Welcome back to This Week in Apps, the TechCrunch series* that recaps the latest OS news, the applications they support and the money that flows through it all.
The app industry is as hot as ever, with a record 204 billion downloads and $120 billion in consumer spending in 2019. People are now spending three hours and 40 minutes per day using apps, rivaling TV. Apps aren’t just a way to pass idle hours — they’re a big business. In 2019, mobile-first companies had a combined $544 billion valuation, 6.5x higher than those without a mobile focus.
In this series, we help you keep up with the latest news from the world of apps, delivered on a weekly basis.
* This Week in Apps was previously available only to Extra Crunch subscribers. We’re now making these reports available to all TechCrunch readers.
Let’s dive in.
Headlines
Top Story: Apple doubles down on its right to take a 30% cut
Image Credits: TechCrunch
Ahead of Apple CEO Tim Cook’s testimony before Congress, Apple on Thursday again took to the press to fight back against claims of anti-competitive practices on its App Store.
Last month, the company detailed the results of a commissioned study that showed how Apple wasn’t receiving a cut of revenue on the majority of App Store transactions — $519 billion in commerce. This time, Apple is touting the results of another study by the same analyst group that is meant to demonstrate how Apple’s App Store commission rate is similar to those of other app stores and digital content marketplaces.
The study exhaustingly compares the App Store’s 30% commission to all other forms of storefronts, online and off. This includes other app stores, game stores, e-commerce marketplaces, digital platforms and even brick-and-mortar retail. Apple’s conclusion is that it’s not doing anything different from the others, so what’s the big deal?
Of course, this misses the point. The antitrust issues surrounding Apple’s App Store are not about whether Apple is charging more than other digital marketplaces. It’s about whether that commission structure is hindering competition, given Apple’s size, wealth and power.
As indie developer Brent Simmons (of NetNewsWire) put it this week, the cut limits developers’ ability to hire and retain talent.
To an app on the App Store it might mean being able to lower prices — or hire a designer or a couple junior developers. It might be the difference between abandoning an app and getting into a virtuous circle where the app thrives.
Quality costs money, and profitability is just simple arithmetic: anything that affects income — such as Apple’s cut — goes into that equation.
To put it in concrete terms: the difference between 30% and something reasonable like 10% would probably have meant some of my friends would still have their jobs at Omni, and Omni would have more resources to devote to making, testing, and supporting their apps.
Apple’s opening of ‘Find My’ to third-parties isn’t as nice as it seems
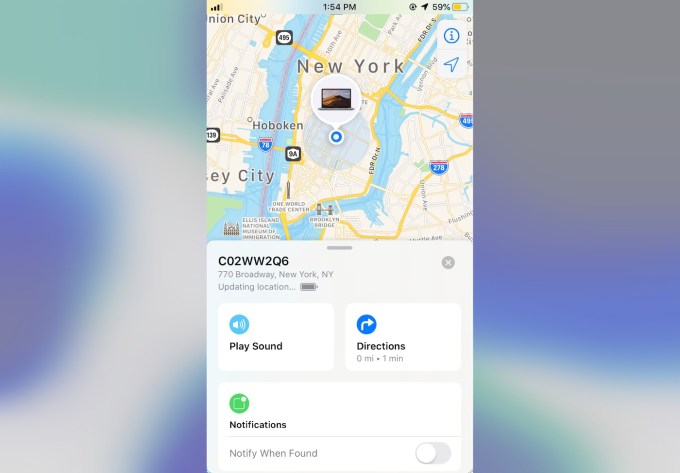
Image Credits: Apple
Apple announced at WWDC 2020 that third-party developers, like Tile, would be able to tap into Apple’s “Find My” technology platform to locate lost items and gadgets that aren’t made by Apple. The move was meant to counteract Tile’s ongoing complaints and testimony to U.S. antitrust investigators that Apple favored its first-party services at the expense of competitors’ businesses.
Tile was particularly concerned over Apple’s plans to announce a direct competitor, AirTags, which would be allowed to leverage the “Find My” technology at a deeper level. The move could potentially have wiped out Tile’s business with a better product — at least from a consumer standpoint.
The Washington Post reported this week that Apple’s opening of “Find My” is not the olive branch it seems, however. The publication acquired the 50-page confidentially agreement that all developers would have to sign, which indicates there are a lot of restrictions on how this integration works. For instance, Apple customers using “Find My” to locate a device will be barred from using competing services simultaneously, the document said. This is an unusual restriction — and one that makers of Bluetooth devices and smart home products don’t have to agree to for their own products.
Amazon turns Alexa into a mobile app launcher

Image Credits: Bryce Durbin
How often do you think Amazon kicks itself over its smartphone failures? Given that the company hasn’t been able to compete directly on mobile, it’s finding another angle by way of Alexa. Amazon this week announced a bevy of new developer tools for its Alexa virtual assistant, including one that will allow the digital helper to launch iOS and Android apps using voice commands.
For example, you’d be able to say things like, “Alexa, start recording a TikTok,” or “Alexa, ask Twitter to search for #BLM.”
It’s unclear how many developers would adopt just a feature, outside of those that already offer one of the more popular Alexa skills. After all, Siri and Google Assistant can already launch and control your apps.
While Amazon is likely hoping that tying Alexa to the world of mobile apps could give it some momentum in terms of building an app ecosystem of its own, consumers so far have seemed to largely prefer using Alexa for first-party activities, like playing music, listening to news, controlling the smart home, asking random questions, making lists, setting reminders and more.
The move, however, may hint that Amazon is thinking about building out a mobile app ecosystem for its Alexa devices with a screen, like forthcoming versions of its Echo Show, for example.
Apple releases beta 3 builds of iOS 14, iPadOS 14
Testers this week received their third set of iOS 14 developer betas, as the software moves closer to its fall launch date. Beyond the usual bug fixes and performance improvements, only small changes were spotted this time around. This includes a new Music app icon, widget and the ability to share music to Snapchat; a new widget from the Clock app; a new pop-up when organizing the home screen that explains how to hide pages; a new pop-up when you use widgets for the first time; an updated design for Memoji masks; and more.
Facebook takes on Zoom with its latest Messenger Rooms update
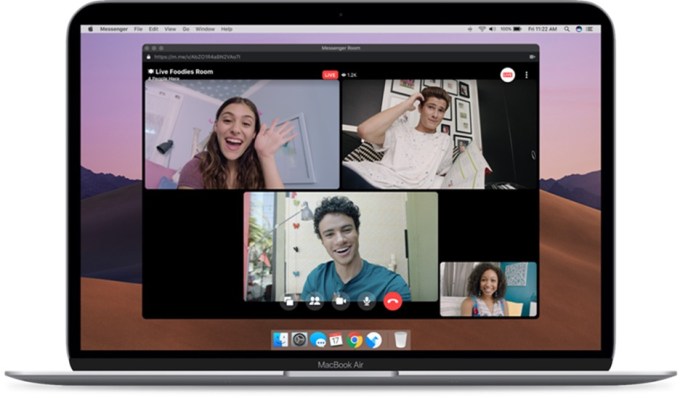
Image Credits: Facebook
Facebook this week announced a new feature that it hopes will give it a better shot at challenging Zoom’s dominance on web conferencing that came about due to the pandemic. The company upgraded its Messenger Rooms group calls platform to support the ability to live broadcast calls to platforms like Facebook, YouTube and Twitch — a move that effectively combined Facebook’s live-streaming capabilities with group video chat. Facebook turned around the feature in a relatively short time, given it has only been a matter of months since Zoom has really taken off. That indicates Facebook understands the threat of online chat and socializing exiting its platform.
The goal with the new addition is to make it simpler to broadcast to social platforms, to encourage users to return. Even if they arrive in order to broadcast to competitors’ sites, like YouTube, the company understands that adding Facebook to the list of destinations will increase the output of live broadcasts on its own platform.
In addition, Facebook also this week announced that Messenger now lets you secure your chats with Touch ID or Face ID on iOS. Why don’t more apps offer this feature?
TikTok unveils a $200M fund to back U.S. creators, as it scrambles for a “Plan B”

LOS ANGELES, CA – AUGUST 01: A general view of the atmosphere during the TikTok US launch celebration at NeueHouse Hollywood on August 1, 2018 in Los Angeles, California. (Photo by Joe Scarnici/Getty Images)
As the U.S. government weighs a ban on the Chinese-headquartered app over privacy concerns, the company announced plans to hire 10,000 employees across the U.S. over the next three years and launched a $200 million fund to invest in new creators. The new fund is aimed at helping top creators in the U.S. supplement their earnings, and potentially find the next big TikTok star in the process. The platform will begin accepting applications from U.S.-based creators starting next month and will then distribute the capital over the coming year.
Meanwhile, TikTok parent company ByteDance continues to discuss a range of other options to keep its popular and profitable app alive in the U.S. The latest, according to The Information, is one that would have a small group of the company’s U.S. investors joining forces to buy a majority stake in TikTok.
The U.S government — and particularly the Trump administration — continues to be skeptical about TikTok’s China ties. This week, the U.S. House voted to ban federal employees from using the app on government-issued devices. The vote passed 336-71, as part of a package of bipartisan amendments to the National Defense Authorization Act.
Robinhood ends plan for a U.K. launch

Image Credits: Andrew Harrer/Bloomberg via Getty Images
Mobile investing app Robinhood said this week it would not be launching in the U.K., as planned. The company said it was now going to hold off on its global expansion plans to instead focus its efforts in its home market, the U.S. The company had already received over 250,000 sign-ups on its U.K. waitlist, which it says will now be deleted in line with local privacy laws. The company said it will transfer 10 U.K. employees to the U.S., but others will be let go.
The app has been more recently facing criticism in the U.S. for how it lures in young, inexperienced traders who then buy and sell some of the riskiest financial products on the market — at rates higher than other retail brokerage firms. With its hip and youthful design and social app-like features, such as confetti and emoji, Robinhood can make investing feel more like a game, The NYT reported in a recent feature. But the reality is that these inexperienced users are taking more speculative risks, sometimes with devastating results. One Robinhood user killed himself after seeing his balance drop to negative $730,000 — a figure that was higher, in part, due to some of his incomplete trades.
Google has its own ‘Onavo’

Image Credits: David Paul Morris/Bloomberg via Getty Images
Google today already allows Android app developers to collect usage data from devices where their app is installed, so it comes as no surprise that Google was doing this itself, too. The Information revealed Google’s program that allows it to access usage data on any device that has its Google apps pre-installed. Similar to Facebook’s Onavo, the data wasn’t just used to make improvements to Android, but was also used as a competitive advantage.
According to the report, Google had used the data to show how Google’s own services compared to rivals. This is what Facebook had used Onavo for, too — even leveraging those learnings to inform its acquisition strategy. APIs aren’t the only way large tech companies collect data on smartphone user habits. App intelligence firms like App Annie and Sensor Tower provide similar data to customers, obtained through a number of apps that downplay their true purpose, but really serve as data collection machines.
Data collection like this has been underway for years, but with the antitrust investigations now underway, the time may have come for regulators to actually do something about it.
Funding and M&A
- Fintech startup Meemo came out of stealth and launched its social finance app with $10 million in seed funding. Investors including Saama Capital, Greycroft, Monashees and Sierra Ventures led the round with additional participation from Amit Singhal, Hans Tung and several former colleagues from Google and Snap.
- Swiss keyboard startup Typewise raises $1 million seed round to build its “privacy-safe” next word prediction engine that works entirely offline. The round consists of $700,000 from more than a dozen local business angels; and $340,000 via the Swiss government through a mechanism akin to a research grant.
- China’s Missfresh raises $495 million for its e-grocery app with deep WeChat integrations. The round was led by state-backed China International Capital Corporation. Other investors included ICBC International Securities, Tencent, Abu Dhabi Capital Group, Tiger Global and a fund managed by the government of Changshu county, home to Missfresh’s east China headquarters
- Levitate raises $6 million for its “keep-in-touch” email marketing solution for small business that works across web and mobile. Investors include Tippet Venture Partners, Durham, North Carolina-based Bull City Venture Partners and angel investor Peter Gassner, the co-founder and CEO of Veeva Systems and investor in Zoom
Downloads
Dilims
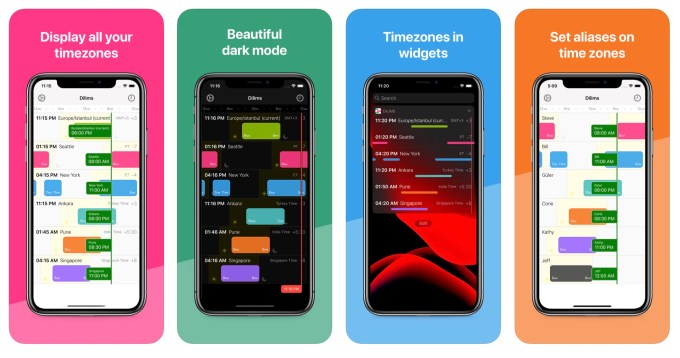
Image Credits: Dilims
This beautifully designed indie iOS app called Dilims lets you display different time zones on one screen, and even name them with aliases or view them as a widget. The simple single-purpose utility is useful for anyone who has to work with teams or clients across time zones, and wants an easier way to see what time it is and where. For $2, that’s kind of a steal, too.
Dark Noise 2
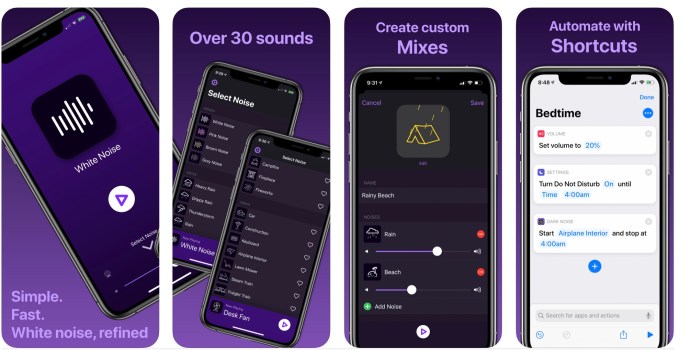
Image Credits: Dark Noise
If you like to play ambient noise to help you focus, sleep or just relax, you’ll want to check out Dark Noise 2. This ambient noise app for iOS just got a big update, which adds new sounds, new icons and introduces iCloud syncing. Plus, it now allows you to create your own custom mix of ambient sounds so you can chill to the sounds of rain at the beach, for example, or whatever else you want to blend. The app is $5.99 on the App Store.
Further Reading (and Listening)
- Apple Kills IDFA: How Will the Fallout Really Affect Marketers?: Dig into the implications of the IDFA changes in the latest episode of the Mobile Presence podcast, in a discussion with Shamanth Rao, veteran growth marketer and CEO of RocketShip HQ, a full-service mobile user acquisition agency.
- What Ever Happened to Digital Contact Tracing?: Lawfare takes a look at how the contact-tracing app landscape is shaping up, given the disappearance of contact tracing apps from the headlines. Though Apple and Google’s API was meant to encourage each country to build their own apps, the U.S. has instead taken a patchwork approach due to its fractured response to COVID-19. Today, there are a handful states with their own apps, and only some that plan to use Apple and Google’s technology. Many states have no plans for an app at all, turning instead to human-led contract tracing efforts.
- Designed for iPad: What makes a good iPad app today? These things, says LookUp Design in a thoughtful post.
Tweets of the Week
Read Full Article