The creatures of the depths live in a very different world — one lethal to us. But our world is lethal to them as well, all sharp edges and rapid movements. If we’re to catch and learn about the soft-bodied denizens of the deep, our machines too must be soft — and that’s what this Harvard robotics research is all about.
Collection of samples from the deep ocean is a difficult task to do safely: Although these animals are subject to pressures and temperatures well beyond what any surface creature could handle, they are nevertheless very easily damaged by handling. Existing methods to collect them for study often involve sucking them into little containers that are kept pressurized and brought to the surface. But it would be nice to be able to snatch an intriguing critter up and inspect it in vivo, wouldn’t it?
To that end researchers at Harvard’s Wyss Institute have been working on simpler, safer ways to entrap these creatures temporarily, letting them go seconds or minutes later once the collector has gotten some good images or (I don’t know) sampled some mucus.
A little more than a year ago, they created an “underwater Pokeball,” a kind of soft geodesic form that could close around something like a jelly or drifting fish. But even with that kind of method, there’s still the possibility that it could get squished during closure.
So they continued their work, pursuing instead “noodle-like appendages” that, when not activated, are as pliable and harmless as cooked spaghetti, or rather fettuccine considering their shape.
Each “finger” is made of an “elastic yet tough silicone matrix,” and inside it are tiny fibers that remain slack when not in use, but which can be stiffened using a tiny amount of hydraulic pressure. This causes the whole finger to bend in a specific direction, in this case inwards at the same time as the others, scooping whatever is in their range into the soft 3D-printed “palm.” The grip is soft enough that it won’t harm the creature, but firm enough that it can’t just wriggle out.
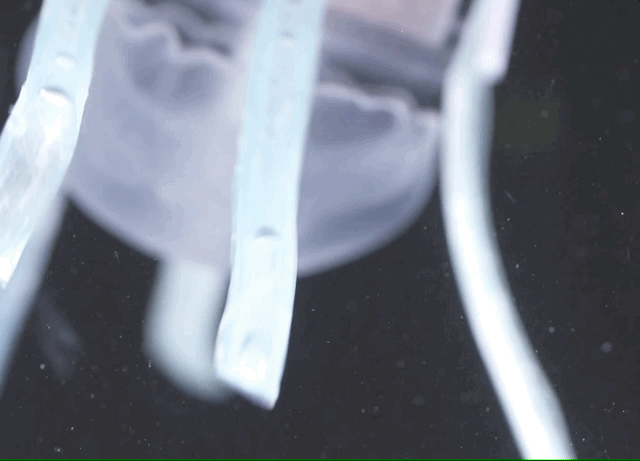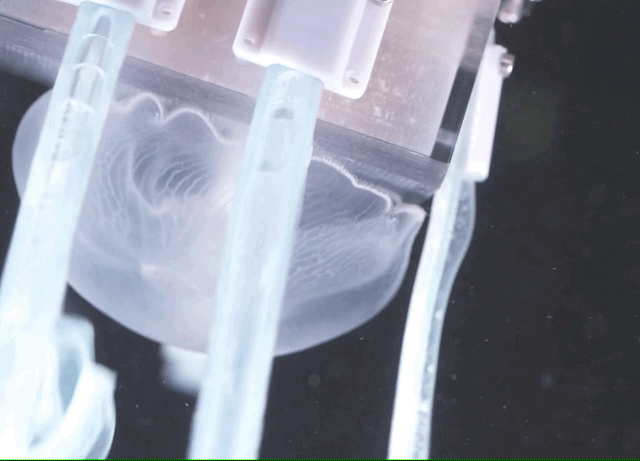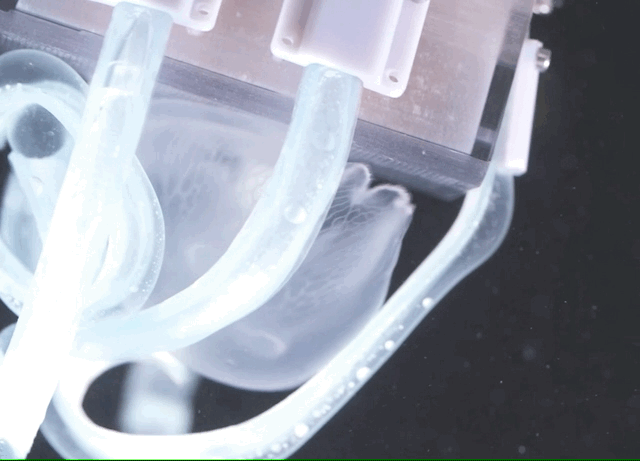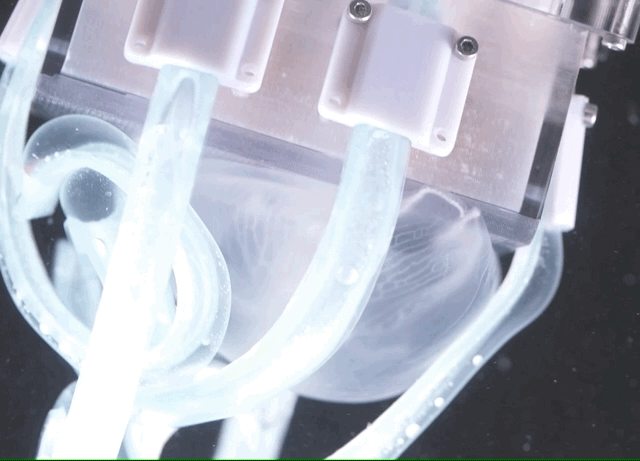
Sinatra et al. / Science Robotics
At that point the researchers are free to do what they wish, though presumably after taking such care to catch the animal unharmed, they won’t be doing anything too rough with it.
There are few limitations on the size or length of the fingers, meaning they can be customized for different operations. The device you see pictured was made to be effective in catching common jellies, but the whole thing could easily be scaled up or down to handle bigger or smaller animals.
Of course the whole thing can be attached to a submersible, but it’s small and simple enough that it can also be made into a handheld gadget for manual sampling, should that what a given researcher prefers. They put together a prototype and “demonstrated the use of this hand-held soft gripper to successfully perform gentle grasping of three canonical jellyfish species.”
Here’s hoping this means less shredded jellies in our oceans, and perhaps one day you’ll be able to rent such a grabber while snorkeling and have a chance to examine fragile marine life closely without having to grab it with your hands (not recommended).
The researchers’ work was published today in the journal Science Robotics.
Read Full Article