Image noise is a problem for every photographer. Those tiny dots of color or grain can spoil even the most perfectly composed image, and sometimes it seems unavoidable.
Luckily, there are many ways to tackle noise in photos. To learn how to reduce noise in pictures, either when shooting or editing, keep reading!
1. Shoot at Low ISO
Noise most commonly occurs when you shoot at high ISO settings.
ISO determines how sensitive the sensor is to light. It’s used in conjunction with shutter speed and aperture to the control the exposure of a photo. Together, these form the so-called “exposure triangle”. Take a look at our photography tips for beginners for a full explanation.
When you double the ISO value, the sensitivity of the sensor also doubles. So, a camera will draw in four times as much light at ISO 1600 as it does at ISO 100. However, the more sensitive it is the more prone to noise it will be.
![how to reduce noise - ISO setting]()
Modern DSLR and mirrorless cameras can shoot with relatively little noise at up to ISO 1600. Small sensor cameras and smartphones might start to show noise at ISO 400 and beyond.
To achieve ISO noise reduction, always keep the ISO setting as low as possible. This is easy in good light, while in low light set a slower shutter speed and select a larger aperture first. Only start bumping the ISO to a level beyond what your camera is comfortable with as a last resort.
Sometimes your pictures can be grainy even at low ISO. This can have many causes. It can come from the sensor getting hot with long exposures, the sensor being too small for the lighting conditions you’re using, or you’ve brightened the image too much in Photoshop.
2. Use Faster Lenses
As we mentioned, setting your lens to shoot at a larger aperture is a good way of keeping the ISO low.
The aperture is the hole at the back of the lens that controls how much light is able to hit the sensor. A larger aperture, indicated by a smaller f-number, increases the amount of light.
![how to reduce noise - camera aperture]()
Every lens is restricted in the maximum aperture it offers, so switching to one with a larger maximum (often referred to as a faster lens) can be hugely beneficial. For instance, a prime lens with an f/1.8 aperture lets in twice as much light as a zoom does at f/3.5. That’s the equivalent of switching from a potentially noisy ISO 1600 to a clean and crisp ISO 400.
Obviously, buying a new lens is an expensive solution to this problem. But if you shoot in low-light conditions often, it is well worth the investment.
3. In-Camera Noise Reduction
A quick and easy solution for how to reduce noise in camera would seem to be to your camera’s built-in settings. Logic states that you should turn this on and set it to the maximum level to get noise free images.
But wait!
In-camera noise reduction can be a rather blunt instrument. It works by smoothing the image to blend in the noise. But it can also end up smoothing out fine details, or giving skin a fake, waxy looking texture.
![how to reduce noise - in-camera reduction]()
Experiment with your camera’s settings to find the level you’re happy with. As a general rule, if you post-process your images in Lightroom then keep it set low. Lightroom can handle noise reduction far better. But if you upload your photos directly to Instagram or elsewhere you can afford to set it a little higher.
4. Long Exposure Noise Reduction
Long exposure photos are highly susceptible to noise because the sensor can get very warm while they’re being shot. This causes hot pixels in the image, resulting in noise at low ISO.
Cameras that can shoot with long exposures, especially DSLR and mirrorless cameras, have a long exposure noise reduction option to fix this. What’s different about it is that it usually works when you’re shooting in RAW, too.
Long exposure noise reduction works by shooting two frames. The first is your intended shot; the second is a “dark frame” shot as if you’d left the lens cap on. The dark frame captures nothing but the hot pixels, which the software then uses as a map to remove them from the original image.
This feature does mean your long exposures take twice as long to shoot, but otherwise there’s no downside to turning it on. It can help you shoot incredible night time photos, and it’s good tool for taking sharp pictures.
5. Reduce Noise in Camera Raw or Lightroom
If you’ve tried to minimize noise while shooting but are still left with some to clean up, where do you go next?
Shoot in RAW and process in Camera Raw or Lightroom. It’s how many professionals gets their photos to look tack-sharp.
Both editors have the same noise reduction tools. They’re simple yet powerful, and tackle the two types of noise.
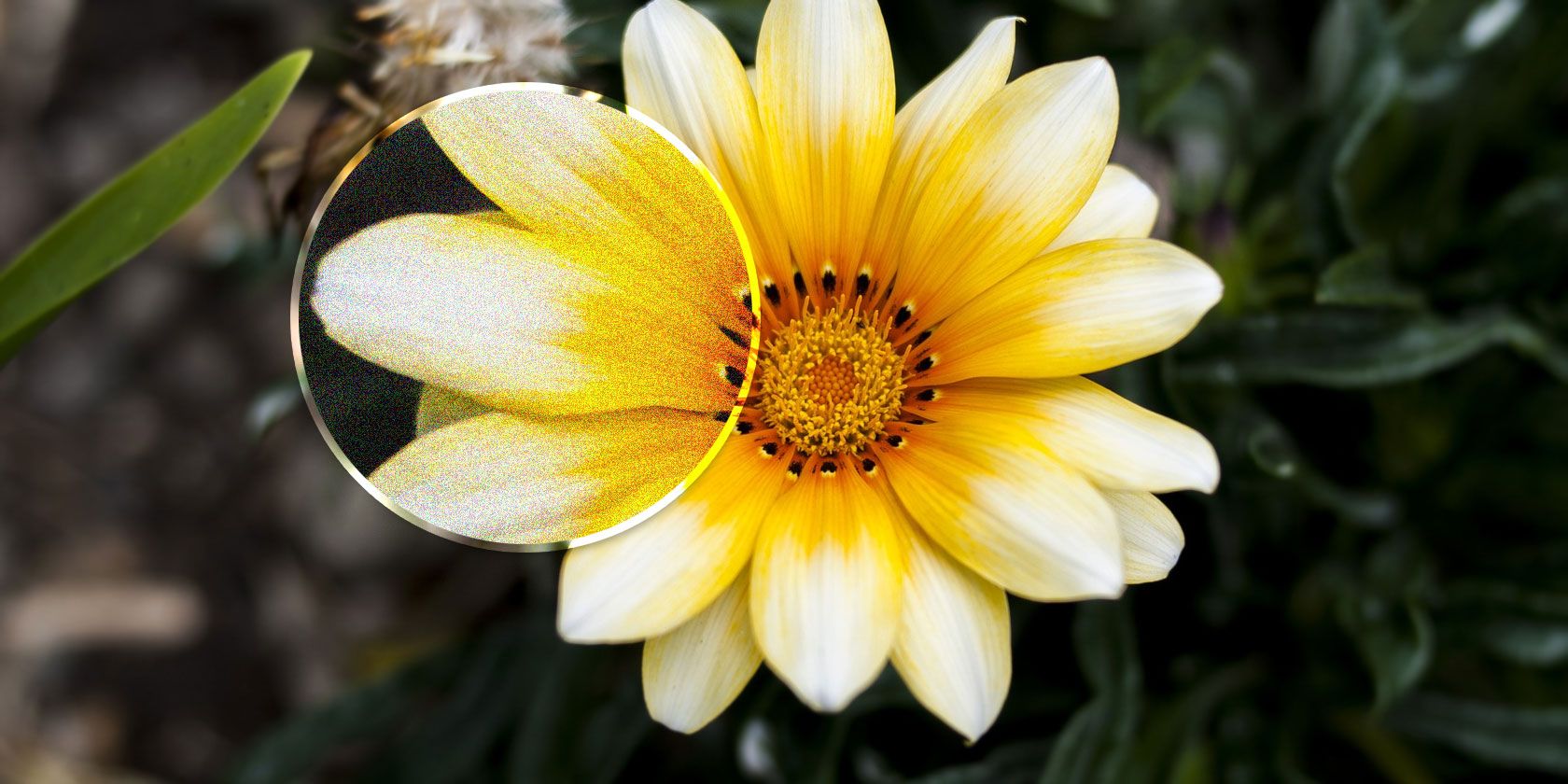
Remove Color Noise
Color noise is seen as specs of random color dotted throughout the image. It’s ugly, and you’ll always want to remove it. Fortunately, it’s a trivial fix, and you might not even need to do anything.
![how to reduce noise - colors]()
You remove color noise by desaturating those random dots. Lightroom automatically applies a setting of 25 on the Color Noise slider to every RAW image, and more often than not that’s enough.
You can increase it if you need to, but don’t go too far or you might start smudging the other colors. On the whole, color noise reduction shouldn’t degrade your image quality in any noticeable way.
Remove Luminance Noise
Luminance noise is random pixels that are brighter or darker than they should be. Not all luminance noise is bad, as it can sometimes look like film grain, giving your image a nice texture. It’s harder to fix fully, though.
Luminance noise is removed by softening the image. This has the effect of removing fine detail, and if you push it too far natural textures will start to look artificial.
![how to reduce noise - luminance]()
Ultimately, it’s about finding the balance between reducing noise and retaining detail. We’d always recommend prioritizing the latter.
To get started, zoom fully into your image. Then get to work on the three noise reduction sliders:
- Luminance: This is the main tool. Drag it to the point where you find a good balance between noise and detail.
- Detail: This allows you to recover some fine detail, but the effect is very subtle. It’s set to 50 by default. Increase it to add more detail, but beware of introducing unwanted artifacts to the image.
- Contrast: This slider lets you recover some of the local contrast that may been smoothed away by the Luminance slider. A value of around 10-20 often works well.
You can also apply local noise reduction in Lightroom using tools like the Adjustment Brush or Graduated Filter. You get less control on the settings, though, and it only works with Luminance noise.
Once you’re done you’ll probably need to sharpen the photo. This can increase the noise once more. Noise reduction can sometimes feel like a game of whack-a-mole.
6. How to Reduce Noise in Photoshop
When you’re shooting on a tripod you can minimize noise by using slower shutter speeds. But you won’t be able to get rid of it entirely.
Photoshop, and other major photo editing apps like Affinity Photo, have an ingenious fix that solves the problem automatically.
![how to reduce noise - exposure stacking]()
It’s called exposure stacking, and it works by blending multiple images that are essentially identical. If they’re shot together, from a tripod, the only differences will be the dots of noise that are distributed randomly on each frame.
The software identifies those differences as noise, and discards them.
The process for Photoshop goes like this:
- Shoot between three and six images (without moving the camera in between).
- Open Photoshop and go to File & Scripts > Open Files into Stack.
- In the Load Layers box that opens, check the options labelled Attempt to Automatically Align Source Images and Create Smart Objects After Loading Layers then hit OK.
- Go to Layer & Smart Objects & Stack Mode & Median.
That should be it.
HDR mode on smartphones use the same process. They shoot multiple frames in succession and combine them. It’s primarily designed to maximize the dynamic range of the camera, but also serves to reduce noise and help you take sharper photos on your phone.
If your phone has an HDR mode, turn it on.
7. Be Careful When Post-Processing
As we’ve seen, it’s easy to learn how to reduce noise in pictures. What’s also easy is to accidentally add noise when you’re post-processing your shots. Too much color correction or over-sharpening can cause it.
But the biggest problem is when you brighten an image too much, and reveal masses of color noise in the shadows.
The answer is to learn how to lighten dark images properly. This will give you perfectly exposed photos without ruining the quality.
Read the full article: How to Take Perfect Noise-Free Photos Every Time
Read Full Article