Apple ID along with your Apple Push Certificate
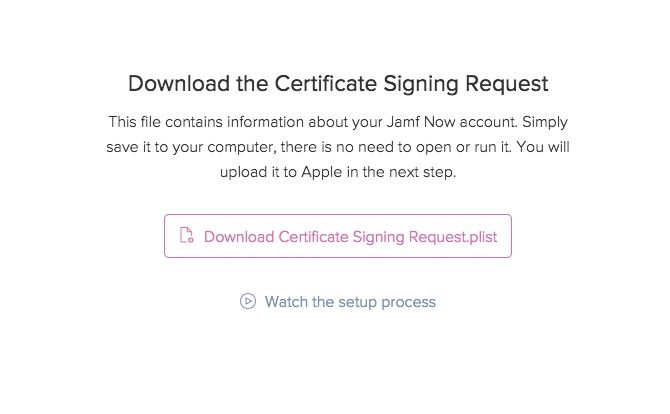
Jamf Now provides you with links, prompts, and videos at each step to make this process as simple as possible.

Once you download the CSR click Next and follow the link which reads Open the Apple Push Certificates Portal.
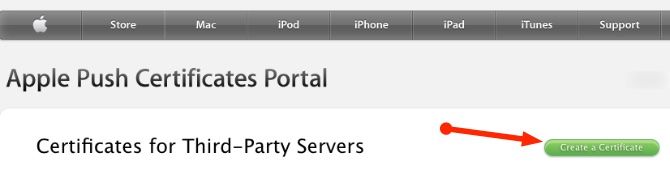
After you sign in to the Apple Push Certificates Portal, click on Create a Certificate.
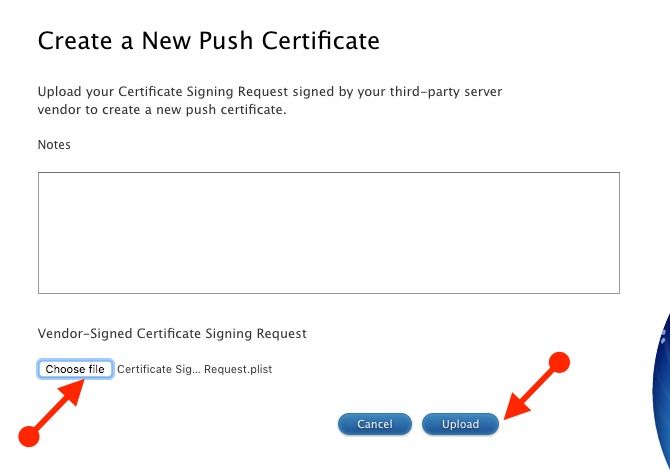
At the Create screen, click on Choose File under Vendor-Signed CSR followed by the Upload button.
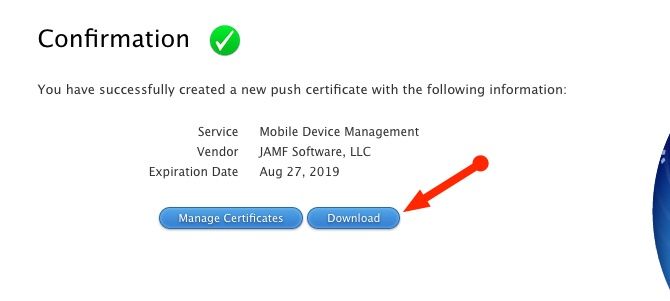
The Apple Portal will confirm that your new certificate is created and is available for download. Download the certificate and head back over to your Jamf Now account for the final steps. Browse for the certificate you downloaded from the Apple Portal which should have a .PEM extension. Jamf Now will now confirm that the upload was successful and the connection between Jamf Now and Apple is complete!
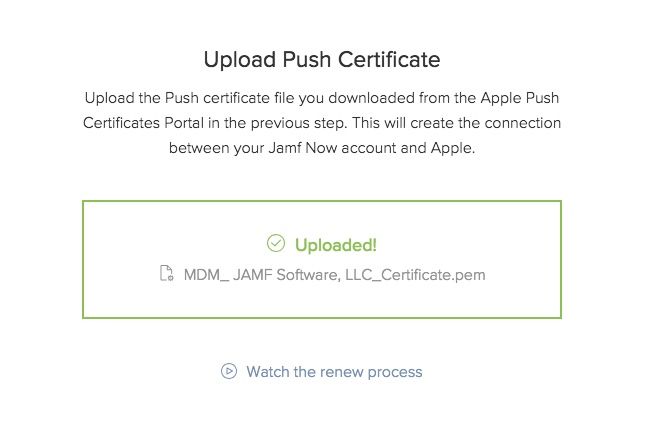
The final step of saving your Apple ID is optional but recommended. Apple Push Certificates are valid for one year. Saving your Apple ID allows Jamf Now to remind you which Apple ID you used when you need to renew your certificate. That’s it! You can now begin enrolling devices in your Jamf Now account!
Step 3: Selecting Apps to Deploy
One great feature of Jamf Now is the ability to provision devices with certain apps. This saves users and the IT team from having to manually download these applications for each user upon enrollment.
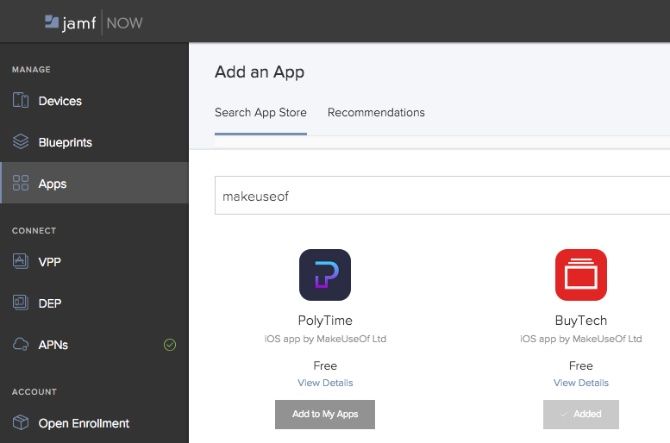
For example, say you wanted to add MakeUseOf’s Invoice Mini app from the App Store to all your devices. To do this click on the Apps tab followed by Add an App and search for either an app name or a developer name. Once you’ve found the app you’re looking for click on Add to My Apps. You will now be able to assign the app to any Blueprints which we’re going to create in the upcoming steps.
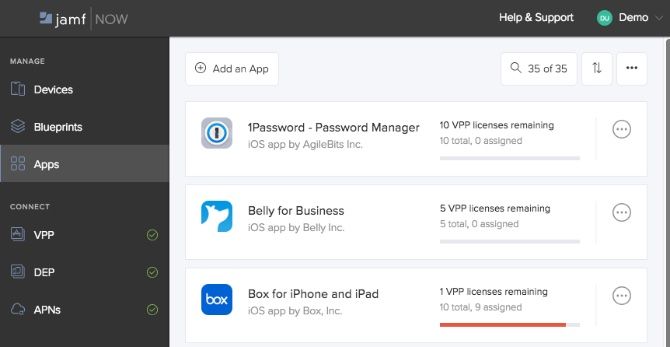
Jamf Now also supports Apple’s Volume Purchase Program (VPP) (part of Apple Business Manager). This means that apps that require a license can be purchased and assigned to your organization. If an employee leaves, you will be able to reclaim the license that was assigned to them and associate it with another user. Brilliant!
Step 4: Configuring Devices With Blueprints
Blueprints are one of the most powerful features of Jamf Now. They are the proverbial cookie cutter used to effortlessly set up and configure devices as soon as they are enrolled. You can either create a blueprint from scratch or begin using one of the templates provided by Jamf Now.
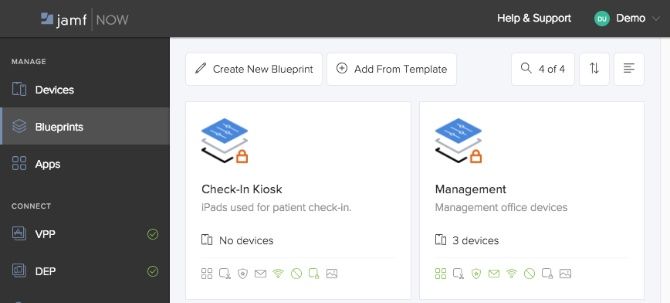
From the predefined apps we configured in the previous section right down to preventing users from changing their wallpaper, Blueprints allow for the fine-grained control and security at the device level.
Deploying Wi-Fi Networks
Let’s say you’ve added a new office and Wi-Fi network specifically for all the users in your sales division. Instead of going to each device and manually adding in a new Wi-Fi network, all you need to do is edit the Blueprint that those devices are assigned to.
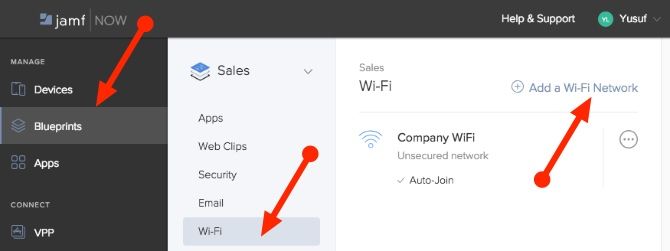
- Select the Blueprints Tab
- Select the Sales Blueprint
- Click on the Wi-Fi tab
- Click on Add a Wi-Fi Network
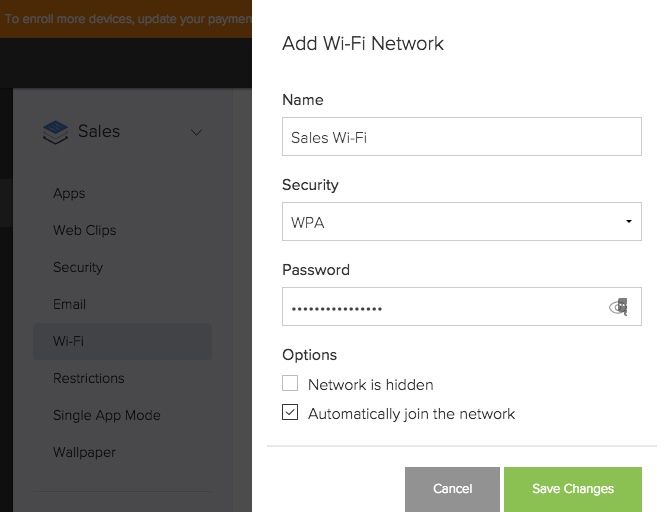
This will bring up the Add Wi-Fi Network menu. After entering the Name (SSID), security and password for the new Wi-Fi network click on Save Changes.
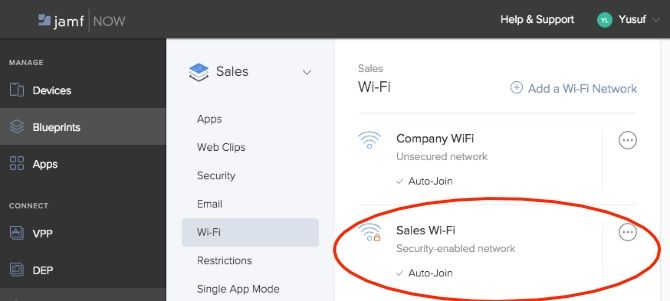
All devices that were under that Blueprint will now have this new Wi-Fi network pushed to them. The devices will also auto-join the new Wi-Fi network. No need to hand the password to any user or manually configure each device!
Restrictions
Restrictions are arguably what makes Jamf Now so special. Jamf Now supports a number of restrictions for iOS devices that helps you keep data secure and prevent users from changing certain settings. Some settings do require Supervision which is covered in the next section.
To add or remove a restriction:
- Login to your Jamf Now accont and select the Blueprints tab.
- Click on Restrictions.
- Choose the area you’d like to restrict like Security and Privacy.
- Enable or disable any settings you want to push to the devices.
- Click on Save Changes.
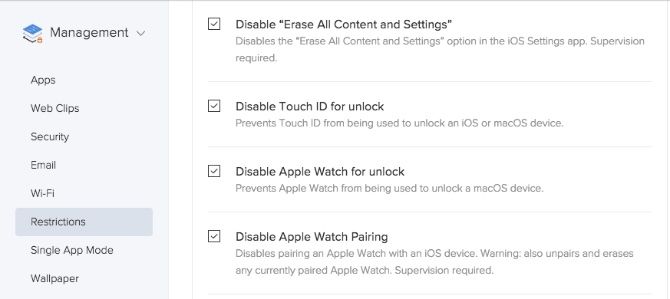
All devices that were under that Blueprint will now have these new restrictions pushed to them. For example, say you Disabled Touch ID for unlock for the management Blueprint; Touch ID will be disabled for all devices that belong to said Blueprint.
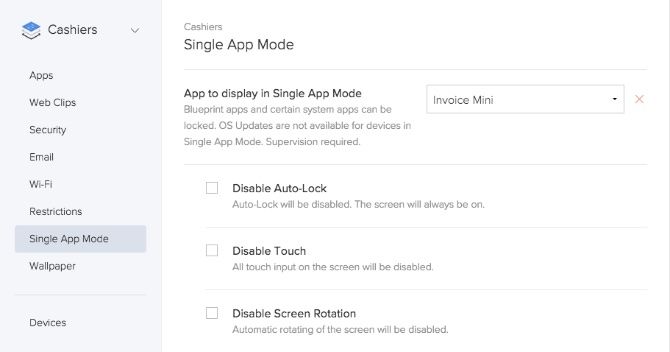
Blueprints can also be used to enable Single App Mode. For example, if you were deploying some iOS devices and you wanted to lock them into a certain app, Single App Mode is a great way to achieve this. Blueprints will ensure all the devices in your organization adhere to any restrictions and turn what was once a very manual process into a much more fluid one.
Step 5: Device Enrollment and Supervision
In order for devices to be managed by Jamf Now they need to be enrolled into your account. There are two methods of enrolling devices: Open Enrollment and Supervision. As mentioned, Open Enrollment is a lower form of management compared to Supervision.
For both instances a device would have already been through the Apple setup process, have created an Apple ID and be connected to a network. The main difference being that Supervised devices get enrolled automatically as part of Apple’s Setup Assistant.
Open Enrollment
The first method of enrollment is referred to as Open Enrollment. This works by providing users with a URL and access code to complete the enrollment process. This is perfect for organizations with a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy.
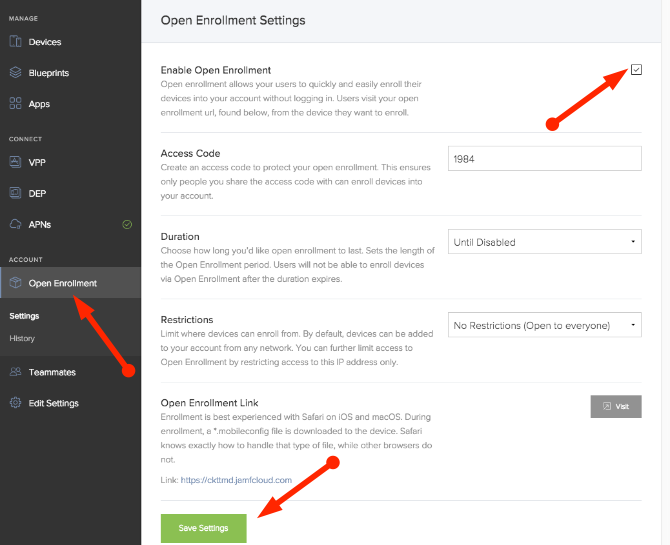
To set up Open Enrollment:
- Log in to Jamf Now
- Under the Account Section, click on Open Enrollment
- Click on the Enable Open Enrollment checkbox
- Choose an Access Code
- Take note of your Open Enrollment Link
- Click on Save Settings
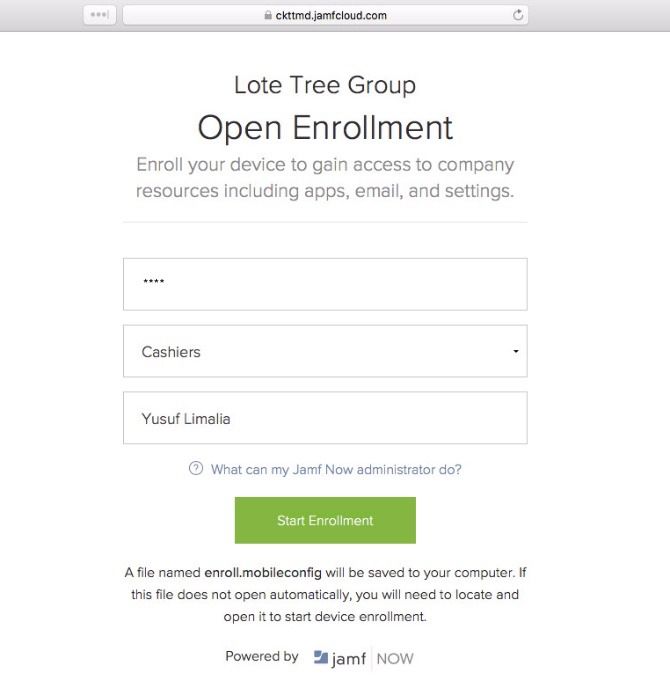
To enroll any device using open enrollment:
- Open Safari on your macOS or iOS device.
- Navigate to the Open Enrollment Link from above.
- Enter the Access Code from above.
- Select a Blueprint.
- Type in a Name for this Device.
- Click on Start Enrollment.
Once again, Safari knows exactly how to handle the downloaded configuration file.
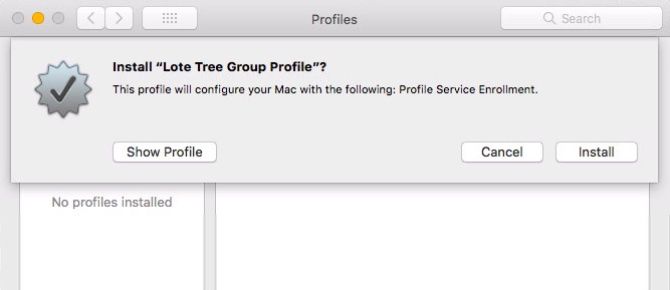
Your device will now ask you for confirmation if you’d like to install a new profile. Simply click Install in the box that pops up.
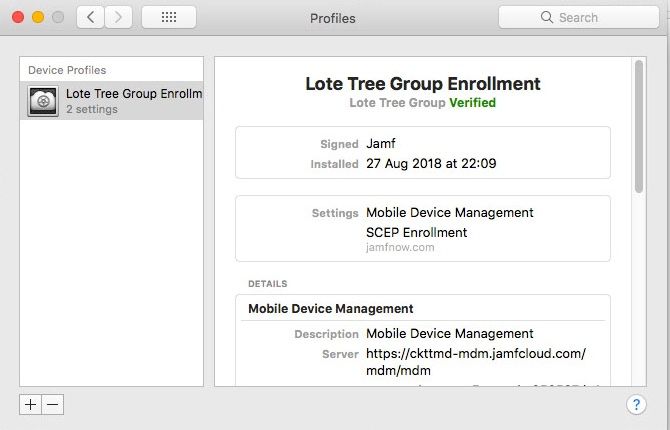
This device is now enrolled and will appear in your Jamf Now console ready for management!
Supervision
The second method of management is Apple’s Device Enrollment. Device Enrollment allows an organization to purchase Apple devices and automatically enroll them into Jamf Now the first time the device turns on. As mentioned, you will need an Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager account to take advantage of Device Enrollment.
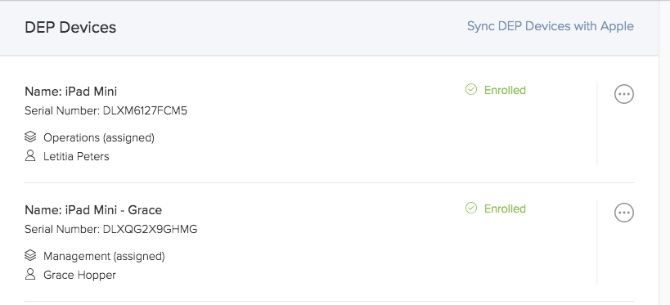
Once you have Device Enrollment (formerly DEP) set up, any devices you purchase through Apple or its authorized resellers will appear in your Jamf Now account. This is done via the device’s unique serial number. All you need to do is assign a Blueprint to the device and that’s it.
Device Enrollment allows you to ship a device directly to a new employee and have it automatically enroll into Jamf Now based on the device’s unique serial number. The user simply unboxes the device and follows Apple’s built-in Setup Assistant. Awesome!
Device Enrollment allows a much deeper level of management referred to as Supervision. Supervision is the recommended level of management for devices that your organization purchases.
Step 6: Managing Devices
From your dashboard, your entire organization’s Apple devices are at your fingertips. At a glance, you can see devices that require your attention and you can to fix and attend to issues quickly and efficiently. Some details include the OS version, available storage and device assignment.
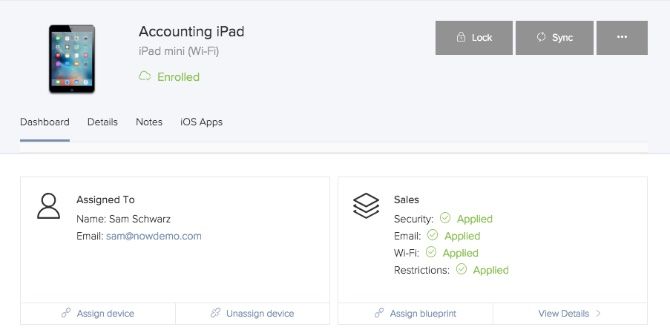
From this screen, you can also lock a device, assign an asset tag for inventory tracking and even remotely wipe the device. Keep in mind that Jamf Now does not handle backups of devices. This must still be done either through iTunes or iCloud.
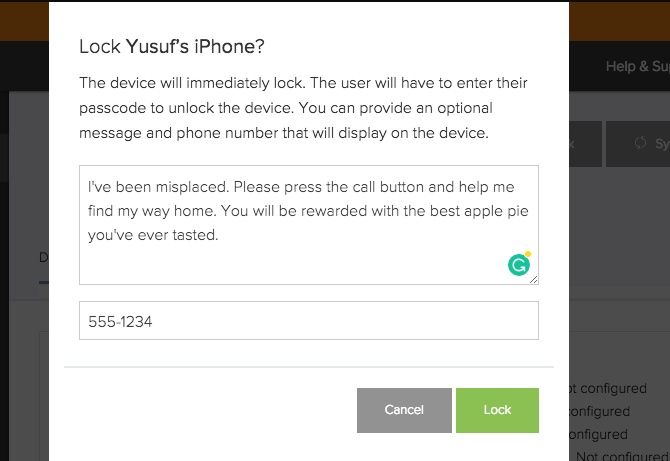
If someone has misplaced their device:
- Select the device from the Devices tab.
- Click on Lock.
- Enter an optional message and phone number.
- Click on Lock.

Jamf Now immediately locks the iPhone over the air and displays your message and phone number. The process is the same if you’d like to remotely erase or wipe the device.
Remote App Installation
One particularly useful feature is the ability to remotely install an application directly from the dashboard!
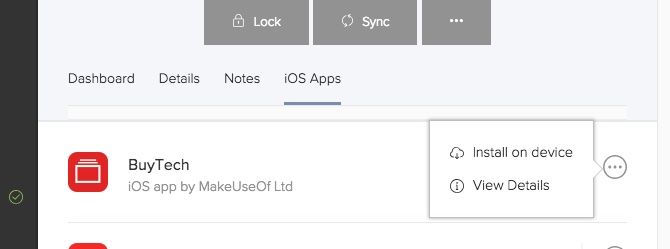
After you’ve added an app to your Jamf Now account using the steps mentioned in the section above:
- Select the device from the Devices tab.
- Select iOS Apps.
- Open the context menu next to the app you’d like to deploy.
- Click Install on device.
A confirmation message will be sent to the user. After they have accepted, the app will be downloaded and installed. Managing groups of devices is done under the Blueprints section which we’ve covered above. Compared to manually making changes on every individual device, this is unbelievably beneficial.
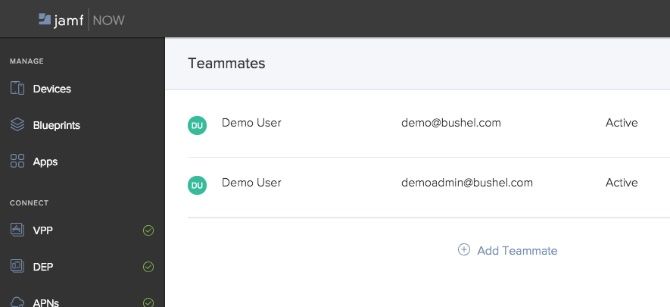
On the subject of IT teams, the Teammates tab allows many members to manage an organization. The only thing to bear in mind is that all teammates have the same permissions within an organization.
Jamf Now Is the Standard of Apple Management
The time saving, security, and ease of deployment make device management from Jamf Now essential if you’re deploying Apple devices to your organization. The user interface is beautifully designed and very easy to use even if you’re not an IT professional.
Jamf Now offers a full-featured demo for you get your hands dirty and decide if Jamf Now is for you. Otherwise, create your free Jamf Now account!
Image Credit: tomeversley/Depositphotos
Read the full article: Jamf Now: The Golden Standard of Apple Device Management
Read Full Article